Abstract
Introduction: T-cell lymphomas (T-NHL) represent rarer entities compared to B-NHL, accounting for 5% -10% of NHL in Western countries and 15%-20% in Asia. They are divided into clinico-pathologic subtypes based on etiology, morphology, and clinical behavior. Because of the rarity and the lack of specific histologic features for the different subtypes, the diagnosis is difficult and clinical picture is usually very helpful to establish the diagnosis. We conducted a retrospective analysis of patients (pts) with T-NHL treated at our Centre, with the purpose of studying overall outcome and possible prognostic factors, including histologic subtypes, from our database.
Patients and methods: Consecutive T-NHL pts (excluding Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma, NK/T NHL, and primary cutaneous T-NHL), receiving primary treatment at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre (PMCC) between 2001-2014 were included. Data were extracted from a prospective patient database and the medical record regarding baseline characteristics, treatment, response and outcome. Response assessment was with CT imaging as per 1999 Working Group criteria.
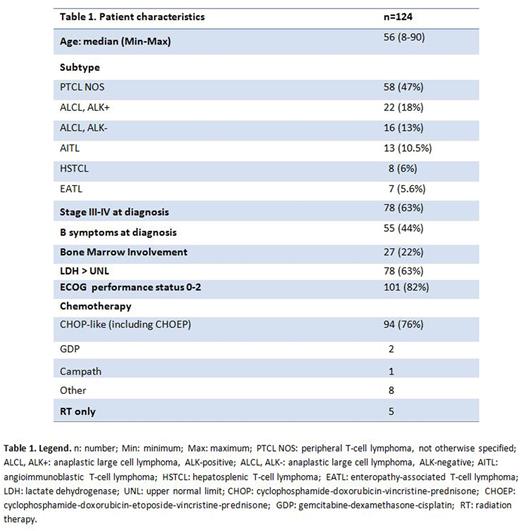
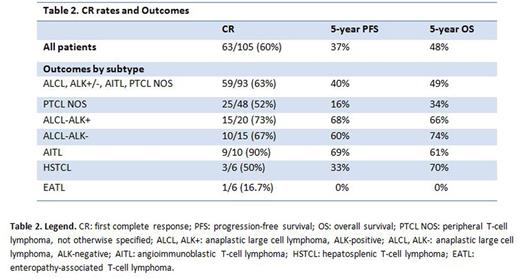
Results: Of a total of 2155 pts with aggressive histology NHL treated at PMCC between 2001-2014, 2031 pts had B-NHL and 124 (5.7%) T-NHL. Median age was 56 years (18-90), male/female ratio: 2.4; 63% presented with advanced stage (III-IV) disease, 22% had bone marrow involvement; 63% had elevated LDH and 44% had B symptoms. Observed subtypes were: Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, NOS 58 pts (PTCL NOS, 47%), Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK-negative 16 pts (ALCL-ALK-, 13%), ALCL, ALK-positive 22 pts (ALCL-ALK+, 18%), Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma 13 pts (AITL, 10.5%), Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma 7 pts (EATL, 5.6%), Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma 8 pts (HSTCL, 6%). 105/124 pts (85%) received induction chemotherapy; CHOP-like regimens were used in 94 pts (90%), and involved field radiation therapy (RT) was included in primary treatment in 24 pts (19%). Nineteen pts were treated palliatively, 5 pts with RT alone, 14 pts received palliative chemotherapy or supportive care only. Complete response (CR) was obtained in 63/105 pts (60%; Table 2), PR in 2 pts (1.9%) and 40 pts had no response or progressive disease (SD and PD; 38%). Considering together the most common subtypes (ALCL-ALK+/-, AITL, PTCL NOS), CR rate was 84% in limited stage vs 52% in advanced stage disease. Among patients with CR, 24 relapsed (38%). Fourteen pts received autologous stem cell transplant (8 at relapse, 6 for PD); 7/14 (50%) were alive at last follow-up. At a median follow-up of 5.3 years, 57/124 (46%) pts are alive. Cause of death was T-NHL in 50/124 (40%) pts. Two pts died of second malignancy (1.6%). Median overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were 4.57 years (95%CI: 2.23-9.53; 5yOS: 48%) and 1.5 years (0.87-3.17; 5yPFS: 37%), respectively (Table 2). For pts with limited stage disease median PFS was 4.57 years (5yPFS: 49%) and median OS 10.0 years (5yOS: 62%), while for pts with stage III/IV, median PFS was 0.82 years (5yPFS: 31%) and OS 1.81 years (5yOS: 38%). Median OS for pts who did not experience relapse (39/63; 62%) was 13.38 years (95%CI: 9.53-NA; 5yOS: 93%) vs 3.12 years (95%CI: 1.69-4.07 years; 5yOS: 25%) in pts who had relapse after CR1 (p<0.001). Pts failing to achieve CR (PR, SD, PD) had a very poor outcome with median OS 1.15 years (95%CI: 0.62-1.32 years; 5yOS: 17%). For PTCL NOS pts, outcomes were poor while those with ALCL had more favorable results regardless of ALK status (Table 2).
Conclusions: Failure to achieve CR with first-line treatment was the main cause of treatment failure in patients with T-NHL treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Patients with limited stage lymphoma and with ALCL ALK+/- subtypes have more favorable outcomes. For PTCL NOS, the most common subtype, and less common entities (HSTCL, EATL), results are poor and new induction strategies are needed.
Kukreti:Celgene: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Lundbeck: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal