Abstract
Background: The BIONIC study tested whether bortezomib (V) improved the complete remission (CR) rate when added to standard bendamustine/rituximab (BR) induction in untreated high risk (HR) FL and whether lenalidomide (Len) integrated as "continuation" treatment (Tx) given concurrently with maintenance rituximab (MR) enhanced remission duration vs MR alone.
Methods: Study eligibility included: ages ≥18 years; untreated; HR disease; and grade I/II or IIIa FL with the latter determined by central pathologic review (NCT01685008). HR disease was defined as high tumor burden by GELF and/or FLIPI score 3-5. Pts were randomized to 1 of 3 arms in a 1:2:2 ratio (stratified by FLIPI & GELF): a) BR induction x 6 followed by MR q 2 months x 2 years (BR-R) vs b) BVR induction x 6 (V: 1.3 mg/m2 IV/SQ days 1, 4, 8, 11) followed by MR q 2 months x 2 years (BVR-R) vs c) BR x 6 followed by q 2 months MR x 2 years + Len 20 mg/day (21/28 days) continuation x 1 year (BR-LR). Initial plans were to enroll 250 pts; due to a high non-enrollment rate to the continuation/maintenance phase of Tx (ie, 10% BR-R arm, 22% of BVR-R, and 26% BR-LR arm), an additional 36 pts were randomized to the BR+R vs BR+LR arms to preserve study power. In these study arms, 54, 66, and 83 FL pts, respectively, received post-induction Tx. Response was assessed by 2007 IWG criteria with PET/CT. The 1st primary objective was previously presented (ie, CR rate BVR 74% vs 59% two BR induction arms combined, P=0.008, Evens et al ASCO 2016). We report here on all study endpoints, including the 2nd primary objective of 1-year disease-free survival (DFS) with Len continuation Tx (ie, BR-LR vs standard BR-R) as well as progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety/tolerability across all Tx arms & phases of Tx.
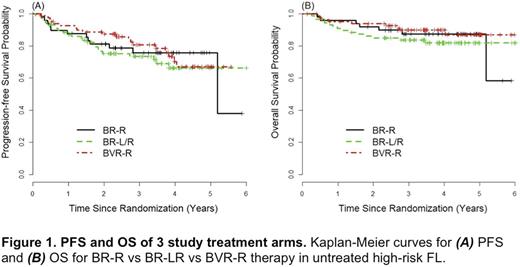
Results: The study enrolled from 1/2011 to 5/2015 with a final accrual of 289 pts. 30 pts were excluded for never starting study Tx (n=9), ineligibility (n=5), and central pathology review (n=16), yielding 257 evaluable pts (ie, BR-R n=60; BVR-R n=85; BR-LR n=112). Among all pts, median age was 61 years (24-89); GELF was high in 91%; FLIPI 3-5 in 57%; ECOG PS: 0=56%, 1=42%, and 2=2%; B symptoms present 28%; marrow involvement 59%; >1 extranodal site 27%; and stages IIB 7%, III 27% and IV 66%. For induction Tx received, 88%, 87%, and 78%, respectively, of pts randomized to the BR-R vs BVR-R vs BR-LR arms received all 6 planned cycles. CR rates for induction Tx by were 71%, 74%, and 55%, respectively. Collectively, the 1-year DFS results suggested no added benefit from lenalidomide (details to be presented at meeting). With a median follow-up of 3.95 years, the median PFS has not been reached in any arm. Among the first 250 pts enrolled, 3-year PFS rates for BR-R vs BVR-R vs BR-LR Tx arms were 76% vs 81% vs 74%, respectively, P=0.49 (see Figure 1A); the 3-year PFS rates including the additional 36 enrolled pts were nearly identical. The most common grade 3/4 AEs among pts randomized to Len-R continuation vs MR were: neutropenia 66% vs 20% (P <0.0001); febrile neutropenia 10% vs 2% (P=0.05); anemia 6% vs 0 (P=0.08); fatigue 6% vs 2% (P=0.40); and pneumonia 6% vs 2% (P=0.40). Of patients assigned to Len-R, 59% had dose reductions of Len, most due to an adverse event (AE). When comparing Len-R continuation vs MR, 17% vs 6% of pts (P=0.06), respectively, came off continuation/maintenance Tx due to AE/toxicity. By study arm, rates of all 2nd cancers (including skin) were 6%, 9%, and 8% for BR-R, BVR-R and BR-LR, respectively (P=0.45); non-melanoma skin cancer rates were 2% on each arm. Overall, there were 34 deaths on study, including 7 grade 5 lethal events (2.7%). Of the latter, 4 (1.4%) were possibly related to Tx with 1 occurring during induction, 2 during maintenance, and 1 post-maintenance off study. The corresponding 3-year OS rates for all pts treated in the BR-R vs BVR-R vs BR-LR arms were 87% vs 90% vs 84%, respectively, P=0.37 (see Figure 1B).
Conclusions: The BIONIC study showed that Tx with standard BR induction followed by MR was safe in HR FL. The addition of V to BR induction enhanced the CR rate, but did not translate into improved PFS. Additionally, Len continuation Tx as prescribed in this study was associated with increased toxicity vs MR, while yielding similar PFS and OS vs BR-R treated pts. Based upon these results, neither V added to BR induction nor Len added to MR following BR induction can be recommended in FL. Quality of life analyses as well as detailed imaging and correlative biomarker studies are underway.
Evens: AbbVie: Consultancy; Millennium: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Affimed: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; • Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Advani: Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Sutro: Consultancy; Nanostring: Consultancy; Infinity: Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy; Janssen: Research Funding; Kura: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; Spectrum: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Agensys: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; FortySeven: Research Funding; Cell Medica: Research Funding. Witzig: Kura: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding. Winter: Glaxo-Smith-Kline: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding. Kahl: Gilead: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal