Background
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is an incurable B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma associated with poor outcomes. First-line treatment incorporates cytotoxic chemotherapy and rituximab, but there is no single standard of care regimen. In British Columbia (BC), between January 2003 and May 2013, R-CHOP was the preferred induction regimen. Based on results from the STIL-1 trial (Rummel et al, Lancet 2013) demonstrating improved CR rate and prolonged progression-free survival (PFS) of bendamustine and rituximab (BR) compared with R-CHOP, in June 2013, BR became the standard first-line therapy for all patients with MCL regardless of age. In both eras, fit patients generally ≤65 years of age responding to induction were eligible for high-dose BEAM and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). Maintenance rituximab (MR) has been offered to responding patients post ASCT since 2004 and for transplant ineligible patients since 2012. The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy of BR as an induction regimen for MCL.
Methods
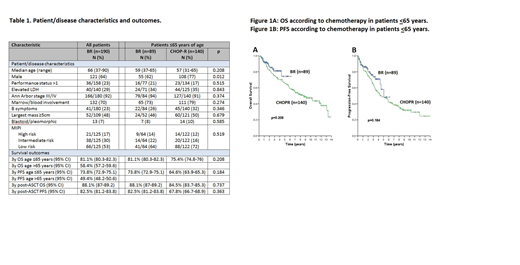
Patients with MCL treated with first-line BR were identified in the BC Cancer clinical and pathology databases as well as the Leukemia/BMT Program of BC transplant database. BR was initiated no later than December 2018. Treatment received was verified using the BC Cancer Provincial Pharmacy database, and clinical characteristics were verified using the BC Cancer Information System. Radiotherapy for localized disease, splenectomy, or a period of observation prior to systemic therapy were permitted. PFS and overall survival (OS) were calculated from the date of initiation of systemic therapy. In the subgroup of patients ≤65 years of age, results were compared to a historical cohort uniformly treated with R-CHOP. Baseline and treatment characteristics associated with PFS or OS (p<0.05) as well as the treatment variable (BR vs. R-CHOP) were included in Cox regression multivariate models using a backward likelihood ratio approach.
Results
A total of 190 BR-treated patients were identified. Table 1 shows clinical and treatment characteristics. Excluding 4 patients with an unknown response to BR, 101 (54%) patients achieved a complete response and 62 (33%) a partial response, for an 87% overall response rate. 23 (12%) patients progressed during or within 3 months after BR, and all had highly proliferative MCL (Ki-67 ≥30%) or blastoid/pleomorphic histology.
Among the 89 BR-treated patients ≤65 years of age, 60 (67%) underwent ASCT and 29 (33%) did not (10 PD, 10 patient preference, 7 comorbidities, 2 pending). Among the 101 patients >65 years old, 9 underwent ASCT (age 66-71) and 92 did not. 63/69 patients received MR after ASCT, and 77/121 received MR after BR (without ASCT). Reasons for not receiving MR (6 after ASCT, 44 after BR) were 25 PD, 10 ASCT/BR toxicity, 7 pending, 3 patient preference, 3 early deaths, 2 physician preference.
With a median follow-up of 2.4y (range 0.2 - 6.1) in living patients the 3y OS was 69.5% (95% CI 69.4-70.6) and 3y PFS 62.8% (95% CI 62.4-63.6). Baseline characteristics and outcomes were similar between patients ≤65y treated with BR vs. R-CHOP (Table 1, Figure 1A and 1B). 81/140 (58%) patients treated with R-CHOP underwent ASCT. In the subgroup of patients who underwent ASCT, outcomes calculated from the point of ASCT were not statistically different between BR vs. R-CHOP.
In univariate analysis, age >65y, ECOG performance status >1, elevated LDH, blastoid/pleomorphic morphology, no ASCT, and no MR were associated with worse PFS and OS. In multivariate analysis including these variables as well as chemoimmunotherapy regimen, treatment with BR was not associated with PFS or OS.
Conclusions
In this population-based analysis, BR is an effective induction regimen for both transplant eligible and ineligible patients. ASCT is feasible in patients treated with BR induction. Even though BR was associated with a numerical improvement in PFS compared to R-CHOP in patients ≤65y, differences in PFS and OS were not statistically significant. Longer follow-up is necessary to fully understand the impact of BR in the frontline setting. We observed PD in 12% patients, suggesting that BR may not be an optimal induction regimen across all patients with MCL, particularly in those with aggressive or highly proliferative disease.
Villa:Roche, Abbvie, Celgene, Seattle Genetics, Lundbeck, AstraZeneca, Nanostring, Janssen, Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria. Sehn:Morphosys: Consultancy, Honoraria; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Acerta: Consultancy, Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Apobiologix: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen-Ortho: Consultancy, Honoraria; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria; F. Hoffmann-La Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Verastem: Consultancy, Honoraria; Lundbeck: Consultancy, Honoraria; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Acerta: Consultancy, Honoraria; F. Hoffmann-La Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria; Morphosys: Consultancy, Honoraria; TEVA Pharmaceuticals Industries: Consultancy, Honoraria; TEVA Pharmaceuticals Industries: Consultancy, Honoraria; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen-Ortho: Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Lundbeck: Consultancy, Honoraria. Savage:BMS, Merck, Novartis, Verastem, Abbvie, Servier, and Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Song:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria. Freeman:Seattle Genetics, Janssen, Amgen, Celgene, Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria. Scott:Roche/Genentech: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; NanoString: Patents & Royalties: Named inventor on a patent licensed to NanoSting [Institution], Research Funding. Gerrie:Lundbeck, Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal