Introduction:
Commercially available chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has improved the outcomes for patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (R/R) large B-cell lymphoma. Many pts have highly symptomatic, rapidly progressive disease that untreated could be fatal during the 3-4 week manufacturing interval. We examined the outcomes of pts treated with axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) and bridging interventions, including systemic therapy (ST) and radiation therapy (RT).
Methods:
We reviewed clinical efficacy and toxicity outcomes for 80 pts who underwent apheresis for axi-cel therapy between 12/2017 and 1/2019 at a single institution. Disease specific survival (DSS), progression free survival (PFS), toxicity free survival (TFS) and overall survival (OS) were defined from the date of CAR T-cell infusion. For the pts who received bridging treatment (defined as therapy given between apheresis and CAR T cell infusion), baseline clinical, treatment and toxicity characteristics were compared between cohorts that received ST versus RT. All comparisons were 2 sided.
Results:
Of the 80 pts who underwent apheresis, 73 (91%) received CAR T-cell therapy. Among these 73, 32 (44%) received bridging therapy and 41 (56%) did not. Pts who received bridging therapy were more likely to have an IPI of ≥3 at the time of apheresis (72%) compared to those that did not (39%; p=0.009). Of the 32 pts who received bridging therapy, 24 (75%) were treated with ST (corticosteroids [n=3], targeted therapy [n=4] and chemotherapy [n=17]) and 8 (25%) with RT. RT was administered to a median dose of 44.6 Gy (range 9-46 Gy) with a median fraction size of 2.5 Gy (range 1.8 -3 Gy). The median time between the end of RT and the CAR T-cell infusion was 16 days (range 0 -21).
The median age of the entire bridging therapy cohort was 59 (range 24 - 85 years). Twenty five pts (78%) were male, 23 had DLBCL (72%). Comparing the ST (n=24) to the RT (n=8) cohort, there were no differences in ECOG PS ≥2 (p=0.296), IPI of ≥3 (p=0.654), double hit or triple hit status by IHC (p=0.378) or FISH (p=0.578), bulky disease (≥10 cm, p=1.0), or elevated LDH at the time of apheresis (p=1.0).
Upon completion of bridging therapy, cytopenias requiring G-CSF administration prior to initiation of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide conditioning occurred in 18 pts with no difference between ST and RT cohorts (p=0.252). The median WBC and absolute lymphocyte count after bridging therapy and just prior to conditioning was 5.3 K/uL (range 1.5 -20.6) and 0.59 K/uL (range 0.07 - 1.9) respectively and was not statistically different between the ST and RT cohorts (p=0.851 and p=0.317). Twenty pts (62.5%) required G-CSF ≥ 14 days post CAR-T cell therapy infusion and did not differ between the groups (p=1.00).
Rates of grade ≥ 3 immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) were 25% in the RT cohort and 63% in the ST group (p=0.106). Rates of grade ≥ 3 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) were 12.5% in the RT cohort compared to 16.7% among ST treated bridging patients (p=1.00). Rates of ICU admission were not significantly different between the groups (p=0.423).
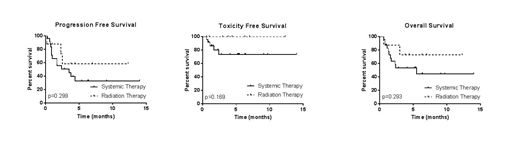
At a median follow up of 6.1 months (95% CI 4.0 - 6.9), there have been 13 deaths; the median OS for the entire bridging cohort has not been reached. Five deaths occurred due to toxicity (5/24 in the ST cohort and 0/8 in the RT group, p=0.296) as a result of infectious complications (n=3), ICANS (n=1) and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH, n=1). Eight deaths occurred due to lymphoma (6/24 in the ST cohort and 2/8 in the RT cohort, p=1.00). For the entire bridging group of 32 pts, 13 experienced lymphoma progression with a median DSS of 4.4 months. The median DSS was 4.43 months among the ST cohort and not reached in the RT cohort (p=0.644). The PFS was 3.5 months for all bridging pts with a median PFS of 3.5 months among the ST treated pts and not reached for the RT pts (p=0.314).
Conclusion:
Bridging therapy is often utilized at physician discretion to temporize aggressive disease and facilitate successful CAR T-cell infusion. In this single institutional study, judicious use of bridging therapy permitted 91% of patients to undergo CAR-T cell infusion. This preliminary data suggests that RT can be an effective bridging tool for pts with R/R large B cell lymphoma prior to axi-cel therapy. Larger cohorts are required to determine if RT bridging strategies may result in lower rates of treatment related mortality and improved disease control.
Pinnix:MD Anderson Cancer Center: Employment; Merck and Company: Research Funding; International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology and Physics: Honoraria; Global Oncology One: Consultancy. Hawkins:Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Other: advisory panels. Westin:Curis: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Novartis: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Kite: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Juno: Other: Advisory Board; Janssen: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Celgene: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; MorphoSys: Other: Advisory Board; Unum: Research Funding; 47 Inc: Research Funding; Genentech: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding. Fowler:Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Iyer:Novartis: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Research Funding; Arog: Research Funding. Parmar:Cellenkos Inc.: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Wang:Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; MoreHealth: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; BioInvent: Consultancy, Research Funding; VelosBio: Research Funding; Pulse Biosciences: Consultancy; Juno Therapeutics: Research Funding; Dava Oncology: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Aviara: Research Funding; BeiGene: Research Funding; Loxo Oncology: Research Funding. Neelapu:Poseida: Research Funding; Cell Medica: Consultancy; Precision Biosciences: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Karus: Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy; Unum Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; Allogene: Consultancy. Nastoupil:Bayer: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech, Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Spectrum: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal