Background: Elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) experience a low complete remission (CR) rate following intensive chemotherapy, a short duration of CR and high treatment-related mortality. Median survival is 7-12 months. Several reports suggest that maintenance therapy may improve survival. In particular, a recent report (Huls G, et al. Blood 2019) has shown that azacitidine (Aza) maintenance treatment improves 1-year disease-free survival (DFS) when adjusted for cytogenetics at diagnosis and platelet (PLT) count at randomization.
Aims: This phase III, randomized, multicenter trial assesses the efficacy of post-remission Aza treatment versus best supportive care (BSC) in 54 AML subjects >60 years of age in CR after homogeneous induction and consolidation chemotherapy. Primary endpoint is the difference in DFS at 2 and 5 years between arms; main secondary endpoints are the difference in overall survival (OS), the number and length of hospitalizations and quality of life (QoL).
Methods: AML subjects with >30% blasts, "de novo" or evolving from myelodysplastic syndrome and fit for intensive chemotherapy, received 2 courses of "3+7" therapy (daunorubicin 40 mg/m2 daily days 1-3 and cytarabine 100 mg/m2 daily IV infusion days 1-7). Subjects obtaining a CR received cytarabine 800 mg/m2 3 hour infusion bid days 1-3 and were randomized 1:1 to receive BSC or Aza at 50 mg/m2 s.c./i.v. for 7 days every 28 days and dose increase after 1st cycle to 75 mg/ m2 for further 5 cycles, followed by cycles every 56 days for 4.5 years or until relapse. QoL was assessed by QOL-E and EORTC QLQ-C30.
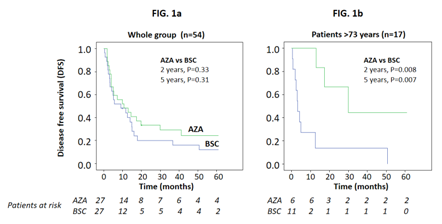
Results: 149 subjects were included of median age 69, interquartile range (IQR) 65-74 years, and male/female 78/71. Amongst subjects not reaching randomization, 59 were relapsed/refractory, 22 died, 10 refused to continue, 3 were excluded for protocol violation, and 1 was lost to follow-up. Randomized patients (27 Aza, 27 BSC) were in study until relapse. Median follow-up was 9.9 months (IQR: 3.2-22.5). At 2 years post-randomization, no deaths occurred and 21 subjects in the BSC arm (median DFS 9 months, 95% CI 0-20) relapsed versus 18 subjects in the Aza arm (median DFS 11 months, 95% CI 1-21; P=0.33; Fig.1a). There was an effect modification by age on the effect of Aza versus BSC on relapse (P for effect modification=0.02) so that the effect of AZA was not significant for subjects <65 years and 65-73 years (P=0.65 and P=0.66, respectively) but was significant in subjects >73 years (P=0.008, Fig.1b). Cytogenetic risk (P=0.84), minimal residual disease (P=0.97), and platelet (PLT) count (below/above 100 Gi/L, P=0.47) did not modify the effect of Aza on DFS. However, cytogenetic risk and PLT count were confounders: after data adjustment, the effect of Aza on DFS just failed to reach statistical significance [HR (Aza vs BSC): 0.53, 95% CI: 0.26-1.05, P=0.068] . At 5 years post-randomization, no subjects died; 2 subjects on Aza and 1 subject on BSC withdrew consent and 1 subject on Aza in CR withdrew for relapse of bladder cancer. In the BSC arm, 23 subjects relapsed (median DFS 9 months, 95% CI: 0-20) versus 20 Aza subjects (median 11 months, 95% CI: 1-21; P=0.31, Fig.1a).Similar to 2 years post-randomization, at 5 years post-randomization an effect modification by age on the effect of Aza versus BSC was confirmed (P for effect modification=0.01) and the effect of Aza was significant only in subjects >73 years of age (P=0.007, Fig.1b). Again, data adjustment for cytogenetic risk and PLT count strengthened the link between Aza and DFS [HR: 0.56, 95% CI: 0.29-1.07, P=0.08]. Grade 3-4 adverse events (mainly neutropenia) were more frequent in the Aza (41%) than in the BSC arm (4%, P=0.002). Two Aza subjects were hospitalized twice for adverse events for a total of 22 and 26 days, respectively, versus no hospitalization for BSC subjects. QOL-E scores were poor at diagnosis and improved significantly at randomization, with further improvement for physical well-being. EORTC QLQ-C30 symptoms improved progressively over time. In linear mixed model analyses, no significant effect of Aza versus BSC was found for any QoL domain, confirming safety of Aza versus BSC.
Summary/Conclusion: With the limitation of a small trial, we conclude that post-remission Aza in elderly AML patients receiving standard induction-consolidation chemotherapy is safe and is well-tolerated. Noteworthy, in patients over 73 years of age, Aza significantly prolongs DFS up to 5 years.
Oliva:Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Apellis: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Candoni:Merck SD: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria. Di Raimondo:Takeda: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Musto:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Mannina:Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Martino:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol myers squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Alati:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal