Abstract
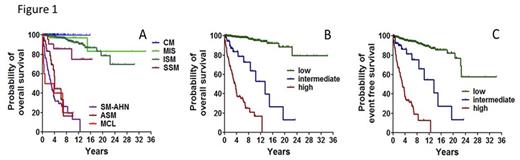
Mastocytosis is a hematopoietic disorder characterized by abnormal growth and accumulation of neoplastic mast cells (MC) in various organ systems. Using updated WHO criteria and the proposal of the consensus group, the disease can be divided into cutaneous mastocytosis (CM), indolent systemic mastocytosis (ISM), smouldering SM (SSM), SM with an associated hematologic neoplasm (SM-AHN), aggressive SM (ASM), and mast cell leukemia (MCL). In adult patients with skin involvement but unknown/unavailable bone marrow (BM) studies, the provisional diagnosis ´mastocytosis in the skin (MIS)´ is appropriate. Although this classification has been validated repeatedly and is of prognostic significance, additional prognostic parameters have been identified in recent years (yrs). We have established a patient-registry in the ECNM where over 1,000 cases with confirmed mastocytosis are included. The aim of this study was to identify and validate new prognostic variables predicting survival in patients with mastocytosis and to prepare a simple prognostic scoring system applicable in daily practice. Using the data set of the ECNM registry we analyzed overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS; i.e. until death or progression) in 1,088 patients with mastocytosis (median age: 45.7 yrs; range: 0.1-83.3 yrs, f:m ratio, 1:0.79), including CM (n=152), MIS (n=126), ISM (n=650), SSM (n=26), SM-AHN (n=89), ASM (n=35), and MCL (n=10). The median observation period was 3.5 yrs (75-25% percentile: 1.5-6.9 yrs, maximum 34.1 yrs). In the entire cohort, the median OS was not reached. The probability to be alive after 5, 10, and 20 yrs was 89%, 83%, and 70%, respectively. As expected, the WHO classification turned out to be of utmost predictive significance (Figure 1A; p<0.005). In patients with non-advanced disease, namely CM, MIS, ISM, and SSM, the median survival was not reached, and the survival at 5 yrs was 100%, 97%, 98%, and 85%, respectively, whereas in advanced SM, namely SM-AHN, ASM, and MCL, the median survival was 2.8, 4.1, and 0.8 yrs, respectively. Patients with advanced SM were found to be older, to have higher serum tryptase- and alkaline phosphatase (aPhos) levels, higher white blood counts (WBC), lower hemoglobin (Hb) and platelet (PLT) counts, and more frequently presented with organomegaly (hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, or lymphadenopathy). Moreover, the male/female ratio was higher in advanced mastocytosis. To define the relative impact of the identified risk factors we randomly divided the total cohort (50:50) into a learning set and a validation set, performed uni- and multivariate analyses, and subsequently calculated cut off values for optimal prognostication. In these studies, the poor prognosis of patients with advanced SM was confirmed. In patients with non-advanced disease, all variables tested were significant concerning OS in univariate analyses. However, WBC, Hb, and lactate dehydrogenase had to be excluded due to variance inflation. In multivariate analyses, age >70 yrs, PLT <80 G/L (not related to SM), and aPhos ≥240 U/L were significant predictors concerning OS. Based on these parameters, we established a simple prognostic scoring system. In this score, patients with non-advanced disease (CM, MIS, ISM, SSM) without additional risk factors comprised the low risk group, those with non-advanced disease and presence of one or more risk factors (age >70 yrs, PLT <80 G/L, aPhos ≥240 U/L) the intermediate risk group, and those with advanced disease (with or without additional risk factors) the high risk group. The median OS in the low risk group was not reached, in the intermediate risk group it was 13.5 yrs, and in the high risk group 3.5 yrs (p<0.005; Figure 1B). Significant differences were also observed regarding EFS (p<0.005, Figure 1C). In conclusion, the WHO classification remains the gold-standard of prognostication in patients with mastocytosis, but additional factors, namely age, PLT, and aPhos, are powerful additional variables predicting OS in these patients. Based on in-depth analyses of the ECNM registry data-set, a simple prognostic scoring system for mastocytosis was established and is recommended to define the probability of OS and EFS in patients with mastocytosis in daily practice.
Sperr:Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria. Gotlib:Incyte Corporation: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Valent:Amgen: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Deciphera Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Ariad: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal