Abstract
Introduction: Patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and high International Prognostic Index (IPI) or extra-nodal disease are at an increased risk of systemic and central nervous system (CNS) relapse. Presently, the management of DLBCL patients at the Rambam Health Care Campus (Haifa, Israel) and Hadassah Medical Center (Jerusalem, Israel) includes 6 cycles of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) along with 4 doses of intrathecal (IT) methotrexate (MTX), which may be followed by 2 additional cycles of an intermediate dose (3 g/m2) of intravenousMTX (ID-MTX). The current study compared progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS) and CNS relapse rate in a cohort of DLBCL patients with risk factors for CNS relapse who did or did not undergo prophylactic therapy with ID-MTX.
Methods: Four hundred and eighty DLBCL patients treated at two tertiary care centers (Rambam and Hadassah) between the years 1991 and 2013 were retrospectively evaluated. The cohort included 224 females and 256 males at a median age of 58 years (range18-76). OS, PFS and CNS involvement at relapse were analyzed. The study incorporated all patients with the primary diagnosis of DLBCL and risk factors for CNS relapse, i.e., Waldeyer ring (2%), breast (1%), testicular (3%) or orbita (1%) involvement, bone marrow involvement (21%), stage IV disease (64%), LDH higher than normal (70%), ≥1 extra-nodal site (28%), IPI ≥3 (36%). Eight percent of patients had stage I-IE disease, 17% - stage II-IIE, 11% - stage III, 64% - stage IV, 29% had B symptoms. Patients with CNS involvement at diagnosis were excluded from the analysis.
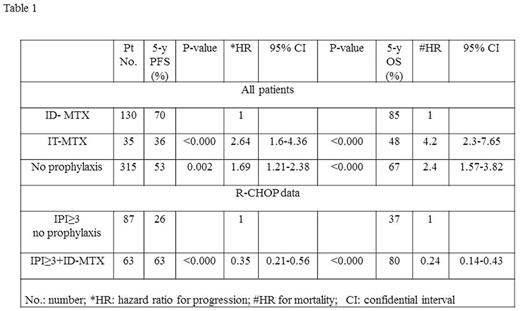
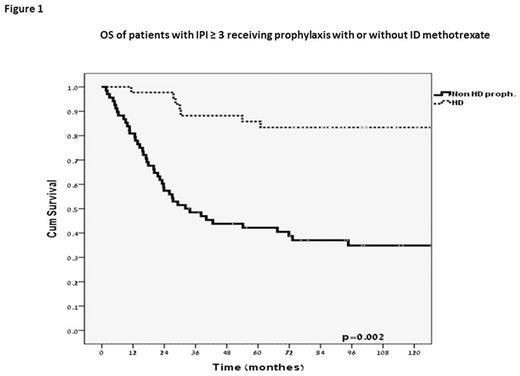
Results: Four hundred and seventy three patients (99%) were treated with either CHOP or CHOP-like regimen, and 384 (80%) patients received rituximab (R). In the R-CHOP cohort, 23% of patients with IPI 0/1, 28% with IPI 2 and 42% with IPI ≥3 were given prophylaxis. One hundred and thirty patients received ID-MTX (27%), 35 patients (7%) received IT-MTX only, while no prophylaxis was administered to 315 patients (66%). The cumulative incidence of CNS relapse at 5 years was 6%, with no difference in the incidence between the patients who received prophylaxis with ID-MTX, IT-MTX or were given no prophylaxis at all. Patients with IPI ≥3 treated with ID-MTX had a decreased overall relapse rate and significantly superior OS and PFS (Table 1; Figure 1).
Conclusion: In the current study, the addition of two cycles of ID-MTX to the standard R-CHOP regimen resulted in improved 5-year PFS and OS of DLBCL patients with IPI ≥3. These data need to be further confirmed in a randomized controlled study.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal