Abstract
Nonmalignant marrow stroma provides a favorable microenvironment for leukemia cell survival. The mechanisms of support are not well understood. Some studies have identified roles for some stromal derived molecules including some growth factors (EGF, FGF, PDGF), adhesion molecules (VCAM, selectins, osteopontins, integrins, fibronectin), cytokines (IL3, IL6, IL7) and others (KITLG, ANGPT1, CXCL12, LGALS3). It is clearly a multifactorial mechanism. We have developed a simple but powerful experimental system of human marrow derived stromal cells co-cultured with primary human high risk ALL cells that allows us to study the molecular mechanisms.
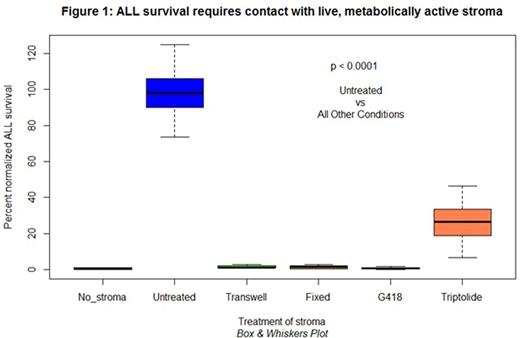
Efficient delivery of the antiapoptotic signals requires leukemia cell contact with living, metabolically active stromal cells. Figure 1 shows several conditions in which stromal cell support for ALL is abrogated: (a) when ALL contact with stroma is prevented by a transwell membrane that allows free flow of extracellular medium; (b) after formalin fixation of stromal cells and their matrix; (c) when live stromal cell protein synthesis is prevented by pretreatment of stromal cells with G418 at nonlethal concentrations; (d) when live stromal cell RNA transcription is impaired by pretreatment with triptolide.
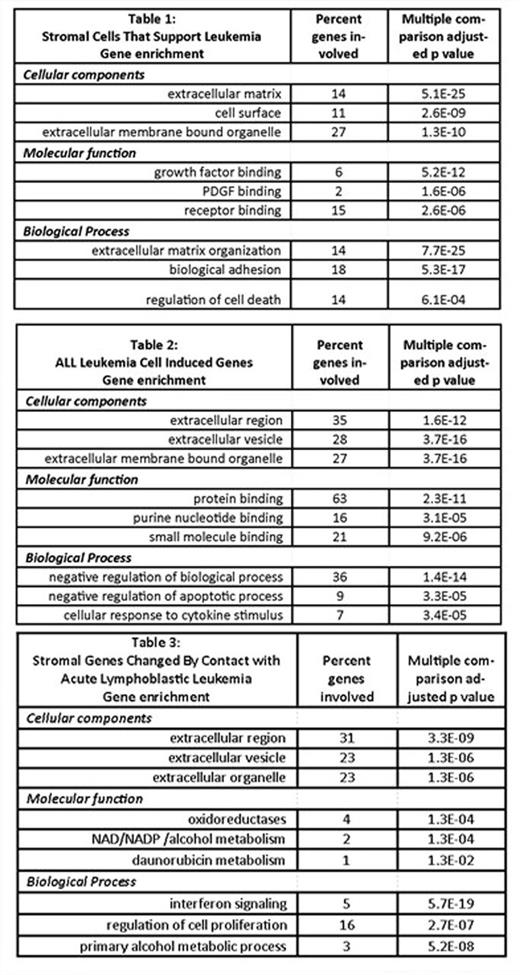
Efficient delivery of antiapoptotic signals to leukemia cells is associated with differential of genes related to the membrane and extracellular region and to regulation of cell death. We performed we performed RNASeq studies of gene expression in stromal cells and ALL cells. We made comparisons (a) between supporting cells that could (n=17) and could not (n=7) provide antiapoptotic support to ALL, and (b) between ALL cells that were (n=3) and were not (n=3) supported by stromal cells. We identified 409 genes differentially expressed in stromal cells that prevent ALL apoptosis including genes known to play roles in cell surface interactions, cell matrix interactions, growth factor binding and regulation of cell death (Table 1). We identified 458 genes upregulated in ALL cells following contact with stromal cells including genes related to interactions with the extracellular environment, purine metabolism and regulation of apoptosis (Table 2). We identified 494 genes upregulated in stromal cells following contact with ALL related to extracellular interactions, regulation of oxidation, regulation of daunorubicin, regulation of NADP and ethanol metabolism, interferon signaling and regulation of cell proliferation (Table 3).
Based on these discoveries we hypothesized that important mechanisms of stromal cell support of ALL might involve direct intercellular exchange of small molecules related to energy metabolism, nucleic metabolism, and messengers regulating cell proliferation and cell apoptosis. Possible mechanisms could include gap junctions, nanotubules or exosomes. The predominant gap junction in human cells is connexin 43 (GJA1). We found that GJA1 is constitutively expressed at high levels by stromal cells, and that GJA1 expression is increased ten-fold in ALL cells upon contact with stromal cells.
Rapid bidirectional exchange of intracellular molecules occurs between stromal cells and ALL. We loaded stromal cells with fluorescent calcien AM which once inside a cell cannot diffuse through the membrane but can pass through gap junctions. We cocultured ALL cells with labelled stromal for 16 hr. We observed calcien in ALL cells in physical contact with stroma, but not in ALL cells separated from labelled stroma by a transwell. When leukemia cells were labeled with calcien we saw transfer of calcien to stroma in contact with ALL but not when separated by a transwell.
Interference with gap junction function increases ALL cell death. GAP27 is an 11-amino acid peptide that specifically interferes with GJA1/connexin 43 gap junctions. Figure 2 shows substantial reduction of ALL survival in cocultures containing 1 mM GAP27 peptide. We observed similar results with use of 75 micromolar carbenoxolone, an FDA approved drug that impairs gap junction function.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal