Abstract

Background: Immunochemotherapy induction followed by maintenance with rituximab (R) is the standard of care (SoC) for pts with advanced-stage symptomatic follicular lymphoma (FL), achieving a median PFS of 6-8 yrs and a median survival of 12-15 yrs. However, FL is incurable and most pts eventually relapse. Relapse occurs in 30% of pts within 3 yrs, and is associated with a poor prognosis. Obinutuzumab (GA101; GAZYVA/GAZYVARO; G) is a glycoengineered type II anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody with enhanced direct cell killing and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity that has promising activity and manageable toxicity when combined with chemotherapy in relapsed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL). We report the results of GALLIUM (NCT01332968), a global, open-label, randomized Phase 3 study comparing the efficacy and safety of R or G with chemotherapy followed by maintenance as first-line treatment in iNHL.
Methods: Pts entered were aged ≥18 yrs with previously untreated FL (grades 1-3a) or chemotherapy-naïve marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), stage III/IV disease or stage II with tumor diameter ≥7cm, ECOG PS 0-2, and requiring treatment according to GELF criteria. CHOP, CVP, or bendamustine (B) were allocated according to center (FL) or pt (MZL). Pts were randomized 1:1 and stratified by chemotherapy, FLIPI or IPI group, and geographic region to R 375mg/m2 on Day (D) 1 of each cycle or G 1000mg on D1, 8 and 15 of Cycle 1 and D1 of subsequent cycles, for either 8 x 21-day cycles (CHOP and CVP) or 6 x 28-day cycles (B). Pts with a CR or PR at the end of induction (EOI) as per modified Cheson criteria received R or G every 2 mo for 2 yrs or until disease progression. The primary endpoint was investigator (INV)-assessed PFS in FL pts. At final analysis, based on 370 PFS events having occurred, the study would have 80% power to detect a HR of 0.741. The current data are from a planned interim efficacy analysis done when 67% of the 370 PFS events had occurred (cut-off date: January 31, 2016) after which the study was unblinded on IDMC recommendation. Efficacy was assessed in all randomized FL pts. Safety was assessed in all FL pts who received any study treatment.
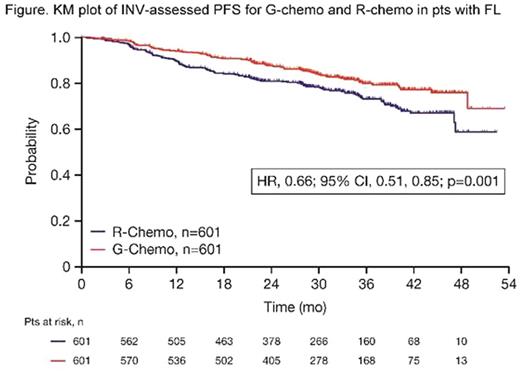
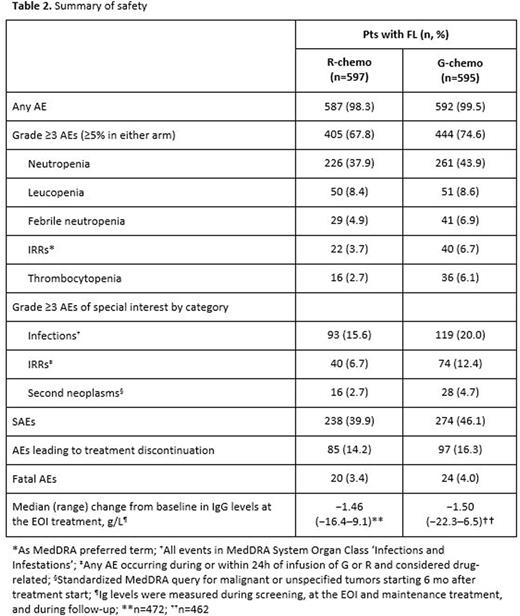
Results: Results are reported for 1202 FL pts (R-chemo, 601; G-chemo, 601) with a median age of 59 yrs (53.2% female); data for 195 MZL pts will be reported elsewhere. Treatment arms were well balanced by disease stage (Ann Arbor: I, 1.5%; II, 7.1%; III, 34.9%; IV, 56.5%) and prognostic factors (FLIPI: 0+1, 21.0%; 2, 37.2%; ≥3, 41.8%; FLIPI-2: 0, 9.1%; 1+2, 50.3%; ≥3, 40.6%). Chemotherapy received was B in 57.1% of pts, CHOP in 33.1%, and CVP in 9.8%. CR and ORR at EOI based on CT/NMR imaging were similar for the two arms (Table 1). After a median follow-up of 34.5 mo (range, 0-54.5), there was a 34% reduction in the risk of progression or death (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.51, 0.85; p=0.001; Figure; Table 1). Although medians have not been reached in GALLIUM or PRIMA, the observed HR of 0.66 would translate to a 1.5x longer median PFS for G-chemo than R-chemo, and to an estimated 3 yr improvement in the G arm if a median PFS of 6 yrs was assumed in the R arm. Three-yr INV-assessed PFS rates were: G-chemo, 80.0% (95% CI, 75.9%, 83.6%); R-chemo, 73.3% (95% CI, 68.8%, 77.2%). A consistent benefit in favor of G-chemo was also seen for PFS assessed by Independent Review Committee (IRC), as well as other time-to-event endpoints (Table 1). Subgroup analyses were broadly consistent with the primary analysis. At the time of the analysis, 35 pts (G-chemo; 5.5%) and 46 pts (R-chemo; 8.7%) had died (HR for overall survival, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.49, 1.17; p=0.210; Table 1). G-chemo pts had a higher frequency of grade 3-5 AEs (74.6%) and SAEs (46.1%) than R-chemo pts (67.8% and 39.9%, respectively). The frequency of fatal AEs was similar (G-chemo, 4.0%; R-chemo, 3.4%). AEs led to treatment discontinuation in 16.3% pts (G-chemo) and 14.2% pts (R-chemo) in the absence of disease progression. Safety results are summarized in Table 2. The median decrease in IgG levels at the EOI treatment was similar in the two arms (Table 2).
Conclusion: In pts with previously-untreated FL, G-based immunochemotherapy and maintenance resulted in a clinically meaningful improvement in PFS, with a 34% reduction in the risk of a PFS event relative to R-based therapy. Frequency of some AEs, e.g. infusion-related reactions (IRRs), cytopenias, and infections, was higher with G. These data support G-chemo becoming a new SoC in previously untreated pts with FL.
Marcus:Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Other: Travel support . Davies:Pfizer: Research Funding; Karyopharma: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, accommodation, expenses, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; GSK: Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel to scientific conferences, Research Funding. Opat:Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Provision of subsidised drugs, Research Funding. Owen:Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Lundbeck: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Pharmacyclics, LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding. Phillips:Roche: Consultancy. Sangha:Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Eli-Lilly: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Lundbeck: Honoraria; Astra-Zeneca: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Boehringer-Ingelheim: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Merck: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Seymour:Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Trněný:Roche, Celgene: Research Funding; Roche, Celgene, Takeda, Janssen, Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Wenger:Genentech: Employment. Fingerle-Rowson:Roche: Employment, Equity Ownership. Rufibach:Roche: Employment, Equity Ownership. Moore:Roche: Employment, Equity Ownership. Herold:Gilead: Other: Personal fees from member advisory board; Celgene: Honoraria; Genentech: Other: Grants; Roche: Honoraria, Other: Grants. Hiddemann:Genentech: Other: Grants; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Other: Grants.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal