Abstract
Intro:
Assessment of induction mortality risk in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients is challenging. Hematopoietic cell transplant comorbidity index (HCT-CI) score was designed for risk assessment of patients undergoing an allogeneic transplant. However, it is often used in clinical practice to assess induction mortality risk in AML patients. We analyzed the predictive power of the score to assess induction mortality risk as well as overall survival in AML patients at our institution.
Methods:
Between Jan 2009 and March 2013, 101 consecutive newly diagnosed AML patients treated at our institution were included for analysis. All patients received bolus HiDAC (3gm/m2) on day 1-5 and high dose mitoxantrone (80mg/m2) on day 2. The median age was 65 years (range18-90). The total number of patients in the age group <60, 60-69 and ≥70 were 30(29.7%), 35(34.6%) and 36(35.6%) respectively. HCT-CI scores were calculated before induction chemotherapy. Kaplan Meir curve was used to calculate OS and PFS. 4-week induction mortality was calculated from the date of the induction chemotherapy. The patient cohort was divided into those with HCT-CI scores of > or ≤3.
Results:
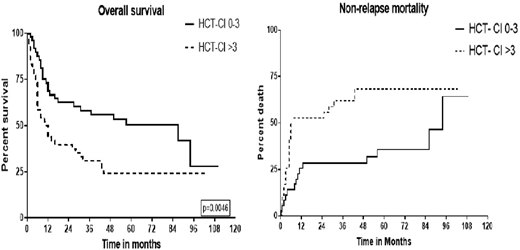
The number of patients with the HCT-CI score of 0,1,2 and 3 were 8,13,17 and 13 respectively. 50% of our patients (51 patients) had a score of 4 or more on the HCT-CI index. The 4 and 8-week mortality in our cohort was 3/101 (2.9%) and 7/99 (7%) respectively. 4-week induction mortality in <60, 60-69 and ≥70 years of age groups were 0/30(0%), 1/35(2.8%) and 2/36(5.5%) respectively. Similarly, in above age groups, 8-week induction mortality were 0/29(0%), 2/34(5.8%) and 5/36(13.8%) respectively. The median OS in patients with an HCT-CI score ≤3 was 87 months versus 11.5 months in those with a score >3 (log-rank, p=0.0046, Fig1). 2-yr NRM rate for patients with HCT-CI score ≤3 and >3 was 47% and 71%, respectively (p=0.01, Fig2). Hazard ratio for overall mortality in patients with HCT-CI score >3 is 1.793 with p=0.023, 95% CI = (1.083 - 2.971). HR for 8-week mortality in patients with an HCT-CI score >3 is 2.035 (p=0.412), although not statistically significant due to a low number of events. However, by Cox multivariable regression analysis HCT-CI retained a significant impact on 8-week mortality (HR=1.24, p= 0.03) and overall survival (HR=1.144, p= 0.006).
Conclusion:
An HCT-CI score is a valuable tool in the assessment of the induction mortality in newly diagnosed AML patients and can be used for risk assessment of overall mortality.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal