Sickle cells disease (SCD) is an inherited red blood disorder that leads to acute and chronic organ complications. The kidneys are among the most commonly affected organ systems and chronic kidney disease (CKD) predicts increased morbidity and early mortality in SCD (PMID 1892333). Risk factors for CKD have been primarily investigated in patients with homozygous inheritance of the hemoglobin (Hb) S mutation but are not as well understood in other SCD variants, such as in those with Hb SC or Hb SB+-thalassemia.
We investigated clinical, laboratory, and genetic predictors (α-thalassemia and the APOL1 G1 and G2 kidney disease risk variants) for CKD in a combined analysis of non-Hb SS patients from the University of Illinois at Chicago and the multi-center Walk-PHaSST cohort. Clinical and laboratory variables were obtained at the time of enrolment. Estimated glomerular filtration (eGFR) rate was calculated using the CKD-EPI formula and CKD stage was defined according to the KDIGO guidelines. Univariate analysis for the association of variables with eGFR, albuminuria, and CKD stage were conducted using the linear trend test and Cochran's test for linear trend. Variables with a P < 0.1 were entered into linear and ordinal logistic regression models adjusting for age and sex. Median and interquartile ranges (IQR) are provided.
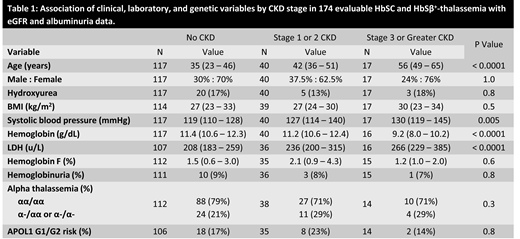
Two hundred and forty-seven patients were included in this analysis. The median age of this cohort was 39 years (IQR, 24 - 50 years), 62% were female, 16% were on hydroxyurea, and 72% were Hb SC genotype. Albuminuria data was available in 174 patients; microalbuminuria (albuminuria 30 - 300 mg/g creatinine) was present in 24% and macroalbuminuria (albuminuria > 300 mg/g creatinine) in 5% of patients. Patients with higher urine albumin concentration were older, had higher systolic blood pressures and LDH concentrations, and lower hemoglobin concentrations (P ≤ 0.03). On multivariate analysis, the urine albumin concentration was independently associated with a higher systolic blood pressure (log transformed β +3.08 ± 1.09; P = 0.005) and a lower hemoglobin concentration (β -0.17 ± 0.09; P = 0.05). Patients with lower eGFR were older, had higher body mass indexes and systolic blood pressures, lower hemoglobin concentrations, and were more frequently female (P ≤ 0.04). No variables were independently associated with eGFR on multivariate analysis after adjusting for age and sex.
When applying the KDIGO CKD staging criteria, 67% were classified as not having CKD (urine albumin < 30mg/g creatinine and eGFR > 60 mL/min/1.73m2), 23% had stage 1 or 2 CKD (urine albumin ≥ 30mg/g creatinine and eGFR > 60 mL/min/1.73m2), and 10% had stage 3 or greater CKD (eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73m2). Patients with increasing CKD stage were older, had higher systolic blood pressures and LDH concentrations, and lower hemoglobin concentrations (Table 1) (P ≤ 0.005). On multivariate analysis, incremental CKD stage was independently associated with lower hemoglobin (OR 0.91, 95%CI: 0.88 - 0.94; P = 0.002) and higher LDH (natural log OR 1.43, 95% CI: 1.27 - 1.61; P = 0.004) concentrations. We did not observe an association between coinheritance of α-thalassemia or the APOL1 G1/G2 risk variants with urine albumin concentration, eGFR, or CKD stage.
In conclusion, we demonstrate that CKD is a common comorbidity that is observed in approximately one third of SCD patients with the Hb SC or Hb Sβ+-thalassemia genotypes. A lower hemoglobin concentration and higher systolic blood pressure were independently associated with greater urine albumin concentration. This may reflect anemia causing reduced oxygen delivery to the renal cortex and hypertension-mediated vascular and glomerular damage. The association of worsening CKD stage with lower hemoglobin and higher LDH concentrations, consistent with increased hemolysis, is similar to what has been observed in the Hb SS genotypes. The potential effects of hemolysis on kidney function in the Hb SC and Sβ+-thalassemia genotypes will need to be explored further.
Gladwin:Bayer Pharmaceuticals: Other: Co-investigator; United Therapeutics: Patents & Royalties: Co-inventor on an NIH government patent for the use of nitrite salts in cardiovascular diseases ; Globin Solutions, Inc: Patents & Royalties: Provisional patents for the use of recombinant neuroglobin and heme-based molecules as antidotes for CO poisoning. Gordeuk:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Global Blood Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Emmaus: Consultancy, Honoraria; Modus Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Modus Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer: Research Funding; Inctye: Research Funding; Inctye: Research Funding; CSL Behring: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; CSL Behring: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Ironwood: Research Funding; Ironwood: Research Funding; Imara: Research Funding; Imara: Research Funding. Saraf:Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal