Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a life-threatening thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), characterized by widespread intravascular thrombosis. Diagnosis of TTP is confirmed by a deficiency in ADAMTS13. However, given the urgency of prompt diagnosis and delayed turnaround time of ADAMTS13 assay in most labs, initial diagnosis is based on clinical acumen. Suspected TTP is empirically treated with plasma exchange (PLEX), which, while beneficial in TTP, may delay appropriate treatment for similar disorders. The PLASMIC score was developed by Bendapudi et al. (Lancet Hematology 2017) to utilize clinical signs and investigations to predict which patients had an ADAMTS13 score < 10%, and therefore TTP, who require PLEX. Validation studies have shown a very high sensitivity (90-98%) and high specificity (46-92%), although these studies included an enriched population with available ADAMTS13 assay results (Jajosky et al. Transfusion and Apheresis Science, 2017, Li et al. Journal of Thrombosis and Hemostasis 2018). The purpose of this study is to validate the PLASMIC score using a Canadian population of suspected TTP regardless if ADAMTS13 was ordered, and compare it to clinical gestalt.
This is a retrospective cohort study of all adults aged 18 years or older who presented or were transferred to any of the two apheresis centres in Alberta, Canada with a suspected diagnosis of TTP from January 1, 2008 - December 31, 2018. A confirmed diagnosis of TTP was defined as an ADAMTS13 level prior to PLEX < 10%, or ADAMTS13 level between 10-20% if drawn after plasma infusion or PLEX. ADAMTS13 testing was done in accordance with the procedures at these institutions.
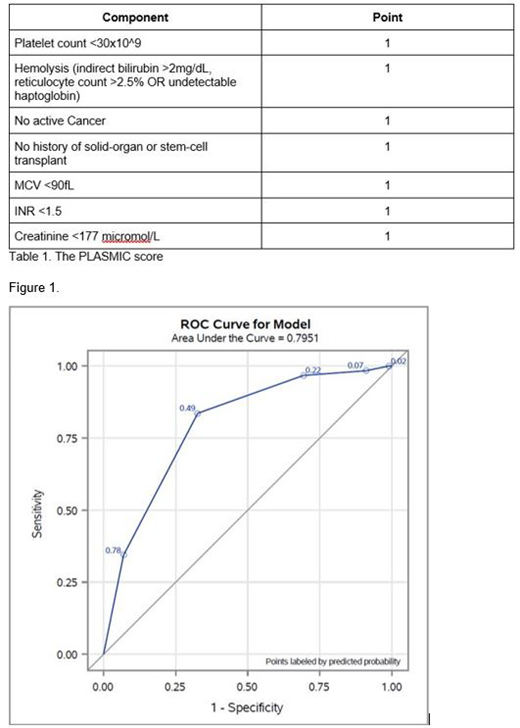
The PLASMIC score was used to stratify patients into low (0-4), intermediate (5) and high (6-7) risk of TTP (Table 1). Descriptive analyses was performed to examine the proportion of patients with low-, intermediate-, and high-risk PLASMIC score who had ADAMTS13 testing done and who received PLEX. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) of PLASMIC score were calculated. Two PLASMIC score cutoffs were used for the analysis, 1) high risk vs low to intermediate risk, and 2) intermediate to high risk vs low risk. Receiver operator curve (ROC) analysis was used to test the association between severe ADAMTS13 deficiency and the PLASMIC score. PLASMIC scores were also compared to clinical gestalt, defined as initiation of PLEX within 48 hours of presentation. The C statistic was calculated from the area under the ROC and compared using the Z-test. As some patients who may have died from TTP did not have ADAMTS13 level sent, sensitivity analysis was performed to assess the ROC curve for the PLASMIC score in detecting both definite and probable TTP. A P-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Of the 162 cases of suspected TTP, 61 (38%) had severe ADAMTS13 <10%. ADAMTS13 was sent prior to plasma exchange in 103 (64%) cases and shortly after PLEX initiation in 15 (9%). Using a high-risk PLASMIC score cut-off (6-7) vs low to intermediate-risk score (0-5), the sensitivity was 83.6%, specificity 67.3%, PPV 60.7% and NPV 87.2%. In contrast, using a cut-off of medium to high-risk PLASMIC score (5-7) vs low-risk score (0-4), the sensitivity improved to 96.7%, whereas the specificity was reduced to 30.7% (PPV 45.7% and NPV 93.9%). The C-statistics were 0.75 (95% CI 0.69-0.82) and 0.64 (95% CI 0.59-0.69) using the high PLASMIC score and medium-high PLASMIC score cut-offs, respectively (Figure 1). In contrast to PLASMIC score-based risk stratification, clinical gestalt has a comparable sensitivity of 83.6%, but a much lower specificity of 38.9%. There was very low correlation between PLASMIC score and clinical gestalt (kappa 0.0883 (95% CI -0.03-0.21).
In our cohort, a high-risk PLASMIC score successfully predicted patients with severe ADAMTS13 deficiency in a Canadian TMA population, with similar sensitivity and improved specificity compared to clinical gestalt. Integration of this scoring system into institutional clinical pathways should be considered to supplement clinician judgment and reduce costs.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal