
The prognosis of patients (pts) with relapsed/ refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) remains poor and novel therapies are needed. The anti-CD22 immunoconjugate inotuzumab ozogamicin (IO) has demonstrated promising results in phase 2 and 3 trials. Pre-clinical studies have demonstrated superior anti-tumor activity when IO is co-administered with cyclophosphamide (C), vincristine (V), and prednisone (P). We assessed the safety of IO in combination with CVP and determined the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of IO in this regimen for pts with relapsed or refractory (R/R) CD22+ acute leukemia. An expansion cohort was treated at the MTD and efficacy results are presented.
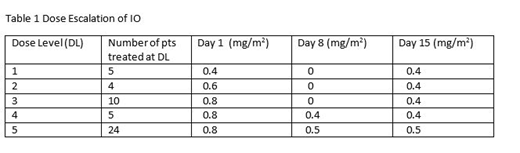
Methods: Pts were treated at SWOG institutions from 2014-19. IO was supplied by Pfizer. Eligibility: age > 18 yrs, > 20% blasts expressing CD22, R/R CD22+ acute leukemia (B-ALL, mixed phenotype, or Burkitts), and adequate organ function. All pts received C (750 mg/m2) intravenous (IV) Day (D) 1, V (1.4 mg/m2) (max 2 mg) IV D1, P (100 mg) orally D 1-5 and IO (dose escalated as in Table 1) up to a maximum of 6 cycles. Each cycle was 28 d. Dose escalation utilized a standard 3+3 design with the plan to treat 12 additional pts at the MTD. Dose limiting toxicities (DLTs) were considered: (1) > Grade (Gr) 4 non-hematologic toxicities (NHTs) with the exception of nausea, vomiting and toxicities secondary to neutropenia and sepsis; (2) prolonged myelosuppression [absolute neutrophil count < 500/ uL or platelet count < 25,000/uL] in a bone marrow with < 5% blasts and no evidence of leukemia that lasts > 35 d beyond the last dose of IO; (3) any Gr 3 NHT (excluding peripheral neuropathy, hyperglycemia, and toxicities secondary to neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and sepsis) that does not resolve to < Gr 2 by 7 d beyond the last dose of IO; (4) any > Gr 3 elevation in SGOT/ SGPT or bilirubin lasting > 7 d; (5) any IO-related toxicity resulting in permanent discontinuation of IO.
Results: 50 pts were enrolled; 2 were ineligible. The median age was 43 yrs (range 20-79), 56% were male, and the median WBC at registration was 2.7 K/uL (range 0.3-59.6). All pts had B-ALL. The median time from initial diagnosis to registration was 515 d. Twenty-one pts were in 1st relapse, 12 in 2nd relapse, 4 in 3rd relapse, 1 in 4th relapse, and 10 pts were refractory to their last treatment. Eighteen pts (38%) had received prior blinatumomab; 9 had prior allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (AHSCT); 30% had poor risk cytogenetics (Ph+, -7, +8, complex, MLL abnormalities, or hypodiploid); 13 pts were tested for the Ph-like signature with 5 pts identified as Ph-like. One death occurred during treatment and was attributed to pneumonia in the setting of active ALL. Gr 3-4 hematologic toxicity related to treatment was common: neutropenia (73%), thrombocytopenia (63%), and anemia (50%). Gr 3-4 NHTs were mainly febrile neutropenia. One DLT occurred at DL 3: prolonged myelosuppression and 1 DLT at DL 5: Gr 3 ascites. Gr 3-4 transaminases or bilirubin occurred in 1 pt (2%) during treatment and in 10 pts (23%) during follow-up. No cases of hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD) occurred during treatment but 3 (7%) occurred during follow up (post-transplant). The MTD was DL 5. Thirteen pts (30%) proceeded to AHSCT after study treatment. The complete remission (CR)/ CR with incomplete count recovery rate was 61% (95% CI 39%-80%) in the 23 evaluable pts treated at the MTD, and 60% (3/ 5) in pts with the Ph-like signature. There was no statistically significant difference in response rates or hepatic toxicities between the various DLs. However, all 3 VOD cases occurred either after 2nd transplant (n=2) and/ or at DL 5 (n=2). The rates of CR/CRi were 60% and 50% respectively in DLs 1 and 2. The median overall survival was 7.7 months for all pts, and 10.9 months for pts treated at the MTD. Notably, 1 pt remains in a remission 3.5 yrs out from registration without having a transplant.
Conclusion: CVP/IO is relatively well tolerated with high response rates and low toxicity despite a heavily pre-treated group of pts. Minimal residual disease data and additional Ph-like signature data are being compiled. Randomized studies will be needed to determine differences in toxicities and response rates with the various doses. However, there is a suggestion that VOD may increase with higher doses of IO and in the setting of 2 transplants. This regimen may represent a promising strategy in the treatment of elderly pts in the newly diagnosed setting.
Advani:Abbvie: Research Funding; Macrogenics: Research Funding; Glycomimetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Amgen: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding. Liedtke:Prothena: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; IQVIA/Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celator: Research Funding; Caelum: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BlueBirdBio: Research Funding; Amgen/Onyx: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Adaptive: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios: Research Funding. Aldoss:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Other: travel/accommodation/expenses, Speakers Bureau; Agios: Consultancy, Honoraria; AUTO1: Consultancy; Helocyte: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel/accommodation/expenses. Othus:Celgene: Other: Data Safety and Monitoring Committee; Glycomimetics: Other: Data Safety and Monitoring Committee. Erba:Amgen, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, ImmunoGen, Incyte, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Millennium, Novartis, Ono, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Sunesis: Consultancy; Celgene, Incyte, Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Agios, Amgen, Astellas Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, ImmunoGen, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Juno, Millennium, Seattle Genetics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal