In Figure 7G on page 99 in the 1 January 2015 issue, the image on the right is a duplicate copy of the middle image in a different orientation. The corrected figure is shown below.
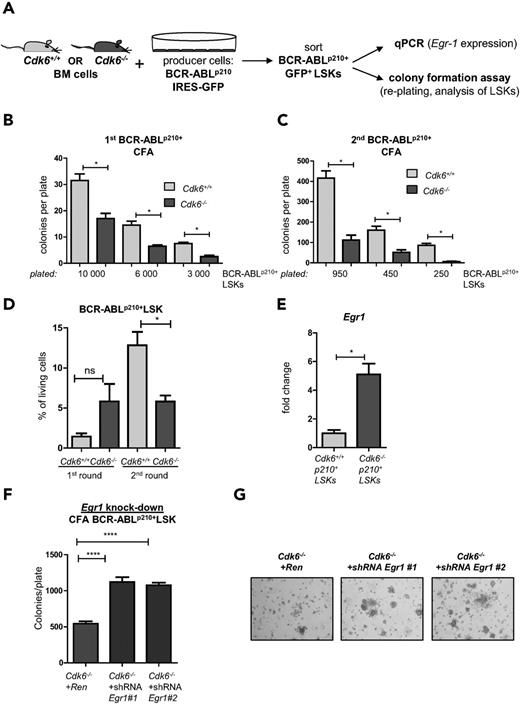
CDK6 influences (re-)plating capacities of BCR-ABLp210+ LSKs in vitro. (A) Experimental setup. Cdk6+/+ and Cdk6−/− BM cells were cocultivated on BCR-ABLp210 producer cells for 48 hours, sorted by high-purity FACS, and either subjected to colony formation assays (CFA) (B-D) or analyzed by qPCR (E). (B) Three different cell numbers of BCR-ABLp210+ LSKs were seeded and colony numbers were counted 8 days after coculture (technical duplicates; *P < .05). (C) All colonies were harvested and reseeded to a second round of replating. Colonies were counted after 8 days (technical duplicates; *P < .05). (D) After each round, colonies were harvested and analyzed by FACS for the presence of remaining BCR-ABLp210+ LSKs (*P < .05). (E) BCR-ABLp210+ LSKs were sorted by FACS and Egr1 expression was analyzed by qPCR (BM cells of 3 individual mice per genotype were pooled; qPCR was performed in technical triplicates; *P < .05). (F) Knockdown constructs Egr1 #1 and Egr1 #2 or a control vector targeting Renilla were introduced into Cdk6−/− BCR-ABLp210+ LSKs and subjected to colony formation. Colonies were again counted 8 days after seeding (****P < .0001). (G) Representative pictures of colonies on day 8 (magnification: ×4).
CDK6 influences (re-)plating capacities of BCR-ABLp210+ LSKs in vitro. (A) Experimental setup. Cdk6+/+ and Cdk6−/− BM cells were cocultivated on BCR-ABLp210 producer cells for 48 hours, sorted by high-purity FACS, and either subjected to colony formation assays (CFA) (B-D) or analyzed by qPCR (E). (B) Three different cell numbers of BCR-ABLp210+ LSKs were seeded and colony numbers were counted 8 days after coculture (technical duplicates; *P < .05). (C) All colonies were harvested and reseeded to a second round of replating. Colonies were counted after 8 days (technical duplicates; *P < .05). (D) After each round, colonies were harvested and analyzed by FACS for the presence of remaining BCR-ABLp210+ LSKs (*P < .05). (E) BCR-ABLp210+ LSKs were sorted by FACS and Egr1 expression was analyzed by qPCR (BM cells of 3 individual mice per genotype were pooled; qPCR was performed in technical triplicates; *P < .05). (F) Knockdown constructs Egr1 #1 and Egr1 #2 or a control vector targeting Renilla were introduced into Cdk6−/− BCR-ABLp210+ LSKs and subjected to colony formation. Colonies were again counted 8 days after seeding (****P < .0001). (G) Representative pictures of colonies on day 8 (magnification: ×4).
The authors apologize for this mistake. The error has been corrected in the online version of the article.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal