Introduction
Recurrent somatic mutations (SM) of the splicing factor 3B subunit 1 (SF3B1) are among the most commonly occurring in MDS patients (pts), detected in ~20% of MDS overall, and in approximately 80% of MDS with ring sideroblasts (RS). SF3B1 SM are singularly associated with favorable outcome in MDS in the absence of adverse mutations. Next generation sequencing (NGS) is being increasingly incorporated into the evaluation of MDS pts. However, current results of NGS are reported and interpreted based solely upon the presence or absence of mutations without regard to the mutation allelic burden. Variant allele frequency (VAF) of somatic mutations has been used to reconstruct the clonal architecture in MDS. We examined the impact of SF3B1 VAF on outcomes and response to treatment.
Methods
We identified all MDS pts informative for SF3B1 mutation status through the Moffitt Cancer Center MDS database. We excluded pts with MDS/MPN or del(5q). We validated the prognostic value of SF3B1 SM in our entire cohort, and then excluded those pts lacking data on SF3B1 VAF. We examined the prognostic value of VAF as a continuous variable using Cox-regression analysis model, and then based on the mean SF3B1 VAF, we divided pts into two groups: VAF ≤ 30 or > 30%. We compared baseline characteristics between the two groups, frequency of other somatic mutations, response to treatment, AML transformation and overall survival (OS). We used the online software (http://molpath.charite.de/cutoff ) (R version 2.15.0), developed for biomarker cutoff determination, to assess the cutoff point of the SF3B1 VAF which best correlates with outcome. The NGS sequencing was performed on an Illumina based platform as part of standard routine clinical assessment.
Results
Among 763 MDS pts in our database tested for SF3B1 SM, 148 (19.4%) were SF3B1 mutated (MT), of whom 109 (74%) were classified with RS subtypes by WHO 2016 classification. SF3B1 MT was independently associated with better OS after adjusting for IPSS-R, Hazard ratio 0.43 (95% CI .28-.66) (P <.001). The most common SF3B1 hot spot mutation was p.K700E in 47% of cases. The most commonly accompanying gene mutations were: TET-2 (30%), DNMT3A (19%), ASXL-1 (17%), RUNX-1 (9%), and JAK-2 (5%). TP53 MT was detected in 3 pts, and interestingly, 4 pts harbored a second concomitant splicing mutation, 2 pts with SRSF2 MT, U2AF1 and ZRSR2 one each. Seven pts harbored accompanying TET-2 and DNMT3A mutations.
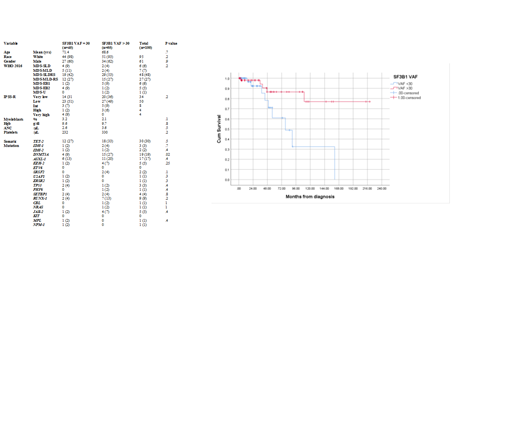
Data on VAF was reported in 100 pts. The mean VAF was 30.45%. As a continuous variable, higher VAF was associated with improved OS, HR 0.95 (95% CI .9-.99) (P .024). We divided patients into two groups SF3B1 VAF ≤ 30 or >30 % using the mean VAF as the cutoff. Table-1 summarizes baseline characteristics between the two groups.
Interestingly, DNMT3A concomitant MT was significantly more frequent among pts with VAF >30 compared to those with VAF ≤ 30%, 15/55 (27.3%) versus 4/45 (8.9%), (p.023). There was no difference in distribution of other accompanying MT among the 2 groups.
The median OS was not reached for those pts with >30% compared to 78 months (95%CI 43-118) for those with VAF ≤ 30% (P .008). The HR for OS was 0.24 (95% CI 0.08-.75) (P .014) for SF3B1 VAF> 30%. There was no difference in the rate of AML transformation 7.3% versus 6.7%, respectively for those with VAF >30 and ≤ 30% respectively, (P 1.0). SF3B1 VAF > 30% was independently associated with favorable OS after adjusting for IPSS-R, HR .29 (95% CI .09-.88) (P .03)
The rate of hematological improvement (HI) with erythroid stimulating agents was 53% (21/39) and 43% (9/21) for those with VAF >30 and ≤ 30% respectively, (P .42). The overall response rate to hypomethylating agents (HMA) measured by HI or better was significantly lower in pts with VAF >30 (9%; 2/22) compared to those pts with VAF ≤ 30%. (10/16, 62.6%; P=0.01). The HI rate with lenalidomide was 21.4% (3/14) for those with VAF >30 and 10 % (1/9) for those with VAF ≤ 30%. (P .46)
The optimal VAF cutoff related to OS using fit of mixture model was 32.37%, with HR for of 0.26 (95% CI .08-.8) (P .013).
Conclusions
To our knowledge, this is the first study to demonstrate an impact of SF3B1 clone size on outcome and response to treatment in MDS. Higher VAF > 30% was associated with significantly more prolonged OS, and surprisingly, a lower probability of response to HMA. DNMT3A MT is the only SM significantly associated with higher SF3B1 allele burden, and had no adverse effect on outcome.
Komrokji:Novartis: Speakers Bureau; JAZZ: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; DSI: Consultancy; pfizer: Consultancy; celgene: Consultancy; JAZZ: Speakers Bureau. Sallman:Celyad: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kuykendall:Abbvie: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy; Celgene: Honoraria. Talati:Agios: Honoraria; Daiichi-Sankyo: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Astellas: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Sweet:Incyte: Research Funding; Stemline: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Agios: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Jazz: Speakers Bureau. Lancet:Agios, Biopath, Biosight, Boehringer Inglheim, Celator, Celgene, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Karyopharm, Novartis: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Other: fees for non-CME/CE services . List:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal