Abstract
The use of mismatched donors is rapidly increasing for pts with hematological malignancies in need of allo HCT. Here we compared the outcomes of melphalan based reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) using haplo-identical transplantation with post transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) and haplo cord transplantation where a CBU graft is supplemented with CD34 selected haplo-identical cells to accelerate engraftment.
Patients and Methods:
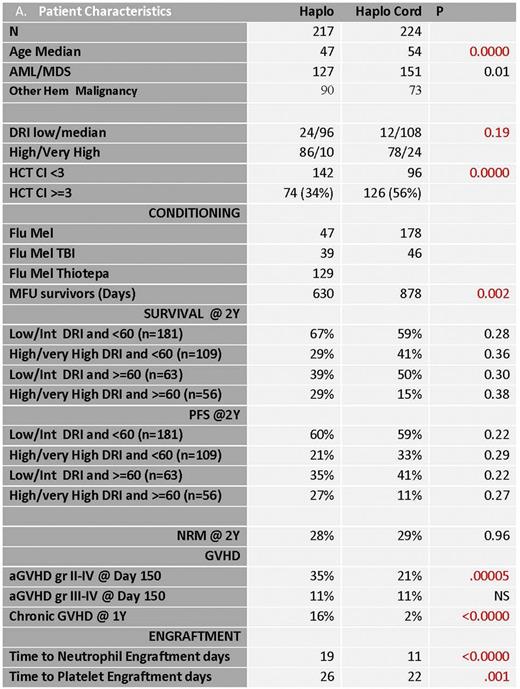
217 pts underwent Haplo transplants at MDACC. Conditioning consisted of fludarabine (flu)-melphalan 140 mg/m2 (mel) (47) flu-mel-thiotepa (129), or flu-mel-TBI 200 cGy (37). Dose of Mel was 140 mg/m2 for 128 and 100 mg/m2 for 88.GVHD prophylaxis was PTCy, tacro and mycophenolate (MMF). Graft source was bone marrow in 206 pts and PBSC in 11. 224 pts underwent HC HCT at Weill Cornell, New York and at the University of Chicago. Conditioning consisted of Flu-Mel (178) or Flu-Mel-TBI 400 cGy (46). Dose of Mel was 140 mg/m2. GVHD prophylaxis was ATG, tacro and MMF. Pt characteristics are in Table 1. 58% of haplo vs 67% of HC recipients had AML or MDS (P=0.01). 36% of HC vs 20% of Haplo were 60 and older (P=0.007) and 56% of HC vs 34% of Haplo had HCTCI >=3 (P=0.0000). Median F/U was 30 mo for HC vs 21 mo for Haplo group.
Results
Median time to neutrophil recovery was 11 days after HC vs 19 after Haplo SCT (p<0.001). Time to plt recovery was 22 d after HC vs 26 Haplo SCT (p =0.001). CI of gr II-IV aGVHD was 21% by d150 after HC vs35% after Haplo SCT (p=0.0005). CI of gr III-IV aGVHD was identical at 11% in each group. CI of all chronic GVHD was 2% at one year after HC vs 16% after Haplo SCT (p<0.001). Overall survival, PFS, CI Relapse and NRM were not significantly different. In multivariable analysis, graft source did not correlate with OS, PFS, Relapse or NRM. In multivariable analysis Disease Risk Index (DRI) and Age>=60 were the major determinants of OS and PFS. For patients with Low and Intermediate DRI under age 60, 2 Y OS was 60% for haplo and 59% for HC.
Conclusions: Melphalan based RIC result in similar and encouraging survival and progression free survival with HC or haplo grafts. HC HCT was associated with more rapid neutrophil and a lower rate of acute and of chronic GVHD.
Liu: Karyopharm: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal