Abstract
Introduction/background:
Clonal TP53 aberrations (del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations) in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) correlates with a poor prognosis. Similar outcome has been demonstrated for patients with subclonal TP53 aberrations (Rossi, Blood, 2014). In order to guide novel targeted therapies approved in frontline treatment of TP53 aberrated (TP53+) CLL, development and clinical validation of robust assays for subclonal TP53 aberrations is warranted.
Methods:
DNA extracted from peripheral blood of CLL patients were diluted 1:5 in DNA derived from a cell line containing a known, but rare TP53 point mutation. TP53 exons 2-10 were PCR amplified from undiluted and diluted DNA in parallel using Phusion proofreading DNA polymerase and subsequently sequenced by targeted Next Generation Sequencing (tNGS) on Illumina MiSeq and HiSeq 2500. Sensitivity and specificity of the assay was tested by serial dilution of patient samples with known TP53 insertions, deletions or substitutions. Consecutive biobanked samples from CLL patients at a single institution were used for validation of the clinical impact of subclonal TP53 aberrations. Nucleotide variants were called by CLC Biomedical Genomics Workbench 3.0. An algorithm for detection of true mutations was developed based on comparison of the diluted and undiluted samples analyzed in parallel. Overall survival (OS) was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier.
Results:
The sensitivity and specificity of the assay was validated by detection of all 8 known TP53 aberrations in serial dilutions with the threshold of the assay established at 0.2% allelic burden. Known mutations were still detectable at 0.02% at the highest dilution. A test sample of patients with known del(17p) demonstrated TP53 mutations in 6 out of 7 patients (5 clonal and 1 subclonal TP53+) in accordance with previously reported frequencies of TP53 mutations among patients with del(17p).
In total, 92 samples from 46 consecutive patients were analyzed. With a median coverage of 93,272 reads (98% above 20,688 reads, range: 5,153-720,025), 27 TP53 aberrations were found in 10 (22%) of the patients. Twenty-six (96%) mutations were subclonal with a median allelic burden of 0.9% (range: 0.2-97.5%). Seven patients had a single aberration. In two previously treated patients, 8 and 10 subclonal aberrations were detected. One patient with a known del(17p) also had subclonal TP53 mutations. Three patients had solely subclonal mutations below 1% allelic burden. Considered the hot spot region of TP53 in CLL, exons 4-8 harbored 93% of the detected mutations.
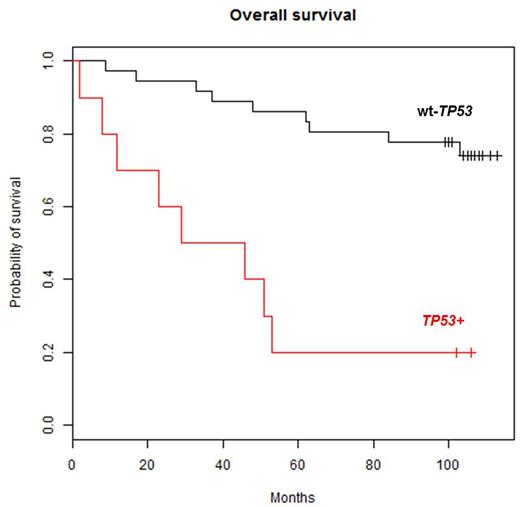
The median (IQR) survival for TP53+ patients and patients with wild type TP53 (wt-TP53) was 37.5 (range: 2-106) and 104 (range: 9-113) months, respectively. In Kaplan-Meier analyses, TP53+ patients had a significantly poorer OS versus patients with wt-TP53 (p=0.00002, Figure 1). The two TP53+ long-term survivors both had an allelic burden below 1%, and the only other TP53+ patient with less than 1% allelic burden survived for 53 months, indicating that the prognostic impact of very low allelic burden TP53 aberrations needs further investigation.
Conclusion:
We have developed a robust assay for TP53 aberrations with a sensitivity of 0.2% allelic burden based on an algorithm including a dilution step. In an initial test cohort of 46 patients, 10 patients demonstrated TP53 mutations as low as 0.2% allelic burden that significantly affected OS. Validation of the clinical impact of subclonal TP53 aberrations is ongoing based on our consecutive biobank with 600+ patients. Establishment of a new cut-off for clinical treatment decisions based on subclonal TP53 aberrations is warranted.
Overall survival in 46 consecutive CLL patients based on TP53 mutation status shows significant difference (p=0.00002) between patients withwild type TP53 (wt-TP53) and TP53 mutations (TP53+) as low as 0.2% allelic burden.
Overall survival in 46 consecutive CLL patients based on TP53 mutation status shows significant difference (p=0.00002) between patients withwild type TP53 (wt-TP53) and TP53 mutations (TP53+) as low as 0.2% allelic burden.
Niemann:Gilead: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal