Object: Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a rare hematologic malignancy with heterogeneous course and always resistant to chemotherapy at advance or relapsed stage. Hippo signaling pathway is one of the most popular pathways in solid tumors. The major role of this pathway is regulating cell proliferation, migration, and maintaining the stemness of cells. However, the relationship between this pathway and MCL had been rarely studied. The purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between MCL and YAP, the key molecule Hippo signaling pathway, to further clarify the mechanism of MCL resistance and to find new therapeutic targets.
Methods: In this study, expression of YAP in B cell non-hodgkin's lymphoma (B-NHL) and mantle cell lymphoma detected by real-time PCR, Western blot analysis, immunofluorescence. Knockdown of YAP by sh-RNA or inhibit the function of YAP using verteporfin (VP). Next, the effects of YAP knockdown and YAP inhibitor on MCL cells were evaluated by fluorescence detection, real-time PCR and Western blot. Cell count, CCK8, Soft Agar Assay and in vitro functional assays were performed to elucidate the function of YAP-mediated cell proliferation, the effect on signaling pathway and the relationship with chemoresistance in MCL.
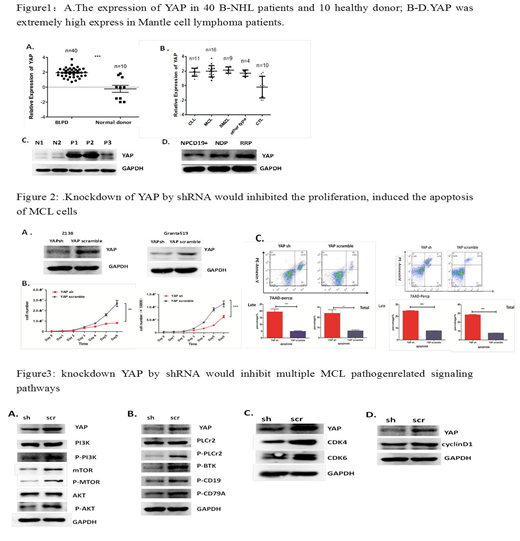
Results: We detected the expression of YAP in 40 B-NHL patients and 10 healthy donor and found that YAP were overexpressed in relapsed and newly diagnosis patients and it was extremely higher in relapsed patients. Moreover, YAP is extremely high express on MCL. Knockdown YAP by shRNA or YAP inhibitor verteporfin (VP) could not only inhibit the proliferation, induce the apoptosis of MCL cell lines, but also lead to cells stopping in G1 phase. In addition, knockdown YAP could sensitize Z138 cells to the cytotoxics of BTK inhibitors ibrutinib and SYK inhibitor R788.Combined VP and ibrutinib or R788 had obvious synergy. Most importantly, knockdown YAP could obviously reduce the expression of protein involved in G1 phase, inhibit the BCR signaling pathway and PI3K AKT signaling pathway, and promote cell apoptosis and DNA damage signaling pathways. Through regulating multiple signaling pathways, YAP played an important role in cell proliferation and drug resistance in B-NHL.
Conclusion: It was the first time to demonstrate that Hippo signaling pathways may associate with the pathogenesis and drug resistance of MCL. Targeting the key molecular of Hippo signaling pathways may be potential therapeutic targets of MCL patients especially the relapse and refractory patients.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal