Abstract
Background: Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is characterized by a poor prognosis. Starting in 2004, the European MCL Network has performed the double randomized MCL Elderly trial for first-line treatment of patients with MCL, Ann-Arbor stage II-IV, aged 60 years or older and not suitable for autologous stem cell transplantation (Kluin-Nelemans et al., NEJM 2012). Median age of the 560 patients included was 70 years (range, 60-87). The first randomization compared 8xR-CHOP with 6xR-FC induction, the second randomization compared rituximab (R) maintenance with interferon-alpha (IFN) maintenance, both given in remission until progression. The primary evaluation of the induction part showed that R-FC could not improve complete remission rates compared with R-CHOP, while overall survival (OS) with R-FC was substantially shortened compared to R-CHOP. The primary evaluation of the maintenance part showed a prolonged progression-free survival (PFS) in remission with R compared to IFN. After R-CHOP induction, PFS and OS were substantially prolonged by R vs. IFN. We report here the long-term follow-up of the time-to-event endpoints with robust 5-year estimates after a median follow-up of 6.7 years.
Methods: While the primary maintenance question was evaluated per protocol adjusting for interim analyses, the other analyses were according to the intention to treat without adjustment. 95% confidence intervals for Kaplan-Meier estimates were calculated by using Greenwood's variance and the log-log transformation. Using competing risk methods, we additionally estimated cumulative incidences of treatment failure (stable or progressive disease) and of death without treatment failure.
Results: Failure-free survival after start of R-FC or R-CHOP induction was overlapping with 5-year probabilities of 31% (95% CI 25%-37%) in both groups. While R-FC showed lower 5-year cumulative incidence of treatment failure compared with R-CHOP (51% vs. 60%, p=0.083), the cumulative incidence of death without treatment failure was higher with R-FC (19% vs. 9% with R-CHOP, p=0.0032). OS was substantially shorter after R-FC with 5-year probabilities of 42% (36%-49%) compared with 58% (51%-64%) after R-CHOP (p=0.0012). This observation was related to the higher cumulative incidence of death without treatment failure after R-FC and a shorter OS after first treatment failure (R-FC: median 1.0 vs. R-CHOP: 2.3 years).
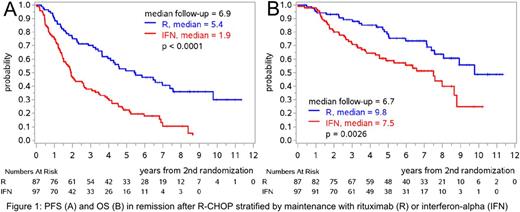
The efficacy of R maintenance was confirmed with a significantly prolonged PFS from end of induction (primary evaluation, p=0.0109, hazard ratio 0.48, 5-year PFS, R: 53%, 44%-61% vs. IFN: 23%, 15%-31%); OS was also prolonged (p=0.008). After response to R-CHOP, the 5-year PFS with R vs. IFN was 51% (40%-62%) vs. 22% (14%-32%, Figure 1A, p<0.0001) in comparison to 52% (39%-63%) vs. 32% (20%-45%) after R-FC (p=0.032, interaction p=0.19). With R-maintenance after R-FC, the 5-year cumulative incidence of death without progression was as high as the cumulative incidence of progression (24% and 23%, respectively). After R-CHOP, OS was prolonged by R vs. IFN with 5-year OS of 79% (67%-86%) vs. 59% (48%-69%, p=0.0026, Figure 1B), in contrast to R-FC with 5-year OS of 57% (44%-68%) vs. 54% (39%-66%, p=0.60, interaction p=0.096).
Conclusions: After long-term follow-up we confirm the substantially prolonged PFS and OS with R-maintenance after R-CHOP induction in first-line treatment of older MCL patients who are no candidates for autologous stem cell transplantation. Despite indications for anti-lymphoma activity, induction with six cycles of R-FC was associated with severe treatment complications leading to a higher cumulative incidence of death without treatment failure and shorter survival compared with 8 cycles of R-CHOP.
Hoster: Roche: Other: Travel support, Research Funding. Hermine: INatherys: Equity Ownership, Research Funding; AB Science: Equity Ownership, Honoraria, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Hybrigenics: Research Funding. Walewski: Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel costs, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen-Cilag: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Servier: Consultancy; GSK/Novartis: Research Funding. Trneny: Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Geisler: Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding. Stilgenbauer: Genzyme: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Boehringer-Ingelheim: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; GSK: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Hoffman La-Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Thieblemont: Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Vehling-Kaiser: Lilly: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; F. Hoffmann-LaRoche: Consultancy; MSD: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy. Doorduijn: Celgene: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria. Karlin: Janssen: Honoraria, Other: Travel expenses. Tilly: Karyopharm: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Immunogen: Honoraria. Ribrag: Gilead: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Nanostring: Honoraria; ArgenX: Research Funding; Infinity: Honoraria; MSD: Honoraria; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria; Epizyme: Honoraria. Andre: Takeda: Honoraria, Other: Advisory board, Research Funding. Hiddemann: Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Dreyling: Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Sandoz: Consultancy; Mundipharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; MorphoSys AG: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Bayer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal