Abstract
Background: Erythropoiesis Stimulating Agents (ESAs) are FDA approved for chemotherapy induced anemia and anemia of chronic kidney disease. These indications are more frequent in patients with multiple myeloma. Use of ESAs has been associated with an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, venous thromboembolism (VTE), and all-cause mortality. In patients with cancer, ESA's have been associated with worse progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) Previous research regarding ESA use in patients with multiple myeloma has been limited and conflicting. In this study, we evaluate the effects of ESA use in patients with multiple myeloma. Additionally, we examined the frequency of ESA usage after the 2007 FDA safety update revising product labeling for ESAs.
Methods: A retrospective chart review was conducted on patients diagnosed with active multiple myeloma between January 1st, 2000 and December 31st, 2015 at Gundersen Health System in La Crosse Wisconsin. Collected data include patient demographics, medications, lab tests, comorbidities, and the dates of any VTE, stroke, or myocardial infarction. Both a logistic regression and a matched case-control analysis were used to compare rates of complications in patients using ESAs to those that did not. ESA effect on median survival time was also calculated for each International Staging System (ISS) stage of disease.
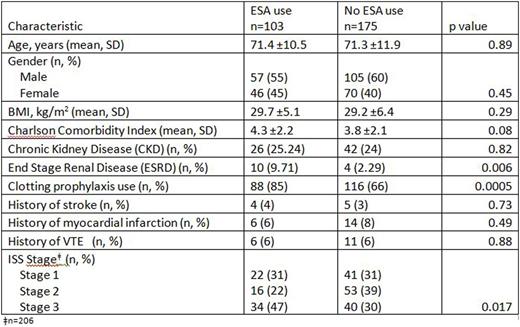
Results:There were 278 patients included for demographic analysis (Table 1), of which 268 were included in the logistic regression analysis and 124 (62 pairs) in the matched case-control analysis.
A logistic regression model constructed via stepwise selection found that bone lesions at diagnosis (Odds Ratio (OR): 2.5 [1.2-5.1]), antiplatelet drug use (OR: 3.7 [1.2-11.3]) and ESA use (OR: 4.7 [2.2-9.9]) were associated with increased risk of VTE in our patient population. Use of an Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitor (OR: 0.4 [0.2-0.9]) was associated with a decreased risk of VTE. Increased odds of VTE with ESA usage (OR: 5.9 [1.9 - 18.8]) were also noted in the matched case-control analysis. There was no association found between rate of stroke and ESA usage in either logistic or matched case-control analysis. No significant association between ESA use and overall survival was noted in either logistic or matched case-control analysis.
When comparing outcomes based upon pre and post FDA revised product labeling, we found a 50% reduction in ESA usage within our institution. In this same time period, the percentage of patients with multiple myeloma developing VTEs has been significantly reduced (18.6% vs 12.8% [p<0.007]).
Conclusions: In our population, the use of ESAs in multiple myeloma patients was associated with increased risk of VTE. No significant association between ESA use and overall survival was noted. The observed decrease in both ESA use and rate of VTE in patients with myeloma after the 2007 revised safety labelling by the FDA may reflect practice changes in response to this revision at our institution. Further study in a prospective large multicenter dataset with further control of confounding variables is warranted.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal