Abstract
Background: Relapsed/refractory (R/R) DLBCL remains an unmet medical need with no approved or standard therapy in the third-line setting. Several new promising classes of drugs are being developed based on emerging understanding of the molecular pathology of DLBCL. These include CC-122, a pleiotropic pathway modifier that promotes CRBN-dependent Aiolos and Ikaros degradation, CC-223, a potent selective ATP-competitive inhibitor of mTOR kinase, and CC-292, a highly selective irreversible-inhibitor of Btk. Early phase studies with these compounds indicated single-agent activity in B cell malignancies including DLBCL. CC-122-DLBCL-001 is a Phase 1b dose escalation and expansion study of CC-122, CC-223 and CC-292 administered orally as doublets, and as triplets in combination with rituximab (R), as well as a CC-122 plus R doublet, in subjects with high risk R/R DLBCL.
Methods: The dose escalation phase of the study explores combinations of one or more doses for each novel agent using a modified 3+3 dose escalation design with higher dose cohorts including the addition of a fixed dose of rituximab 375 mg/m2 IV Q28 days. CC-122 1mg, 2mg, 3mg, or 4mg is given orally QD or for 5 out of 7 days/week (5/7d). CC-223 15mg, 20mg, or 30mg is given orally QD. CC-292 500mg is given orally BID. Subjects were treated until progression or intolerable side effects. Study endpoints were: safety, tolerability, PK, PD and preliminary efficacy [overall response rate (ORR) and complete response (CR)]. Subjects were considered efficacy evaluable if they received at least one cycle of treatment and had one post-baseline tumor assessment. Peripheral blood PD biomarkers on treatment were compared to baseline levels by flow cytometry for CC-223 mTOR pathway targets p4EBP1 and pAKT and CC-122 target Aiolos. CC-292 500mg BID was previously demonstrated to result in >90% Btk receptor occupancy at 24 hours (Blood 2013 122:4169).
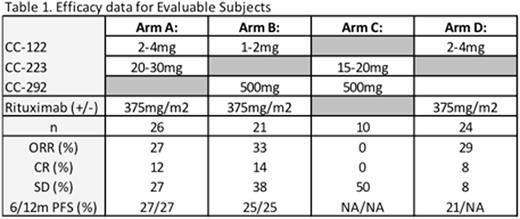
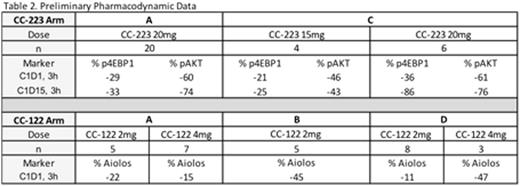
Results: As of May 02, 2016, a total of 102 subjects were enrolled into the ongoing dose escalation phase of the study. The median no. of prior anti-lymphoma regimens was 3 (range, 1-10), 30% had prior ASCT and 30% were refractory to any prior therapy. Arm A (CC-122 + CC-223 +/- R) enrolled 31 subjects (28 treated) on 5 dose levels. As of the data-cutoff, the MTD had not been established. The most common (> 10%) related grade 3/4 adverse events (AEs) were neutropenia (43%), thrombocytopenia (14%), diarrhea (18%), and rash (11%). Arm B (CC-122 + CC-292 +/- R) enrolled 28 (27 treated) subjects on 5 dose levels. The MTD was determined to be CC-122 1mg 5/7d + CC-292 500mg BID + R. The most common (> 10%) related grade 3/4 AEs were neutropenia (37%), thrombocytopenia (22%), anemia (11%) and febrile neutropenia (15%) Arm C (CC-223 + CC-292) included 14 enrolled (all treated) subjects on 2 dose levels. A tolerable dose demonstrating sufficient PD biomarker inhibition was not established. The most common (> 10%) related grade 3/4 AEs were neutropenia (14%), thrombocytopenia (29%) and diarrhea (14%). Arm D (CC-122 + R) included 29 subjects enrolled (28 treated) on 5 dose levels. As of the data-cutoff, the MTD had not been established. The most common (> 10%) related grade 3/4 AEs were neutropenia (32%). Generally, response rates of interest were noted in Arms A, B and D (Table 1). ORR increased at higher dose levels and responses were durable. Preliminary PD data (Table 2) demonstrated differential effects of CC-223 20mg dose on p4EBP1 inhibition between Arms A and C and differential effects of low and high dose CC-122 dosing on Aiolos inhibition between Arms A, B and D. Preliminary PK analysis for drug-drug interactions will be presented.
Conclusions: Preliminary data from this ongoing novel-novel dose escalation study indicate that safe and tolerable combinations of CC-122 with CC-223, CC-292, and/or rituximab can be achieved. Combination effects on toxicity, efficacy and PD biomarkers were seen. The observed signals of efficacy are encouraging in this R/R DLBCL population and will be further explored in dose expansion of selected arms at the optimized doses.
Ribrag:Infinity: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Esai: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ArgenX: Research Funding; Pharmamar: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; NanoString: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Chavez:Janssen: Speakers Bureau. Kaplan:Janssen: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding. Vitolo:Gilead: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Santoro:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ArQule: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Corradini:Servier: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Gentium: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Cassier:Celgene Corporation: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; MSD: Research Funding; Merck Serono: Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Eli Lilly: Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria. Flinn:Janssen: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; RainTree Oncology Services: Equity Ownership. Advani:Janssen: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Kura: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Kyowa Hakko Kirin: Consultancy, Honoraria; FortySeven: Consultancy, Honoraria; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Sutro: Consultancy, Honoraria; Spectrum: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Juno: Consultancy, Honoraria; Stanford University: Employment; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding; Agensys: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding. Sangha:Boehringer-Ingelheim: Honoraria; Astra-Zeneca: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Lundbeck: Honoraria; Eli-Lilly: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria. Hagner:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Trowe:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Gandhi:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Wu:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. Hege:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Pourdehnad:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Kuruvilla:BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Merck: Honoraria; Roche Canada: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Lundbeck: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal