Introduction: Stage I disease represents a minor subset of aggressive Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) accounting around 10%. Overall prognosis is generally good but varied upon different histologic subtypes and topographic presentation. Herein, we describe an implication of event free survival at 12 months (EFS12) as a predictor for outcomes of stage I aggressive NHL including real-world data on clinical characteristics and treatment patterns of stage I aggressive NHL in a resource-limited country.
Patients and methods: Thai lymphoma study group conducted the lymphoma registry which prospectively enrolled and systematically followed newly diagnosed lymphoma patients between 2007 and 2014 from 13 nationwide major University hospitals. We abstracted data of stage I aggressive NHL patients from the registry and obtained additional information from medical record. Clinical characteristics, treatment patterns and survival outcomes were described. EFS12 was a binary endpoint defined as whether patients developed events at 12 months after treatment initiation. Overall survival (OS) was defined as duration from a specific time-point either at the time of diagnosis, at EFS12 time-point to or at the event to death from any causes. Logistic regression model was used to evaluate the association between clinical characteristics and EFS12. Cox regression with EFS12 as a time-dependent co-variate and other clinical parameters were applied to evaluate association between EFS12 and OS.
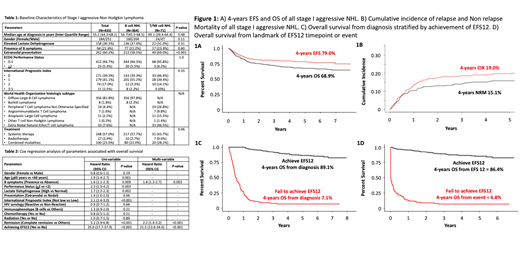
Results: Of 4,371 newly diagnosed lymphomas, there was a total of 636 stage I lymphoma patients (6.86%) including 590 NHL (519 B cell, 71 T/NK cell) and 46 HL. Among 590 stage 1 NHL, 435 were considered patients (356 diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 8 Burkitt lymphoma (BL), 19 peripheral T cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS), 7 angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL), 11 anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), 1 other PTCL subtypes and 33 extranodal NK T cell lymphoma (ENKTL)). Table 1 summarizes baseline characteristics and treatment data of stage I aggressive NHL. At the time of analysis 61 patients relapsed and 146 patients had died. Major causes of death included infection related events (n=37, 25.3%), non-infectious related complication (n=21, 14.4%) and disease progression (n=60, 41.1%) respectively. With a median follow up of 47.3 months, both median event free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) were not reached with corresponding 4 years EFS and 4 years OS of 79.0% and 68.9% respectively (Figure 1A). Four-years OS of patients with aggressive B cell NHL, PTCL and ENKTL was 70.2%, 75.5% and 48.0% respectively. A total of 328 patients achieved EFS12 (No event within the first 12 months after first line treatment initiation). Patients who achieved EFS12 had significant better OS than patients who failed to achieve EFS12 (4-years OS 89.1% vs 7.1%, Hazard ratio 25.9, 95% Confidence Interval 17.7-37.9, P<0.001) (Figure 1C, 1D). Non-relapsed mortality and cumulative incidence of relapse was 15.1% and 19.0% respectively (Figure 1B). By using multivariable cox regression analysis, factors associated with favorable survival outcomes included absence of B symptoms, complete remission from therapy and achieving EFS12 (Table 2).
Conclusion: Stage I disease represented a small proportion of aggressive NHL. Natural history and prognosis were highly varied depending upon histology. EFS12 was a power prognostic factor for stage I aggressive NHL and could be used as a clinical tool to stratify patients. Optimal treatment is to be defined to improve outcome and meanwhile minimize toxicities for stage I aggressive NHL patients.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal