Abstract
Background and Objectives
The development of neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) to factor VIII (FVIII) represents the major complication following replacement therapy with FVIII products in patients with hemophilia A. Why some patients develop FVIII inhibitors while others do not is poorly understood. Identification of early biomarkers which predict inhibitor development in previously untreated patients (PUPs) with hemophilia A will assist in risk identification and possible early intervention strategies. Previous analysis of FVIII-specific antibodies in different cohorts of patients with severe hemophilia A and in healthy individuals indicated distinct spectra of neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibodies (Whelan SFJ et al. Blood 2013). FVIII-specific antibodies found in hemophilia A patients with inhibitors have approximately 100-fold higher apparent affinities than that of antibodies found in patients without inhibitors or in healthy individuals (Hofbauer CJ et al. Blood 2015). In one individual, high affinity FVIII-specific antibodies were detectable prior to the diagnosis of FVIII inhibitors. The Hemophilia Inhibitor PUP Study (HIPS) is a prospective multicenter observational study of PUPs with severe hemophilia A during their first 50 exposure days (EDs) to recombinant FVIII (Advate TM). The objective is to elucidate immune system changes and identify potential early biomarkers of inhibitor development in PUPs. This is the first report of FVIII-specific antibody development in the first 10 subjects who have completed the study.
Methods
HIPS study procedures have been previously described (Hofbauer CJ et al. 2015; clinicaltrials.gov NCT01652027). FVIII inhibitor testing by Nijmegen methodology performed in a central laboratory (Medical College of Vienna) and FVIII-specific antibody analytics were done prior to first exposure, 7-9 days after exposure day (ED) 1 and 5-7 days after EDs 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50. FVIII-specific antibody analytics, including specifications of isotypes, IgG subclasses and apparent affinities were done using methodology described in Whelan 2013 and Hofbauer 2015.
Results:
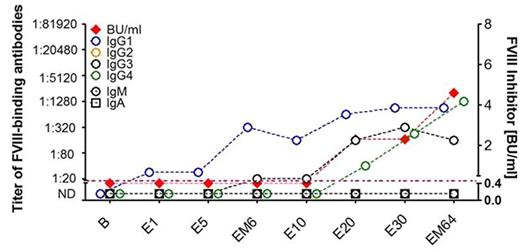
Currently, 24 subjects have been enrolled among 19 study sites. Data for 10 subjects were available for analysis. Among these 10 subjects, 2 developed FVIII inhibitors by study criteria (B.U. > 0.6 B.U. x 2 measurements in central laboratory) by exposure days 6 and 20 (see figure 1). A third subject is expected to meet study criteria for FVIII inhibitor due to multiple high titer measurements reported over time at a local laboratory. All three inhibitor patients revealed antibody class switching from IgG1 to IgG4 and affinity maturation resulting in the generation of high affinity FVIII-specific antibodies. High-affinity FVIII-specific IgG1 antibodies were detectable prior to inhibitor diagnosis in all 3 inhibitor subjects.
One subject with a transient FVIII inhibitor showed medium affinity FVIII-specific IgG1 antibodies which persisted until ED50, but never developed high-affinity antibodies. Another subject without a detectable inhibitor developed low titer, low affinity IgG1 antibodies that persisted to ED 50 without the development of high-affinity antibodies. The remaining subjects had no inhibitor and no detectable FVIII-specific antibodies.
Conclusions:
Interim data from HIPS suggests that FVIII inhibitor development is preceded by the detection of high-affinity FVIII-specific antibodies which undergo class switch from IgG1 and IgG3 to IgG4.
The findings confirm affinity maturation of FVIII-specific antibodies which require T-cell dependent antibody responses resulting from germinal center reactions. While low affinity IgG1 antibodies were sometimes seen in subjects without inhibitors, high-affinity antibodies were only seen in subjects who developed inhibitors. Our data indicate that high affinity FVIII-specific antibodies preceded the clinical diagnosis of an inhibitor and may serve as early biomarkers of FVIII inhibitor development facilitating early immune intervention.
Kinetic of FVIII-binding antibodies and FVIII inhibitors in patient 0902. High-affinity FVIII-specific IgG1 antibodies were first detected after exposure day 6, FVIII inhibitors were first diagnosed after exposure day 20.
Kinetic of FVIII-binding antibodies and FVIII inhibitors in patient 0902. High-affinity FVIII-specific IgG1 antibodies were first detected after exposure day 6, FVIII inhibitors were first diagnosed after exposure day 20.
Reipert:Shire: Employment, Research Funding. Gangadharan:Shire: Employment, Research Funding. Hofbauer:Shire: Employment. Scheiflinger:Shire: Employment, Research Funding. Bowen:Baxalta: Research Funding. Donnachie:Baxalta: Research Funding; CSL Behring: Research Funding; Bayer Healthcare: Research Funding. Fijvandraat:CSL Behring: Research Funding; Bayer Healthcare: Research Funding; Baxalta: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Gruppo:Baxalta: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Male:Baxalta: Other: travel support; Novo Nordisk: Other: travel support; Biotest: Other: travel support; Bayer Healthcare: Other: travel support; CSL Behring: Other: travel support; Pfizer: Other: travel support. McGuinn:Baxalta: Research Funding; Novo Nordisk: Research Funding; Spark: Research Funding; Biogen: Research Funding. Meeks:Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer Healthcare: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Grifols: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Biogen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CSL Behring: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shire: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Recht:Novo Nordisk: Consultancy, Research Funding; Baxalta: Research Funding; Biogen Idec: Research Funding; Kedrion: Consultancy. Ragni:Biogen: Research Funding. Yaish:Octapharma: Consultancy; Bayer Healthcare: Consultancy; Baxalta: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Santagostino:Sobi: Consultancy; Biogen Idec: Consultancy; Novo Nordisk: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Octapharma: Consultancy; Baxalta: Consultancy; Kedrion: Consultancy; CSL Behring: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; Grifols: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy. Brown:Baxalta/Shire: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal