Patients with sickle cell anemia (SCA) have increased susceptibility to infections partially explained by functional splenic and alternative complement pathway defects. Cord blood transplants (CBT) and high doses anti-thymoglobulin (ATG) are suspected to be responsible for viral complications and EBV lymphoma but most of the reports concerned unrelated SCT. The aim of the present study was to compare the immune reconstitution after CBT vs BMT from HLA-identical sibling, in patients prepared with the same myeloablative conditioning regimen (MAC).
This retrospective analysis concerns SCA-children all followed in the same CHI-Créteil referral center and transplanted from a HLA-identical sibling with MAC consisting of busulfan, cyclophosphamide and rabbit ATG (Genzyme at 20mg/kg). Pre- and post-transplant clinical and biological data were prospectively recorded in the local database. Lymphocyte subpopulations (CD3+, CD4+, CD8+), IgG, IgA, IgM were recorded each month during the first year post-transplant. Jolly bodies (classified as 0=absent, 1=rare, 2=a few, 3=numerous) and HBs, DTPolio vaccinal serologies were assessed at transplant time (T0), 1 (T1) and 2 years (T2) post-transplant. Revaccination with DTPolio was performed at 1y post-transplant
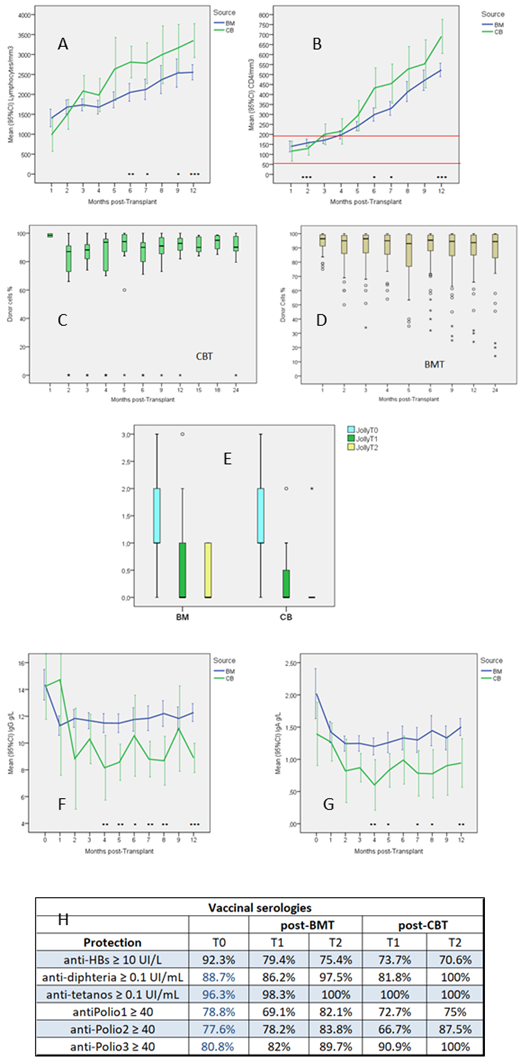
One-hundred-seven SCA-patients (41F,56M) with severe disease were transplanted (1992-2012) with BM (n=83), CB (n=21), CB+BM (=3) at median (range) age: 9.7y (3.4-22.2) for BMT and 6.1y (3.2-12.9) for CBT (p=0.002). Four patients had splenectomy and 5 others partial splenectomy. Rate of rejection was higher after CBT (p=0.002) with 2 non-engraftments and no late rejection whatever the source. TRM was not different despite the occurrence of 3 deaths only after BMT (obliterant bronchiolitis at 1.1year, hemorrhagic stroke at day36, adenoviral encephalitis at month5). Acute GVHD ≥II was observed in 18 patients (16 BMT, 2 CBT) and mild and extensive chronic-GVHD in 5 and 2 patients respectively after BMT and 1 mild after CB+BMT. At 5-year DFS was 95.3% (CI:91.3-99.3%). No significant difference in GVHD and DFS rates was observed according to the source. Neutrophils reached 500/mm3 at mean day32 vs day21 (p<0.001) and platelets reached 50,000/mm3 at day 45 vs 26.5 (p=0.001) after CBT vs BMT. While CD3+ and CD8+ counts never differed between 2 cell sources, CD4+ count was significantly lower until M3 and lymphocyte and CD4+ counts higher after M6 after CBT than BMT (FigAB). After transplant, CMV replications were observed in 38 patients (36 reactivation and 2 primary infection) among the 107 patients but no CMV-disease and no significant difference in the incidence between BMT: 29/83 (34.9%) and CBT: 7/21 (33.3%). EBV replication required anti-CD20 treatment in 5 patients (1 CB, 4 BMT) but no lymphoma occurred. No late infectious complication nor malignant disease was observed in this series. Chimerism outcome (FigCD) was not different between 2 sources after exclusion of the 2 non-engrafted patients: Donor cells % at 1- and 2-year post-T: 92.8% (4.7) vs 87.9% (16.4) and 92.6% (5.4) vs 86.1% (19.1) after CBT vs BMT.
Paired analysis comparing results at T0 vs T1 and T2 showed a significant decrease of the mean (SD) Jolly bodies score from 1.38 (0.85) at T0 to 0.50 (0.81) at T1 and 0.28 at T2 (p<0.001). This improvement was not different after BMT vs CBT (FigE). Mean (SD) IgG decreased from 14.2 g/L (4.0) to 12.6 (4.1) at T1 (p=0.003) and 13.1 (3.0) at T2, IgA from 1.89 g/L (1.24) at T0 to 1.33 (0.80) at T1 (p<0.001) and 1.40 (0.64) at T2 whereas IgM were not significantly modified (Fig FG). This decrease of IgG between T0 and T1 was significantly more important after CBT than BMT (p=0.05). Only 2 patients had IgG< 4g/L, one at 9 and 12m post-BMT and another at 3m post-CBT. Mean (SD) anti-HBs (all from vaccinal origin) decreased significantly from 350 UI/L (395) at T0 to 241 (352) at T1 (p<0.001) with 271 (385) at T2 but no difference was observed in the proportion of protected patients (antiHBs≥10UI/L) after CBT vs BMT. No significant difference was found after BMT vs CBT at T0, T1 and T2 in DTPolio123 serologies nor in the proportion of patients protected against DTPolio123 at T0, T1 and T2 (FigH)
We confirm the improvement of splenic function after SCT and conclude that contrary to unrelated CBT and SCT using high dose ATG, CBT from HLA-identical sibling do not expose significantly to more frequent viral infections or reactivations and have satisfactory vaccinal response
Bernaudin:BlueBirdBio: Consultancy; AddMedica: Honoraria, Other: Help for travel; GBT: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Socie:Alexion: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal