Abstract
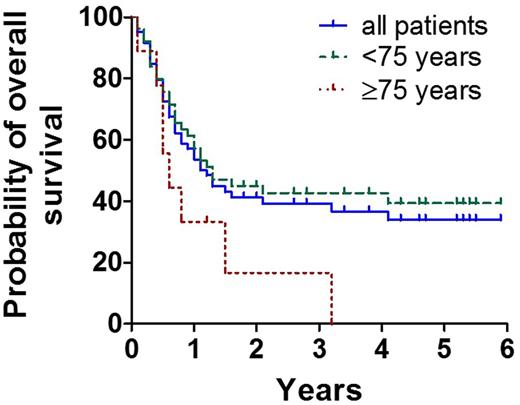
Treatment of AML in elderly patients (≥60 years) deserves special considerations and has to balance toxicity against efficacy as well as life expectancy against the risk of AML-related death and relapse after intensive treatment. We have previously shown that induction chemotherapy followed by repetitive cycles of intermediate dose ARA-C (IDAC) is a well-tolerated and highly effective approach for elderly patients with AML (Sperr et al, Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:3965-3971). The aim of the current multi-center study (EudraCT number: 2007-005806-29) was to evaluate the efficacy and feasibility of intensified consolidation therapy employing FLAG (cycle 1; fludarabine, 30 mg/m² iv, days 1-5, ARA-C, 2000 mg/m² iv, days 1-5) and IDAC (cycles 2-4; ARA-C, 2x1,000 mg/m2 iv, days 1,3,5) in elderly AML patients and to analyze the effect of pegfilgrastim (6 mg s.c. on day 6) on the duration of neutropenia, overall toxicity, and hospitalization-time during consolidation in these patients. In addition, overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival were captured. To evaluate the efficacy of pegfilgrastim we compared consolidation cycles where pegfilgrastim was given routinely on day 6 (IDAC-P; consolidation 2 and 4) with cycles where pegfilgrastim was only used in case of infections and/or prolonged neutropenia (consolidation 3). Between Jul/2008 and Nov/2012 (observation period until Sept/2014) 64 patients with de novo AML were included (median age: 69.9 years; range 60.1- 85.2 years; 53 patients < 75 years, 11 patients ≥75 years; f:m ratio 1:1.56). Following induction therapy, 43 patients (68%) entered complete remission (CR), 33 after the 1st (DAV), 9 after a 2nd (MiDAC light: ARA-C 2x1g/m², days 1,3,5; mitoxantron 12 mg/m², days 3,5), and 1 patient after a 3rd (FLAG) induction cycle. In 16 patients no remission (NR) was achieved. Of these, 7 received only one induction cycle, 3 two, and 6 three cycles. Two patients died and 2 patients were withdrawn from the study during the 1st induction. Thirty-nine CR-patients (91%) were eligible for consolidation therapy. All 4 planned consolidation cycles could be administered in 23/39 patients (59.0%), 5/39 (12.8%) received 3 cycles, 3/39 (7.7%) 2 cycles, and 8/39 (20.5%) 1 cycle of consolidation therapy. Relapse (n=8; 20.5%) was the major cause of withdrawal, followed by persistent cytopenia (n=4; 10.2%), severe infections (n=2; 5.1%), and stem cell transplantation (n=1). Four patients died in the consolidation phase (treatment related, n=2; not treatment related, n=2). In 17 patients the efficacy of pegfilgrastim could be evaluated. The median duration of severe neutropenia (ANC<500/µL) was 7 days (range: 3-14 days) in the 2nd (IDAC-P), 12 days (range: 3-21 days) in the 3rd (IDAC), and 7.5 days (range: 5-19 days) in the 4th (IDAC-P) consolidation cycle. Differences in the duration of severe neutropenia between consolidation 2 and 3 and between consolidation 3 and 4, were significant (p<0.05). The duration of hospitalization differed also significantly among these patient-groups, with 21 days (range 13-42) in consolidation 2 (IDAC-P), 28 days (range 7-41) in consolidation 3 (IDAC), and 22 days (range: 9-40) in consolidation 4 (IDAC-P) (p<0.05). The median OS, continuous complete remission and disease-free survival were 1.1, 1.3, and 1.2 years respectively. The probability to be alive after 5 years was 32% (Figure). The median OS differed significantly between patients aged <75 years (1.5 years) and ≥75 years (0.5 years) (p<0.05) (Figure). Together, our data show that intensified consolidation can be safely administered in AML patients aged ≥60 years. Patients aged <75 years seem to benefit from this strategy. Moreover, the administration of pegfilgrastim on day 6 in IDAC consolidation cycles shortened the duration of neutropenia and the duration of hospitalization significantly.
Sperr:Novartis: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding. Knoebl:Baxalta, now part of Shire: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Jaeger:Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Geissler:Novartis: Honoraria. Valent:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ariad: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Deciphera Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal