Abstract
Background:There are multiple prognostic markers used to risk stratify pts with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) including the MCL International Prognostic Index (MIPI) which divides newly diagnosed patients into three groups based on available clinical and laboratory data.Complex karyotype (CK) defined as equal to or greater than 3 chromosomal abnormalities has also been associated with inferior outcomes in MCL although its association with MIPI is lesswell-described. We conducted a multicenter analysis of MCL pts to assess the relative contributions of MIPI, CK and Ki67 as predictors of progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
Methods:Untreated pts atleast18 years of age with MCL from 5 academic centers diagnosed between 1993 and 2015 who had available data describing MIPI, Ki67, and cytogenetics were included. Patients with 3 or more chromosomal abnormalities were defined as having CK. High Ki67 was defined as immunohistochemistry staining >30%. We described the associations between MIPI risk group, CK, Ki67, and other clinical factors of interest as predictors of PFS and OS in univariate and multivariable models.
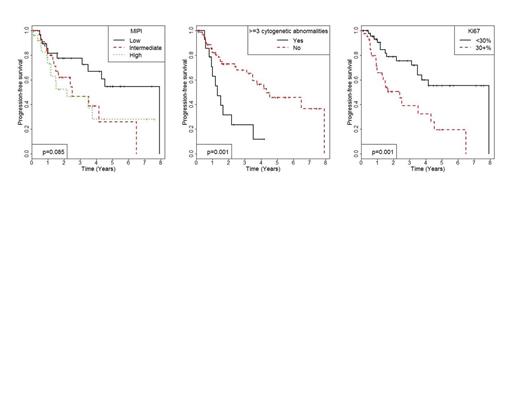
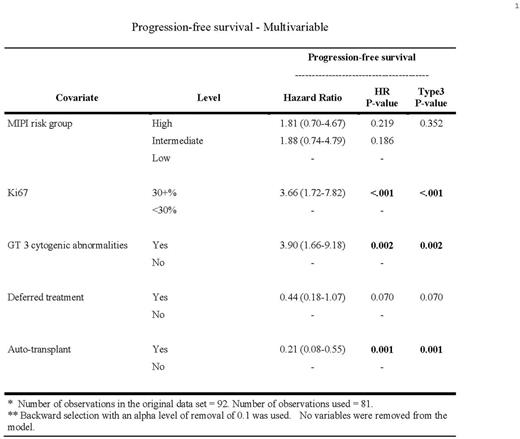
Results:Of 92 eligible MCL patients, 30 (32.6%) had low-risk, 36 pts (39.1%) had intermediate-risk, and 26 pts (28.3%) had high-risk MIPI scores. Ki67 index was >30% in 44.6% of patients, and 17.4% had CK. Neither Ki67 > 30% (p=0.548) norpresence of CK (p=0.409) wereassociated with MIPI risk category. In the low-risk MIPI subgroup, 37% of patients had Ki67 > 30% and 10% had CK. Induction regimens included: R-HyperCVAD (n=15), R-CHOP/R-DHAP (n=7), Nordic regimen (n=13), R-CHOP (n=10), B-R (n=19), and others (n=28). Thirty-two patients (39%) had an autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) in first remission. Median PFS for the entire cohort was 3.8 years, and median OS has not yet been reached. Median PFS for was 2.2 years, 2.5 years, and 7.9 years for patients with high-, intermediate-, and low- risk MIPI scores, respectively, at diagnosis. Median PFS was 2.4 years for patients with Ki67 > 30% and 7.9 years for patients with Ki67 < 30%. Median PFS was 1.3 years for patients with CK and 4.3 years for patients without CK. High risk MIPI (p=0.042), CK (p=0.002), and Ki67 index > 30% (p=0.002) were all associated with inferior PFS in a univariable analyses (See Figure). In a multivariable analysis (See Table) Ki67 >30% (HR=3.66, p<0.001), and complex karyotype (HR=3.9, p=0.002) were associated with inferior PFS while autologous stem cell transplantation in first CR was associated with improved PFS (HR=0.21, p=0.002). MIPI risk score was not independently associated with PFS.
Conclusions:Our findings suggest that Ki67> 30% and CK are independently associated with inferior outcomes in MCL. In this analysis, MIPI risk score was not independently associated with PFS or OS when considering these additional prognostic markers, which needs to be confirmed in other retrospective and prospective cohort studies. Our high-risk MIPI patients, in general, have an improved outcome compared to prior reports. (Hoster2008, 2014;Lex2014), suggesting that alternative markers may play an important role in MCL risk-assessment. Efforts to incorporate additional patients and develop a new prognostic model in MCL are underway.
Danilov:Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; GIlead Sciences: Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Consultancy; Dava Oncology: Honoraria; Prime Oncology: Honoraria. Hamadani:Janssen: Consultancy; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Flowers:TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Millenium/Takeda: Research Funding; Mayo Clinic: Research Funding; NIH: Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics, LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding; ECOG: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding. Cohen:Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Infinity: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Millennium/Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal