Abstract
Background-
Currently combination regimens for induction therapy based around a proteasome inhibitor (PI), an immunomodulatory agent (IMiD) or both are standard for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM). In phase II studies the combination of Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (Dex) has led to very high rates of overall and deep responses as induction therapy (Jakubowiak Blood 2012). According to the Norton-Simon hypothesis, the sequential, dose-dense use of agents that are not cross-resistant and have minimal overlapping toxicity may eliminate the emergence of residual inherently resistant sub-clones which are responsible for relapse. A sequential approach may also allow for medications to be administered at higher doses and the incorporation of more active agents into an initial therapeutic platform than can be tolerated in a single combinatorial induction approach. To date limited research has been done which evaluates a planned sequential therapeutic protocol built around the successive administration of a highly active PI and IMiD for NDMM. We conducted a phase II study evaluating high dose Carfilzomib and Dex induction (Kd) followed by Lenalidomide, clarithromycin and Dex (BiRD) consolidation and Lenalidomide maintenance in NDMM to evaluate safety and efficacy of this approach
Methods
Between 2012 and 2015, 72 patients were enrolled in a phase II trial of the CarBiRD regimen for initial treatment of symptomatic NDMM. Patients received Carfilzomib intravenously over 30 minutes on days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, 16 of a 28 day cycle with Dex 20mg orally on days of Carfilzomib therapy. Carfilzomib was administered at a dose of 20mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of cycle one of therapy before escalation to target dosing on all subsequent treatment days. The initial protocol was designed with a target Carfilzomib dosing of 45mg/m2, following the enrollment of the first 26 patients on protocol the dosing was increased to 56mg/m2. After maximum response was achieved with Kd, defined as complete response or stable m-protein for 2 consecutive cycles, patients who were eligible for autologous stem cell transplant underwent stem cell collection. Patients then initiated consolidation with Lenalidomide, clarithromycin and Dex (BiRD). BiRD consisted of Lenalidomide 25mg daily on days 1-21 of 28 day cycles, with clarithromycin 500mg twice daily and Dex 40mg on days 1, 8, 15 and 22. BiRD was also continued until achievement of maximum response and patients subsequently initiated maintenance Lenalidomide (Len) at a dose of 10mg on 21 of 28 day cycles.
Results
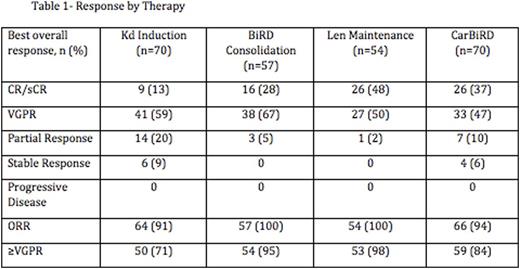
70 out off 72 patients completed at least one cycle of Kd and were evaluated for response. 15 patients came off trial during Carfilzomib therapy: 7 for toxicity, 2 for progression of disease and 6 for either withdrawal of consent, insurance issues or non-compliance. 3 patients came off trial during BiRD consolidation: 1 each for toxicity, progression of disease and withdrawal of consent. The remaining 57 patients initiated BiRD and 54 Len maintenance respectively. Responses are summarized in table 1. The overall response rate was 94% with 84% of patient's achieving a VGPR or better and 37% achieving CR or stringent CR. The rate of CR/sCR increased from 13% (9 of 70 patients) with Kd induction to 28% (16 of 57) with BiRD consolidation and 48% (26 of 54) with Len maintenance. 30% of patients (17 of 57) experience an increased depth of response by at least 1 IMWG response category during BiRD consolidation from their maximum response to Kd. 19% (10 of 54) had an increased depth of response category during Len maintenance.
The large majority of adverse events were grade 1 or 2. The most common toxicities across protocol were low-grade gastrointestinal events. The most common grade 3 or higher toxicities were infectious with 17% of patients (12 of 72) experiencing at least one grade 3 or higher infection. Peripheral neuropathy developed in 31% of patients with no grade 3 or higher neuropathy emerging during treatment. The rate of emergent hematologic toxicities was very low across protocol.
Discussion
CarBiRD is an effective and well-tolerated treatment regimen for patients with NDMM. Using a sequential treatment approach with a highly effective PI and IMiD as the back bones of successive therapies led to high rates of overall response, VGPR or better and complete response in a deferred transplant and transplant ineligible setting.
Rossi:Takeda: Speakers Bureau; Onyx: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Perry:Celgene: Speakers Bureau. Pekle:Millenium: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Coleman:Immunomedies: Equity Ownership, Other: Leadership; AbbVie: Equity Ownership; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics, LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Research Funding; GSK: Research Funding; Karyoharm: Research Funding. Allan:Pharmacyclics: Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Speakers Bureau. Niesvizky:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Millenium: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Onyx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Mark:Onyx: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Millenium: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal