Abstract
Introduction
High dose chemotherapy (HDC) followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) has been adopted as an effective treatment in patients with relapsed or refractory primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) and also has been proposed as a consolidative treatment option for newly diagnosed PCNSL. HDC-ASCT may overcome chemoresistance mediated by blood-brain barrier by affording higher drug concentrations in the central nervous system. We investigated the feasibility of thiotepa, busulfan, and cyclophosphamide (TBC) conditioning followed by ASCT in patients with PCNSL.
Method
Between December 2012 and July 2015, a total of 27 patients with PCNSL underwent TBC conditioning followed by ASCT. Those with a complete or partial response after induction chemotherapy or salvage chemotherapy proceeded with TBC conditioning followed by ASCT. TBC conditioning consists of thiotepa 250 mg/m2 on days -9 to day -7, busulfan 3.2 mg/kg on days -6 to day -4 and cyclophosphamide 60 mg/kg on days -3 to day -2. The event free survival (EFS) was defined from the date of transplant to the date of relapse, progression or any cause of death, while overall survival (OS) was calculated from the date of transplant to death.
Result
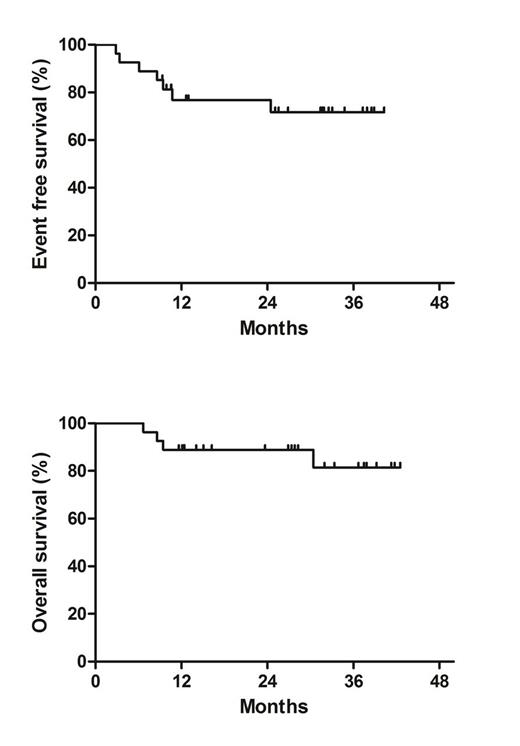
Baseline characteristics were summarized in table 1. Twenty patients received TBC conditioning followed by ASCT as a consolidative therapy after high-dose methotrexate-based induction chemotherapy and the other 7 patients received TBC conditioning followed by ASCT after salvage chemotherapy due to relapsed or refractory disease. The median time to neutrophil recovery (absolute neutrophil count >500/uL) and platelet recovery (>20000 x103/uL) were 8 (range, 7-9) and 8 (range, 4-15) days, respectively. All 27 patients experienced febrile neutropenia and 33.3% of patients (9/27) and 7.4% of patients (2/27) had documented bacterial and viral infection, respectively. Commonly observed nonhematologic grade 3 or 4 toxicities were mucositis (63%), diarrhea (59.3%) and nausea (25.9%). The 100-day transplant-related mortality rate was 0%. With median follow-up duration of 27.8 months (range 6.7-42.6), median EFS and OS were not reached. The 2-year EFS and OS estimates were 76.8% (95% CI: 68.4-85.2) and 88.9% (95% CI: 82.9-94.9), respectively (Figure 1).
Conclusion
ASCT with TBC conditioning appears to be feasible in patients with PCNSL. Although survival outcomes are encouraging, longer follow-up is required. Further studies are warranted to investigate the role of ASCT with TBC conditioning in both clinical settings of consolidative treatment of newly diagnosed PCNSL and salvage treatment of relapsed or refractory PCNSL.
Baseline characteristics (n=27)
*Conventional cytology; flow cytometry not performed
$The cutoff for normal CSF protein concentration was 45 mg/dL in patients ¡Â 60 years old
and 60 mg/dL in patients more than 60 years old.
*MSK RPA, Memorial Sloan-Kettering prognostic score determined by recursive partitioning
$Periventricular, basal ganglia, brainstem and cerebellar lesion
Baseline characteristics (n=27)
*Conventional cytology; flow cytometry not performed
$The cutoff for normal CSF protein concentration was 45 mg/dL in patients ¡Â 60 years old
and 60 mg/dL in patients more than 60 years old.
*MSK RPA, Memorial Sloan-Kettering prognostic score determined by recursive partitioning
$Periventricular, basal ganglia, brainstem and cerebellar lesion
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal