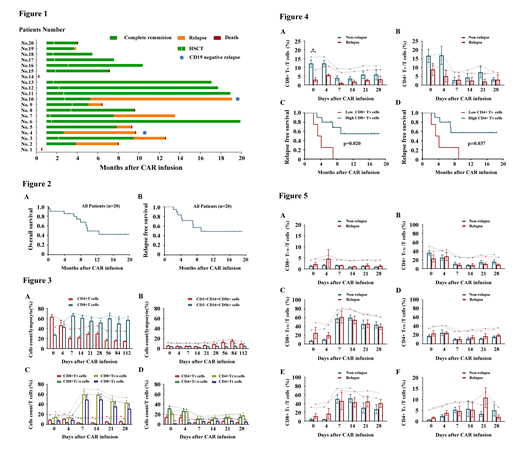
Data from systemic clinical trials about chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cell therapy against CD19 (CD19 CAR) differ in CAR design, T-cell activation and transduction methods at different institutions. However, according to these clinical trials, the single-chain fragment variable (scFv) sequence specific for tumor antigen were mostly derived from the FMC63 or SJ25C1 clones. Our previous study showed that the CD19 CAR constructed in our laboratory derived from clone HI19α (HI19α-4-1BB-ζ CAR) was highly effective in preclinical models. Herein, we conducted a single-arm, phase I clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of HI19α-4-1BB-ζ CAR (CNCT19) in patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (R/R B-ALL). From November 2016 through December 2018, 20 R/R B-ALL patients were enrolled into this clinical trial. Complete remission (CR) or complete remission with incomplete count recovery (CRi) was achieved in 100% (18/18) of patients that could be evaluated on day 28 after infusion, which accounted for 90% of all 20 enrolled patients. After a median follow-up of 17.0 months (range, 0.2 - 19.8), the median overall survival (OS) for the entire cohort of patients was 9.6 months (95% CI 4.2 - 15.0), and was not reached for 14 patients bridge to allogeneic transplantation. The median relapse free survival (RFS) of all patients was 9.0 months (95% CI, 6.7 - 11.2). Two patients died within 28 days due to cytokine release syndrome (CRS), while other patients experienced controllable cytokine-release syndrome and neurotoxicity. In order to better understand the correlation between T cell subsets and long-term response, we consistently evaluated the T cell phenotype and expansion kinetics in peripheral blood after CART infusion. The results revealed that the percentage of CD8+ naïve T cells (TN) collected from peripheral blood 20min after CAR infusion, were significantly lower in patients who relapsed from CART therapy than patients with continues CR (p=0.003), while central memory T cells (TCM), effective memory T cells (TEM) and effector T cells (TE) had similar proliferation kinetics between these two groups. In addition, multivariate analysis indicated that low percentage of CD8+TN cells was an independent factor associated with shorter RFS (p=0.033, 95% CI 0.031-0.861). This report is the first trial to provide evidence that CNCT19, a CD19 CAR constructed of a new anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor HI19α, has potent antileukemia activities in patients with R/R B-ALL. Furthermore, our results indicate the phenotype and kinetics of T cells are possible biomarkers to predict the long-term prognosis of CART treatment.
Lv:Juventas Cell Therapy Ltd.: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal