Abstract
Background T-cell receptors (TCRs) can be used to redirect the specificity of T-cells for human application. This has particular appeal for the targeting of neoantigens. However, efficient identification, cloning, and characterization of antigen (Ag)-specific TCRs is needed to enable the timely adoptive transfer of T-cells genetically modified to express therapeutic TCRs. We have harnessed next generation sequencing (NGS) to identify desirable TCRs. This approach enables us to simultaneously identify hundreds of Ag-specific TCRs, along with the expression of genes to characterize functional and phenotypical values of individual Ag-specific T-cells (e.g. related to cytotoxicity, exhaustion, etc...). To take advantage of NGS technology, a sister high-throughput technology was developed to evaluate harvested TCRs. A reporter system was implemented using (immortalized) Jurkat T-ALL cells genetically modified to (i) enforce expression of CD8aβ, (ii) conditionally express GFP under minimal elements of NR4A1 promoter, and (iii) prevent expression of both endogenous TCRα and β chains. Sequenced CDR3 regions were coded within DNA plasmids from Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposons as TCR Vα and Vβ libraries that were expressed on the reporter cell to identify both TCR specificity as well as TCR avidity. Thus, we implemented (i) a TCR cloning system based on CDR3 sequencing of Ag-specific T-cells identified by NGS and (ii) a novel reporter cell based on the TCR-mediated induction of GFP expression. As a proof-of-concept to evaluate the entire platform, we used HLA-A2-restricted CMV peptide (NLVPMVATV: CMV/A2) and NY-ESO-1 peptide (SLLMWITQC: NY-ESO-1/A2) as model Ags.
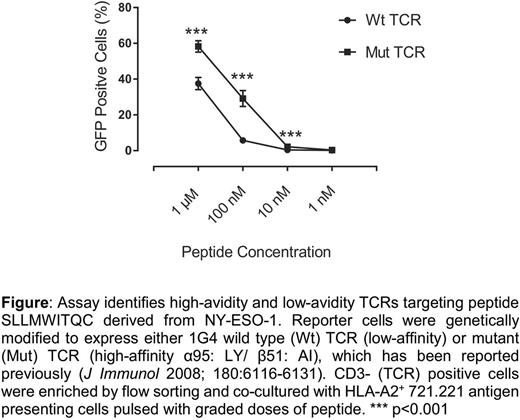
Results The reporter cell was initially genetically modified with either high- or low-avidity TCRs against a NY-ESO-1/A2. Upon stimulation with HLA-A2+ 721.221 immortalized B cells, it was found that the expression of GFP positively correlated with the avidity of TCRs (Figure). Next, we isolated naïve Ag-specific T-cells from umbilical cord blood using CMV/A2 tetramer. Single CMV/A2-specific CD8+ T-cells were sorted and their TCRαβ CDR3 sequences were amplified by reverse transcription and PCR with bar-coded probes. The pooled PCR products were sequenced in MiSeq Sequencer (illumina) to obtain TCRαβ CDR3 regions and analyzed in silico using IMGT (International Immunogenetics Information System). The efficiency of identifying individual TCRαβ pairs was 65% to 76% (using 96-well plate or 384-well plates, respectively). Individual SB-derived DNA transposons expressing TCRαβ constructs were synthesized by Gibson assembly and electroporated, with SB transposase, into the reporter cell. These cells were co-cultured with HLA-A2+ 721.221 stimulator cells loaded with graded doses of cognate peptide. The percentage and intensity of GFP expression was evaluated by high-throughput flow-cytometer (IntelliCyt) which revealed high-avidity Ag-specific TCRαβs.
Conclusion Our new high-throughput system can identify and characterize, based on specificity and avidity, Ag-specific TCRαβs within a week. This system will be used to generate neoantigen-specific TCRαβs for human application.
Zong:ZIOPHARM Oncology, Inc.: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties; Intrexon: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties; Immatics US, Inc: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties. Cooper:Ziopharm Oncology: Employment, Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties; Intrexon: Equity Ownership; City of Hope: Patents & Royalties; Targazyme, Inc.,: Equity Ownership; Immatics: Equity Ownership; Sangamo BioSciences: Patents & Royalties; MD Anderson Cancer Center: Employment; Miltenyi Biotec: Honoraria. McNamara:GeoMcNamara: Consultancy, Other: Consultant in immuno-oncology field; ZIOPHARM Oncology, Inc: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties; Intrexon: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties. Torikai:intrexon: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties; ZIOPHARM Oncology, Inc.: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties; Immatics US, Inc: Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal