Abstract
Activation of the membrane-bound Suppression of Tumorigenecity 2 (mST2) by Interleukin-33 (IL-33) in T cells leads to type-2 (Th2) and Foxp3+ regulatory (Tregs) immune responses. The mST2/IL-33 axis is not engaged when a ST2 splice isoform containing only the ST2 ectodomain and acting as a decoy receptor, called soluble ST2 (sST2), sequesters IL-33. Clinically, elevated plasma sST2 has been reported and used as a prognostic biomarker in cardiac allo-rejection, inflammatory bowel disease, and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). We hypothesized that releasing IL-33 from circulating sST2 may augment the mST2/IL-33 axis activation to modulate the Th1 and Th2/Tregs responses for treating immune related diseases. This is supported by our study of a ST2 antibody in the GVHD models (Zhang et. al., Sci. Trans. Med. 2015). Advantages of small-molecule therapies over biologics include easier administration especially by oral, superior tissue penetration, modifiable pharmacokinetic properties including half-life, and lower manufacturing cost. Here, we present the proof-of-concept of this approach using three small molecule ST2 inhibitors we discovered recently. Our data show two inhibitors cause reduction of sST2, alleviate GVHD and improve survival in two in vivo GVHD models.
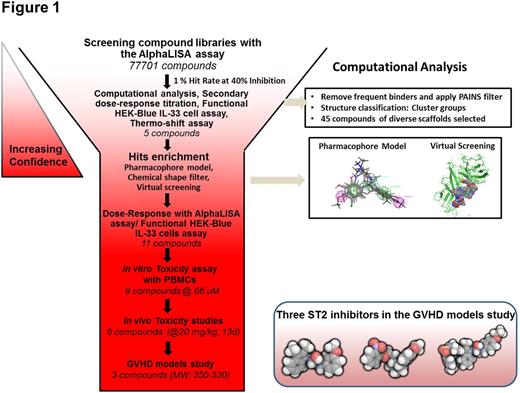
Our high throughput screening (HTS) using the AlphaLISA assay and computational analysis led to discover three classes of small molecules inhibiting ST2 binding to IL-33 which were confirmed by the functional cell-based HEK-Blue assay. Seven compounds showing low toxicity at 66 uM to peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were selected for the dose escalation toxicity study in mice. Six of them showed no toxicity up to 20 mg/kg in 13 days while five of them can be tolerated at 40 mg/kg. The HTS workflow is summarized in Fig. 1.
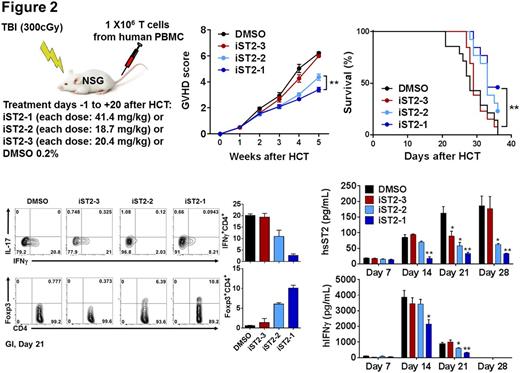
Three compounds (named iST2-1-3) were evaluated in the in vivo GVHD disease models. The first model is the transplantation of human PBMC to the NOD/SCID/IL2rgnull (NSG) mice one day after the mice received 300 cGy total body irradiation (TBI). Compounds were injected via the intraperitoneal route to the mice the day before transplantation and continued daily at their respective IC50 dosages for 21 days. At Day 14, both iST2-1 and iST2-2 caused reduction of IFNg+ CD4+ T cells and increase of Foxp3+CD4+ Tregs population in the human CD45+CD4+ cells extracted from the gastrointestinal (GI), the main GVHD target organ, compared with the DMSO control (Fig. 2). More profound effect exerted by iST2-1 was observed at Day 21. Plasma concentrations of human IFNg and sST2, indicators of Th1 response, showed the highest reduction in the iST2-1 treatment group. While the hsST2 plasma concentration is maintained at < 30 pg/ml throughout 28 days in the iST2-1 treatment group, escalation of hsST2 up to 180 pg/ml was found in the DMSO control and iST2-3 treated group. Plasma hIFNg was at least 50% lower in the iST2-1 treated group at day 14 and 21. The GVHD scores and survival of NSG mouse models paralleled the changes of GI T cell populations and systemic cytokines data; iST2-1 treatment showed decreased GVHD score to 3 from 6 in the DMSO control and improvement of survival rate to 45 % on day 35 whereas all mice in the DMSO control group were dead.
The second model is the minor mismatched model of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) from B6 to C3H.SW mice. We observed similar trends of IFNg+ reduction and Foxp3+ increase in CD4+ Tcells from the GI (Fig. 3). Plasma sST2 and IFNg concentrations were greatly reduced on day 14 in the iST2-1 treated group compared with DMSO control (50 versus 10 ng/ml for sST2 and 350 versus 100 pg/ml for IFNg).
Finally, we have collected the Small Angle X-ray Scattering data to construct structural models between iST2-1 and sST2 to guide the inhibitor optimization. The CRISP-Cas9 technology was also used to obtain sST2 deficient B6 mice. Allo-HCT using these donor sST2 deficient T cells will delineate the specific mode of action by our ST2 inhibitors on mST2 and sST2. Our findings reveal iST2-1 is an attractive small molecule ST2 inhibitor that can be used to study the mST2/IL-33 axis in disease models and further developed as therapeutics to treat GVHD.
Paczesny:Viracor-IBT Laboratories: Patents & Royalties.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal