Abstract
Background:
Bortezomib was originally incorporated into DT-PACE (thalidomide, dexamethasone, cisplatin, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and etoposide) as an intensive induction regimen (VTD-PACE) prior to high-dose melphalan and autologous transplant for multiple myeloma (MM). This regimen is effective in the induction setting, and also for patients with relapsed disease (Barlogie British Journal of Haematology 2007, Singh ASCO 2013). At our center, we examined the outcomes of MM patients undergoing chemomobilization with a regimen that substituted carfilzomib and lenalidomide for bortezomib and thalidomide (CarRD-PACE).
Methods:
Twenty MM patients with measureable disease received CarRD-PACE for chemomobilization. We excluded in this report patients with plasma cell leukemia, renal insufficiency, heart failure, or those patients who were refractory to carfilzomib.
Results:
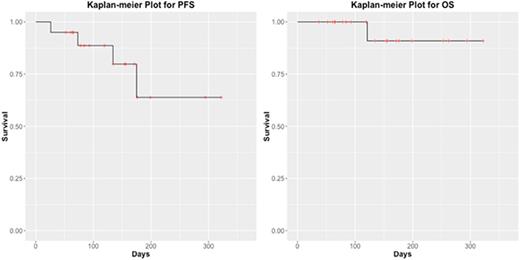
The median age was 61.5 years (range, 35- 69). Nine of these patients were women (45%). The median left ventricular ejection fraction pre-treatment was 62% (range, 50 - 77%). Of patients with initial staging information, 8 were ISS stage I (47%), 5 patients ISS II (29%), and 4 were ISS III (24%). High risk cytogenetics, defined as presence of deletion 17p, t(4;14), t(14;16), were present in 5 patients at time of chemomobilization (25%). Fourteen patients (82%) had bulky disease (defined as having > 3 lesions, or having a single lesion > 3 cm on PET-CT or MRI) prior to treatment, assessed by MRI (n=12) or PET-CT (n= 2). The median time from diagnosis to mobilization was 9.5 months (range, 4- 44). Patients had previously received a median of 2 regimens of therapy (range, 1- 5). Fifteen patients received 1 cycle of CarRD-PACE, and 5 patients received 2 cycles. Eighteen patients response evaluable; in these patients, the overall CR/PR response rate after completion of treatment was 25% (4 PR, 1 CR), with fifteen patients (75%) having SD. A total of 18 patients (90%) collected stem cells after mobilization, requiring a median of 1 day of collection (range, 1-2), and collected a median of 18.3 x 10^6 CD34+ cells/kg (range, 4.8 - 69.88). Grade 3-4 toxicities occurred in 6 patients (30%), most common was neutropenic fever (n=4) (20%). No patients experienced a cardiac toxicity. Hospital readmission following treatment occurred in 4 patients (20%) for a median of 6.5 days (range, 3 - 15). Eighteen patients (90%) underwent a single autologous transplant, and 2 (10%) received tandem autologous-allogeneic transplant. Following autologous transplant, the median time to neutrophil engraftment was 18 days (range, 14 - 29 days), and the median time to platelet engraftment was 13 days (range, 7 - 19 days). The PFS at 6 months was 63% (95% CI, 0.382 - 1), and the OS at 6 months was 91% (95% CI, 0.754 - 1) (Figure).
Discussion:
CarRD-PACE is a well-tolerated and effective therapy in heavily treated multiple myeloma patients with substantial disease burden at the time of autologous transplant, and can successfully mobilize autologous PBSC. Despite the theoretical concern regarding the combination of 2 agents with cardiac toxicity (carfilzomib and doxorubicin), we did not observe any cardiac toxicities of any grade during treatment. This approach may be particularly useful in individuals with bortezomib associated neuropathy and or those with bortezomib refractory disease.
Becker:GlycoMimetics: Research Funding. Shadman:Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding; Emergent: Research Funding. Gopal:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal