Abstract
Background
Compared to the general population, patients with multiple myeloma (MM) have a 9-fold increased risk of developing venous thromboembolism (VTE). VTE is a preventable disease that causes death and morbidity. Thromboprophylaxis is a safe and effective way to decrease VTE in other high-risk populations (i.e. atrial fibrillation). Current guidelines recommend pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis in patients with MM receiving an immunomodulatory agent in the presence of additional VTE risk factors. However, putative risk factors vary across guidelines and lack validation. Recently, an attempt to validate the International Myeloma Working Group 2014 guidelines for thromboprophylaxis found current risk factors to be inadequate. Identification of risk factors for VTE in MM can allow for effective risk-stratification to clarify thromboprophylaxis in the MM population. We sought to identify risk factors for VTE in patients with MM.
Methods
We identified patients diagnosed with MM within the Veterans Administration Central Cancer Registry from September 1, 1999 and December 31, 2013 and followed them through October 2014. We excluded patients who did not receive MM-directed therapy within 6 months of diagnosis. Using a previously validated algorithm, (Thromb Res, 2015), we identified patients diagnosed with VTE after MM diagnosis by a combination of ICD-9 code for VTE plus pharmacologic treatment for VTE or IVC filter placement. We obtained information on baseline patient demographics, medical comorbidities, laboratory data, MM-directed therapy, and use of aspirin and/or warfarin. Univariate analyses identified the association between individual variables and VTE in the cohort. Clinically meaningful and significant associations were included in the multivariate model. Multivariate analysis was done using competing risks regression modeling. The study was approved by the Saint Louis VHA Medical Center and Washington University institutional review boards.
Results
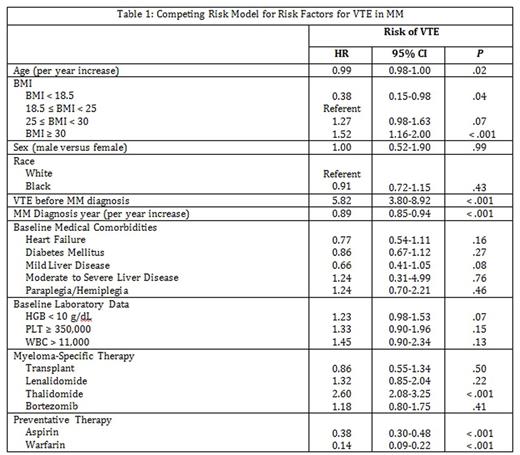
A total of 3,384 patients comprised the final cohort of whom 414 developed a VTE. Patients who developed VTE were more likely to be younger (66.2 vs 68.5, p < .001), have a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 25 (p < .001), be diagnosed with MM prior to 2007 (p < .001), have a VTE before MM diagnosis (p < .001), have a lower comorbidities (p < .001), have received autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) (p < .001), have received lenalidomide, thalidomide, or bortezomib (p < .001), and less likely to have received warfarin (p < .001). Among predefined risk factors, age (Hazard Ratio (HR) 0.99, 95% Confidence Interval (CI) 0.98-1.00, p = 0.02), VTE before MM diagnosis (HR 4.13, 95% CI 2.81-6.05, p < .001), heart failure (HR 0.70, 95% CI 0.51-0.96, p = 0.03), treatment with thalidomide (HR 2.02, 95% CI 1.63-2.50, p < 0.001), BMI ≥ 30 (HR 1.34, 95% CI 1.03-1.74, p = 0.03), and diabetes mellitus (HR 0.79, 95% CI 0.63-0.99, p = 0.04) were associated with VTE. After inclusion into multivariate analysis and adjusting for warfarin/aspirin use; age, BMI, year of MM diagnosis, VTE before MM, thalidomide, warfarin, and aspirin were all associated with VTE in MM (Table 1).
Conclusion
We identified several risk factors associated with VTE in MM. Incorporation of these risk factors into a MM-specific risk model has the potential to reduce risk of VTE in MM.
Sanfilippo:National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: Research Funding. Gage:National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: Research Funding. Carson:American Cancer Society: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal