Background: The development of novel treatment strategies has extended the median survival of MM to nearly a decade but the disease remains incurable and relapse is inevitable. The Bcl-2 pathway is highly relevant to MM cell survival and can be mitigated therapeutically. AT-101 is a novel, orally available pan Bcl-2 inhibitor (Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, Mcl-1, and Bcl-w). Preclinical in vitro and in vivo studies showed that AT-101 enhanced cytotoxicity of lenalidomide-dexamethasone (Rd). We conducted a phase I study in RRMM patients to establish the effective dose of AT-101 with Ld as well as record safety and preliminary efficacy of this combination (NCT02697344).
Methods: Key eligibility criteria included: RRMM with measurable disease (serum monoclonal protein ≥1.0 g/dL or urine monoclonal protein >200mg/24 hour or serum immunoglobulin free light chain >10mg/dL AND abnormal serum free light chain ratio). Patients must have received 1-3 prior treatment regimens and have an absolute neutrophil count ≥1.0 x 109, platelets 75 x 109, creatinine clearance ≥50 mL/min, and ECOG performance status ≤2. AT-101 dosing was designed to reach a maximum daily target of 20mg (Cohort 1; 10 mg PO QD, Cohort 2; 20 mg PO QD) utilizing a standard 3 +3 dose escalation design in combination with standard doses of Rd. Treatment was given as outpatient for a maximum of 12, 28-day cycles. For pharmacodynamic studies, AT-101 alone was given in cycle 1, with R (25 mg on days 1-21) and d (40 mg weekly) added cycle 2 onwards.
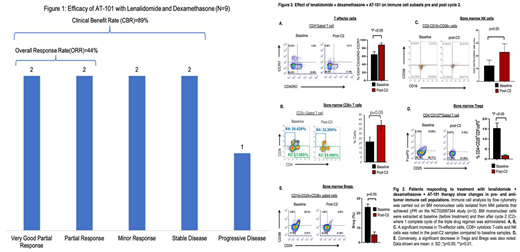
Results: Enrolled patients (n=10) included 60% males with median age 68.5 years (range 55-75) and median time since MM diagnosis 4.5 years (range 0.6-8.3). MM ISS stage was II/III in 7 patients and 8/10 had high-risk cytogenetics with 4 each having del17p and 1q+. Only 1 patient had t(11;14).Patients had received median 2 prior lines of therapy (range 1-3), with 7 having had prior autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) and the initial induction regimen being bortezomib (V), R and dexamethasone (d) (VRd) in 8, Rd in 1 and cyclophosphamide (C) with Vd (VCd) in 1 patient. At the time of study entry, 3 patients were R refractory while 2 were refractory to both, V and daratumumab (Dara). Median duration of treatment was 7.5 cycles (range 2-12) and 3 patients completed all planned 12 cycles of treatment. Among the evaluable patients, dose limiting toxicities (DLTs) at 20 mg daily dose of AT-101 with 25 mg of R and 40 mg weekly included one patient with grade 4 febrile neutropenia and grade 4 neutropenia lasting 9 days and one patient with grade 4 thrombocytopenia lasting 8 days. G3/4 adverse events (AEs) included atrial flutter (n=1), white blood cell count decrease (n=3), neutropenia (n=5), febrile neutropenia (n=1) and thrombocytopenia (n=2), and back pain (n=1) . No G3/4 non-hematological AEs were noted. Any grade non-hematologic AEs seen in at least 20% (n=2) patients included fatigue (n=9), neuropathy (n=6), nausea (n=3), diarrhea (n=5), constipation (n=3), and creatinine increased (n=2). No patients experienced tumor lysis syndrome. Overall response rate (ORR) was 44% (2 each with very good partial response, VGPR and PR) and clinical benefit rate (CBR) was 89% with 2 additional patients showing minor response (MR) and 2 experiencing stable disease (SD) (Fig 1). Patients with high-risk disease had an ORR of 43% and a CBR of 100%. Median progression-free survival (PFS) for all patients was 8.1 months. Correlative analysis from patients who showed an objective response to treatment revealed a significant increase in bone marrow Th-effector cells, NK cells and cytotoxic CD8+ T-cells along with a significant decrease in immunosuppressive T-regulatory and B-regulatory cells was noted after 1 complete cycle of the combination therapy (p<0.05, Fig 2).
Conclusions: This is the first reported clinical trial combining a Bcl-2 inhibitor with immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) in MM. AT-101-Rd is a clinically active regimen with an ORR of 40% in predominantly high-risk RRMM patients with an acceptable toxicity profile. Additional patients with MM experienced clinical benefit despite refractory status to prior therapy in this early phase clinical trial. These early findings support the further investigation of AT-101 specifically, and Bcl-2 inhibitors in general, with IMiDs in patients with MM.
Ailawadhi:Celgene: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Cellectar: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy. Chanan-Khan:Xencor: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Jansen: Research Funding; Mayo Clinic: Employment; Ascentage: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding.
AT-101 is not currently FDA-approved for treatment of any condition.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal