Introduction
Hemophila A patients treated with replacement products are routinely monitored for Factor VIII (FVIII) activity during therapy using either one-stage clotting assays (OSA) or chromogenic assays (CA). It is well known that laboratory assay results can be affected by extended half-life FVIII products. BAY 94-9027 (damoctocog alfa pegol; Jivi®) is a site-specific pegylated FVIII in which a 60-kDA PEG is conjugated to an introduced cysteine residue substitution on the light chain of B-domain deleted FVIII. The purpose of this study was to investigate the characteristics of BAY 94-9027 in different one-stage and chromogenic assays using a sample set composed of plasma samples spiked with 5 different BAY 94-9027 levels.
Materials and Methods:
FVIII deficient plasma was spiked with different levels of BAY 94-9027 ranging from 0.05 - 1.5 IU/mL. The spiked samples were filled into tubes in 2 mL aliquots and lyophilised. The target values were established using the same assay procedure used by Bayer for potency labelling of the product. Samples were stored at -20°C until distribution to participating laboratories. Laboratories were asked to measure the samples according to their standard procedures for OSA and CA. Currently, samples have been distributed to 135 laboratories in 12 different countries with 65 laboratories returned results included in the current data analysis. For each of the samples, the recovery with respect to the target value was calculated.
Results:
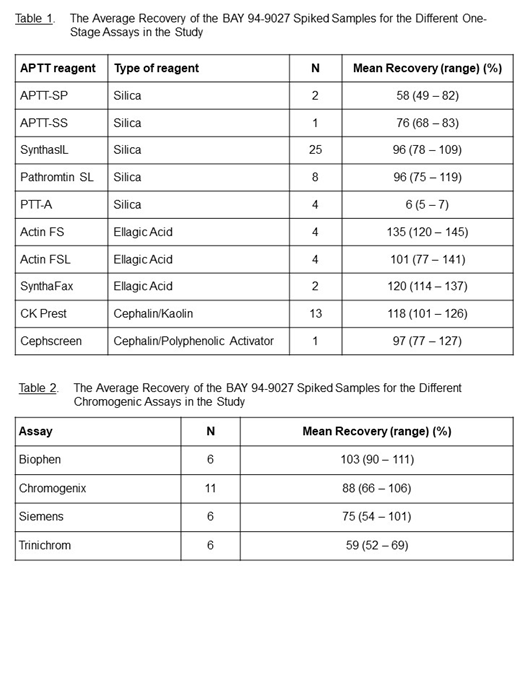
Table 1 shows the average recovery over the entire concentration range for the different APTT reagents.
For most of the APTT reagents used by laboratories in this study, an average recovery between 76% and 120% was observed. Only APTT-SP and PTT-A, both silica-based APTT reagents, showed a significant underestimation of BAY 94-9027 (recovery of approximately 60% and < 10%, respectively), while Actin FS showed on average an overestimation (135% recovery). Within the different reagent groups the inter-laboratory variation ranged between 8 and 31%.
Table 2 shows the average recovery over the entire concentration range for the different chromogenic assays.
For two CA methods (Biophen and Chromogenix) the recovery ranged between 66 and 111% over the full range of BAY 94-9027 concentrations. For the Siemens method, the recovery decreases from 101% to 54% as the Bay 94-9027 concentration decreases, while the Trinichrom method showed a decreased recovery over the full range of BAY 94-9027 concentrations. For the CA methods the inter-laboratory variation ranged from 6 and 39%.
Conclusion:
With most of the APTT reagents included in this study (except APTT-SP and PTT-A) BAY 94-9027 can be reliably measured in a one-stage clotting assay over a wide concentration range. BAY 94-9027 can also be reliably measured with the Biophen and Chromogenix method, while a systematic underestimation was observed with the Trinichrom method. The Siemens chromogenic method demonstrates a concentration-dependent decline in the recovery.
The large inter-laboratory variation within certain reagent group is not unexpected given that the replacement product is a modified FVIII protein and emphasizes the need for local laboratory verification of the accuracy of measurement of BAY 94-9027.
Teare:Bayer: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal