Abstract
#the authors contributed equally to this work
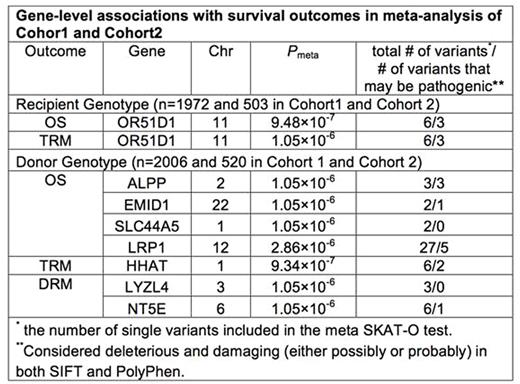
While survival outcomes after HLA-matched unrelated donor (URD) blood and marrow transplant (BMT) have significantly improved over the last two decades, about 40% of patients die before 1-year post URD BMT. Previously we performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) named DISCOVeRY-BMT (Determining the Influence of Susceptibility COnveying Variants Related to one-Year mortality after BMT) to investigate the contributions of common genetic variants on survival outcomes. To address the specific contributions of low frequency (≤ 1%) exonic variants on survival outcomes, we used the DISCOVeRY-BMT cohorts typed with the Illumina HumanExome BeadChip containing 242,901 variants, which are mainly protein-coding variants. We used a gene-based test (the optimal sequence kernel association test (SKAT-O)) to evaluate the cumulative effects of multiple genetic variants within a gene on overall survival (OS), transplant-related mortality (TRM), and disease-related mortality (DRM) 1 year after URD BMT. SKAT-O measures the overall significance of the gene and allows the variants to have different directions and magnitude of effects. We used a 2-stage study design: SKAT-O analysis was carried out in Cohort 1 consisting of 1,972 AML, ALL or MDS patients reported to the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research from 2000 to 2008 and their 2,006 10/10 HLA-matched URD. Genes with a suggestive association with each outcome (P < 1×10-3) entered the final meta-analysis including Cohort 1 and an independent cohort (Cohort 2), consisting of 503 recipients and 520 10/10 HLA-matched URD from 2009 to 2011. The analysis included recipients and URD of European descent due to the low frequency of other populations. All association models included age at BMT, diagnosis (AML, ALL, MDS), disease status at BMT, cell source (peripheral blood, marrow), year of BMT, and principal components from EIGENSTRAT to control for population stratification. Only coding variants (missense and nonsense) with minor allele frequency ≤ 1% were included in our analysis, which resulted in > 12,000 genes tested in our gene-based analysis in recipients and donors. Exome-wide significance was set at Pmeta< 4.10×10-6 after Bonferroni correction for the total number of genes tested. The likely pathogenicity of these variants was determined in silico using SIFT and PolyPhen. In recipients, we identified OR51D1, a member of the olfactory receptor gene family, as significantly associated with both OS and TRM. The OS association with ORD51D1 is driven by TRM as the same six missense variants contribute to both TRM and OS, but not to DRM. In donors, four (ALPP, EMID1, SLC44A5, LRP1), one (HHAT), and two (LYZL4, NT5E) genes were significantly associated with OS, TRM, and DRM, respectively (Table). ALPP encodes an alkaline phosphatase. SLC44A5 is a member of the solute carrier gene family. LRP1 (low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1) encodes an endocytic receptor involved in several cellular processes, including intracellular signaling, lipid homeostasis, and clearance of apoptotic cells. HHAT encodes an enzyme that acts within the hedgehog secretory pathway, which is involved in hematologic malignancy. LYZL4 is a member of a family of lysozyme-like genes, which have a protective role in host defense. The encoded protein of NT5E, CD270, is used as a determinant of lymphocyte differentiation. The likely pathogenicity of several of the functional variants in all significant genes identified was predicted to be both (possibly or probably) damaging and deleterious (Table), thus indicating that the amino acid substitution of the variant may not be well tolerated. One damaging variant in LRP1 has been identified as a somatic mutation in hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue. Our study is the first analysis of the low-frequency coding variant contribution to URD BMT survival outcomes. We found that the missense variants contributing to many of these significant gene associations shows evidence of pathogenicity and thus it is biologically plausible these variants are contributing to survival outcomes. Further confirmation of these findings, and studies of the functional consequences of protein-coding changes in these genes, may provide more individualized risk prediction and prognosis as well as alternative donor selection strategies.
McCarthy:Gamida Cell: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Onyx: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Karyopharm: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; The Binding Site: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Hahn:Novartis: Equity Ownership; NIH: Research Funding. Sucheston-Campbell:NIH/NCI: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal