Abstract

Background
Effects of haploidentical stem cells (Hap-SC) and unrelated cord blood (UCB) transplant are unsatisfactory in thalassemia major (TM) so far. High rejection and low TM-free survive (TFS) were key clinical issues. Increased rejection often offset the effort of lowered GVHD. The effect of alloreactive clone destruction in post-transplant cyclophosphamide (Cy, PTCy) transplant resulted in low GVHD and high relapse but nice immuno-recovery and immuno-tolerance by keeping antivirus and regulatory T cells. These may just complement the congenital insufficiency, delay engraftment and slow immuno-recovery, of UCB transplantation. Conversely, graft vs. leukemia effect and controllable GVHD from naive T cells of UCB offset the lack above of hap-SC transplant with PTCy. Therefore, we developed a novel complementary transplant with Hap-SC and UCB (CT-hap-CB) for leukemia and TM patients.
Patients and method
Thirty-six TM patients received CT-hap-CB between December 2013 and June 2016. Median age was 8 (range, 3-24) years old. Median follow-up time was 19 (2-25) months. Conditioning (Regimen, CT-13) included Cy on day-8 to -7, Busulfan on day-6 to -4, Fludarabine on day-6 to -2 and Thiotepa on day-3. GVHD prophylaxis consisted of Cy on day+3 to +4, Mycophenolate mofetil and Tacrolimus from day+6. Noteworthily, UCB was infused on day+6. The latter 26 TM patients received additionally Thymoglobuline on day -11 to -9 (Regimen, CT-14).
Results
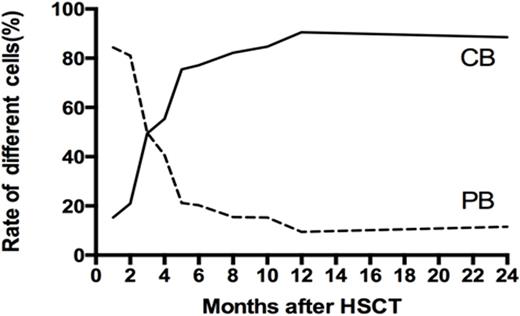
Preponderance engraftment of hap-SC, UCB, mixed stem cells (MSC) and rejection in16, 14, 3 and 3 patients, respectively, at the last follow-up. Initial (day+28) full hap-SC, UCB and MSC chimerism occurred in 15, 7 and 12 patients. Cells derived from UCB overtime were dominant instead of initial majority from hap-SC (Fig. 1) in MSC group. 7/10 UBS with centromeric B motif engrafted.
Median times to neutrophil ≥ 0.5x109/L, platelet ≥ 20 x109/L and hemoglobin ≥ 80 g/L were day+20.0 (range; 14-47), 11.0 (9-162) and 11 (1-39); 47.0 (34-113), 66.0 (12-227) and 46.0 (13-63); and 24 (1-46), 14 (11-116) and 8 (4-91), respectively, in initial hap-SC (n, 15), UCB (n, 7) and MSC (n, 12) groups. Overall survive, thalassemia free survive (TFS), rejection and mortality related transplant were 91.2%, 85.7%, 5.6% and 8.8%, respectively. Impressively, all of the 26 patients who received CT-14 protocol were alive without TM (Fig. 2). Grade II, III and IV acute GVHD occurred in 3 patients, respectively. One patient died of grade IV GVHD and another died of infection when the parents abandoned therapy after rejecting graft. Chronic GVHD was mild and rare.
Summary
CT-hap-CB resulted in high OS and TFS, especially CT-14 leaded to 100% TFS with low GVHD rate. MSC engraftment improved hematopoietic recovery of UCB. KIR and HLA typing impacted what stem cells engraftment. The multicenter study should be developed in the future.
Kinetics of Mixed Chimerism in TM-SCT
Thalassemia-free survive resulted from regimen CT-14 in thalassemia transplant
Thalassemia-free survive resulted from regimen CT-14 in thalassemia transplant
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal