Abstract
Background: Obesity, defined as a body mass index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2, is a well-known risk factor for venous thromboembolism (VTE). Despite this observation, obese patients are under-represented in anticoagulation safety trials. Current guidelines recommend patients with active malignancy and VTE to be treated with long-term low molecular weight heparin (LMWH), but it is unclear whether this practice is safe in obese cancer patients.
Objectives: We hypothesized there would be an increased risk of major or clinically significant non-major bleeding in obese cancer patients receiving long-term, actual weight-adjusted LMWH compared to non-obese patients with cancer- associated VTE.
Methods: We conducted a single centre retrospective cohort study of obese cancer patients referred to our thrombosis clinic from January 2010 to December 2015. We included all obese cancer patients assessed at the Thrombosis unit who received anticoagulation with LMWH. Obesity was defined as weight above 90 Kg or BMI of 30 kg/m2 or more. The obese patients' data was compared to a non-obese control group of patients with active malignancy treated with LMWH. Major bleeding was defined as a hemoglobin drop of > 20 g/L; clinically overt bleeding; bleeding requiring 2 units or more of packed red blood cells; a hemorrhage requiring permanent cessation of anti-coagulation; or any retroperitoneal or intracranial hemorrhage. Diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis was confirmed when compression ultrasound of the lower extremities showed evidence of thrombus in the calf trifurcation or more proximal veins; or calf thrombosis associated with pulmonary embolism (PE). PE was confirmed when the ventilation-perfusion lung showed at least a large mismatched defect or CT pulmonary angiography demonstrated at least one segmental intra-luminal filling defect.
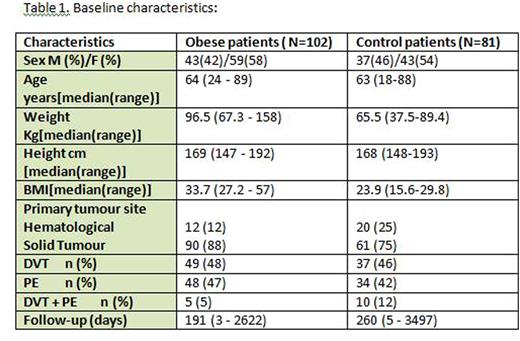
Results: In total, 102 obese cancer patients and 81 non-obese cancer patients met our eligibility criteria. In the obese cohort, 43 (42%) were male, median age 64 (24-89), median weight 96.5 kg (67.3-158), and median BMI 33.7 kg/m2 (27.2-57). 90 (88%) patients had a solid tumour. Median dose of LMWH was 18,000 units (10,000 - 30,000): 78 (76%) were prescribed dalteparin and 22 (22%) tinzaparin. Median follow-up was 191 days (3 - 2622). Baseline characteristics of the control group were similar (Table 1). Total bleeding episodes were significantly different in the 2 groups: total bleeding events were 10 (9.8%) in the obese group (4 were under-dosed based on their weight) and 1 in the control group [RR=7.9; 95% CI (1.04 -60.76) p=0.046)]. Major bleeding events occurred in 6 (5.9%) obese and in none of the non-obese patients [RR=10.4; 95% CI (0.59 -181.05) p=0.11)]. Platelet counts were appropriate in all cases but one, where a non-major bleed occurred in an obese patient with a platelet count of 27. Recurrent VTE occurred in 8 (7.8%) obese and 4 control patients. In the obese cohort, 5 of those patients were receiving under-dosed LMWH based on their weight. There was no statistically significant difference regarding VTE recurrence risk in the obese and control groups [RR=1.59; 95% CI (0.50 -5.09) p=0.44)]. Interestingly, 31 of 96 obese patients (31%) with BMI 30 or above weighed less than 90 kg.
Conclusions: Our findings differ from the available literature. In the CLOT trial, total and major bleeding episodes in the LMWH group occurred in 14% and 7%, respectively, with VTE recurrence of 9%. In comparison, our results demonstrate total and major bleeding episodes in our obese cancer patients on LMWH of 9.8% and 5.9%, respectively, with VTE recurrence of 7.8%. Total bleeding was statistically significant compared to a non-obese cancer population, however, limitations in sample size and event rate need to be taken into consideration when interpreting these results.
Kovacs:Daiichi Sankyo Pharma: Research Funding; Bayer: Honoraria, Research Funding; LEO Pharma: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding. Lazo-Langner:Bayer: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding. Louzada:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Bayer: Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal