
Background: The addition of the anti-CD33 targeting antibody Mylotarg (MY) to conventional "3+7" induction has been shown to improve the outcome of patients affected by acute myeloid leukemia (AML) without adverse cytogenetic alterations. Early reports suggested that MY was particularly effective among low risk patients, such as core binding factor AML, particularly if included in a high dose cytarabine-based induction therapy. The role of MY for intermediate risk patients appears to be less clear. Cytogenetically defined intermediate risk patients may be further stratified considering two frequent molecular aberrations: FLT3 "internal tandem duplication" (FLT3-ITD) mutation, associated with poor prognosis and NPM1 mutation (NPM1-mut), associated with a good prognosis. The concomitant presence of NPM1-mutpartially overcomes the negative prognostic impact of FLT3-ITD, which is also modulated by FLT3-ITD/wild type allelic ratio. NPM1 and FLT3 mutational status assessment is strongly recommended for risk stratification at diagnosis by the last ELN 2017 guidelines.
Aims: To investigate the efficacy of MY added to an intensive fludarabine, high dose cytarabine and Idarubicin-based induction regimen (FLAI) as frontline treatment for younger (<65 years), cytogenetically normal AML patients according to NPM1 and FLT3-ITD mutational status.
Methods:One-hundred and forty eight consecutive AML patients, treated in 3 Italian Hematology centersbetween 2008 and 2018and harboring at least one molecular alteration among NPM1-mut and FLT3-ITD, were included in the analysis. Thirty three patients carried isolated FLT3-ITD, 50patients showed concomitant FLT3-ITD and NPM1-mut and 65 isolated mutated NPM-1.Median age was 50 years(range: 18-65). All patients received FLAI induction (fludarabine 30 mg/sqm and ARA-C 2g/sqm on days1 to 5 plus idarubicin 10 mg/sqm on days 1-3-5), with or without low dose MY(3 mg/sqm, added in 42 patients), followed by a second induction without fludarabine and with idarubicin at the increased dose of 12 mg/sqm. Before 2017, patients with isolated FLT3-ITD mutation were scheduled for allogeneic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), if an HLA-matched sibling donor was available, whereas after 2017 only patients with high allelic burden isolated FLT3-ITD mutation received HSCT in first CR. The other patients received conventional high dose cytarabine consolidation for a total of 3 cycles.
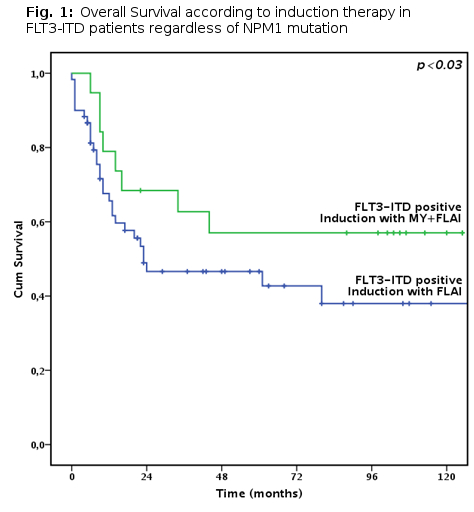
Results: Overall, 60-days mortality was 3%, and was not significantly influenced by receiving or not MY during induction. After one induction cycle, 126 patients achieved CR (85%) with no difference between patients receiving or not MY. After a median follow up of 70months, 3-year overall survival (OS) was 59.5% (median not reached). OS duration was significantly longer in NPM1 mutated patients (p <0.05).Patients with isolated FLT3-ITD mutation had a significantly worse prognosis (3-year OS 38.3%, p<0.05). The addiction of MY did not significantly improve outcome in the whole cohort but did show a significant positive effect on survival among FLT3-ITD patients (3-year OS 66.7% vs 46.6% for FLT3-ITD patients receiving or not MY, respectively, p<0.03, Fig. 1). This effect was more evident among the 33 NPM1 negative/FLT3-ITD patients: in this subgroup, patients who received MY had an overall good outcome that was similar to patients with double mutation who received the same therapy(median OS not reached in both groups, p=n.s.). On the contrary, among patients who did not receive MY, NPM1 negative/FLT3-ITD positive patients had a poor outcome, significantly inferior to double positive patients receiving the same regimen(3-Year OS 39.8% and 57.3%, respectively, p<0.05). The favorable effect of MY among FLT3-ITD patients was not influenced by FLT3-ITD allelic burden.Of note, the proportion of patients receiving HSCT in first CR, as expected, was higher among patients harboring isolated FLT3-ITD mutation, but there was no significant difference among patients receiving or not MY.
Conclusions: Despite the potential bias due to the retrospective nature of the analysis, our data seem to indicate that Mylotarg, added to an intensive fludarabine/high dose cytarabine-based induction, provides a significant improvement in anti-leukemic efficacy in patients carrying FLT3-ITD mutation, especially if concomitant NPM1 mutation is not present.
Candoni:Gilead: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Merck SD: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Bocchia:Novartis: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal