Abstract
Background: PAC is an oral kinase inhibitor with specificity for JAK2, FLT3, IRAK1, and CSF1R that has demonstrated significant and sustained spleen volume reduction (SVR) and symptom control vs BAT (excluding JAK2 inhibitors) in MF pts regardless of platelet count (PERSIST-1). The PERSIST-2 study was a randomized, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial of PAC 200 mg BID and PAC 400 mg QD vs BAT (including JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor ruxolitinib [RUX]) in pts with 10 or 20 MF whose platelet counts were ≤100,000/µL, a recognized adverse prognostic variable. Prior JAK2 inhibitor use was allowed.
Methods: Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to PAC BID, PAC QD, or BAT. The co-primary efficacy endpoints were the percentages of pts achieving ≥35% SVR (MRI or CT) and ≥50% reduction in total symptom score (TSS; MPN-SAF TSS 2.0), both from baseline to Week 24. The primary objective was to compare the efficacy of pooled PAC (BID+QD) to BAT and the secondary objectives were to compare PAC BID and PAC QD individually to BAT. PK samples were collected and analyzed for PAC. Safety analyses were based on all pts exposed to study treatment of any duration (safety population); efficacy analyses were based on ITT pts with a randomization date allowing Week 24 endpoint evaluations prior to the full clinical hold* (ITT efficacy population).
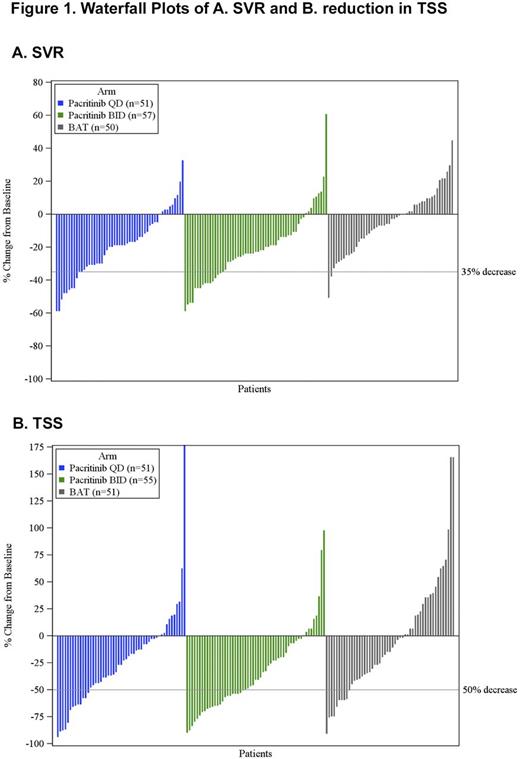
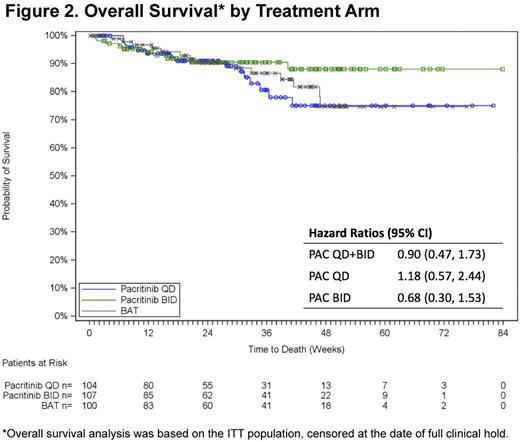
Results: 311 pts were randomized (107 PAC BID, 104 PAC QD, 100 BAT), 308 received study drug, and 221 were included in the ITT efficacy population (74 PAC BID, 75 PAC QD, 72 BAT). Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were generally balanced among the treatment arms (Table) and analysis populations. A total of 32 (44%) BAT pts in the ITT efficacy population received RUX as treatment at some point on study. Population PK analyses showed that the steady-state plasma levels achieved with BID were higher than with QD, however the Cmax levels were lower. A significantly higher percentage of pts in the pooled PAC arm achieved SVR ≥35% (18% [27/149]) vs the BAT arm (3% [2/72]; p=0.001; Figure 1A). 25% of PAC pts (37/149) had ≥50% reduction in TSS vs 14% of BAT pts (p=0.079; Figure 1B). In secondary analyses vs BAT, PAC BID demonstrated significant improvement over BAT for both efficacy endpoints with 22% achieving SVR ≥35% (BAT=3%; p=0.001) and 32% achieving ≥50% reduction in TSS (BAT=14%; p=0.011). The PAC QD arm had a significant SVR ≥35% (15% v 3%, respectively; p=0.017), but a similar proportion with ≥50% reduction in TSS (17% v 14%, respectively; p=0.652). More PAC pts reduced their red blood cell transfusion dependence at Week 24 (defined as a ≥50% reduction in average transfusions/month for 3 months relative to baseline) with 19% (7/37) in the PAC QD arm, 22% (8/36) in PAC BID, and 9% (3/35) in BAT. There was no significant difference observed in OS across the treatment arms (Figure 2). Hazard ratios for OS (95% confidence intervals) were 0.68 (0.30, 1.53) for PAC BID v BAT, 1.18 (0.57, 2.44) for PAC QD v BAT, and 0.61 (0.27, 1.35) for PAC BID v QD. PAC BID maintained this survival advantage vs BAT across nearly all demographic and MF-associated risk factors. During the course of the study, 10 (9%), 15 (14%), and 15 (14%) died on PAC BID, PAC QD, and BAT, respectively. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) associated with PAC were gastrointestinal (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting) and hematologic (anemia and thrombocytopenia), and were generally less frequent for BID vs QD administration. Grade 3/4 cardiac AEs occurred in 7%, 13% and 9% of PAC BID, PAC QD, and BAT pts, respectively, and grade 3/4 bleeding AEs occurred in 14%, 7%, and 7%, respectively. Grade 3/4 bleeding AEs were associated with grade 3/4 thrombocytopenia, which was also more common in the PAC BID group. Nine pts had cardiac failure (2% PAC QD, 4% PAC BID, 3% BAT) and 1 (1%, PAC QD) had intracranial hemorrhage.*
Conclusions: The PERSIST-2 study is the only randomized, controlled trial to date in pts with MF and thrombocytopenia (platelets ≤100,000/µL), allowed prior JAK2 inhibitor treatment exposure (including RUX), and allowed RUX as BAT comparator. Irrespective of prior JAK2 inhibitor treatment, both PAC arms were more effective at SVR than BAT; however, PAC BID appeared more active than QD dosing and achieved significance versus BAT for both SVR and TSS. The most frequent AEs with PAC were gastrointestinal and hematologic toxicities.
*PAC on full clinical hold by the FDA on 2/8/2016 based on concerns around excess deaths and cardiac and hemorrhagic events in PERSIST-1.
Mascarenhas:Incyte: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; CTI BioPharma: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding. Talpaz:CTI BioPharma: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Research Funding; Ariad: Other: Expense reimbursement, travel accomodation expenses, Research Funding; Gilead: Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; BMS - Canada: Consultancy. Gerds:CTI BioPharma: Research Funding; Astra-Zeneca: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding. Stein:Incyte Corporation: Consultancy. Gupta:Incyte Corporation: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Drummond:CTI BioPharma: Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Speakers Bureau. Granston:CTI BioPharma Corp.: Employment. Daly:CTI BioPharma Corp.: Employment. Dean:CTI BioPharma Corp.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Al-Fayoumi:CTI BioPharma Corp.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Callahan:CTI BioPharma: Employment. Singer:CTI BioPharma Corp.: Employment, Equity Ownership, Other: Leadership . Gotlib:Novartis: Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Steering Committee Chairman, Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding. Jamieson:GSK: Research Funding; Johnson & Johnson: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma: Research Funding. Harrison:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; CTI BioPharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Baxter: Consultancy, Honoraria; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Speakers Bureau. Mesa:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Incyte: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Genetech: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding. Verstovsek:CTI BioPharma Corp: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal