Abstract
Monopoiesis is the process in which hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) continuously give rise to monocytes. Accumulating evidence has identified cellular constituents of monopoiesis. Common myeloid progenitors (CMPs), granulocyte-macrophage progenitors (GMPs), macrophage-dendritic cell precursors (MDPs) and common monocyte progenitors (cMoPs) are the intermediates during the differentiation of HSCs into mature monocytes. In mice, CD11b+ CD115+ monocytes are further divided into two subsets based on the expression of Ly6C. Classical monocytes express Ly6C on their surface. By contrast, Ly6C− patrolling monocytes have been recently identified, and the molecular mechanisms which regulate the development and homeostasis of Ly6C−monocytes still remain elusive.
C/EBPβ is a leucine zipper transcription factor which regulates stress-induced granulopoiesis (Hirai et al. Nat Immunol, 2006, Hayashi et al. Leukemia 2013). We have recently found that peripheral blood (PB) monocytes are significantly reduced in steady-state Cebpb−/− mice (Tamura et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2015). In addition, last year at this meeting, we have reported that cell death of Ly6C− monocytes was accelerated through reduced expression of Csf1r (encoding a receptor for M-CSF) in Cebpb−/− mice. Here in this study, we determined the precise developmental stage where C/EBPβ is mandatory for survival of Ly6C− monocytes, and investigated the mechanism of Csf1r regulation by C/EBPβ.
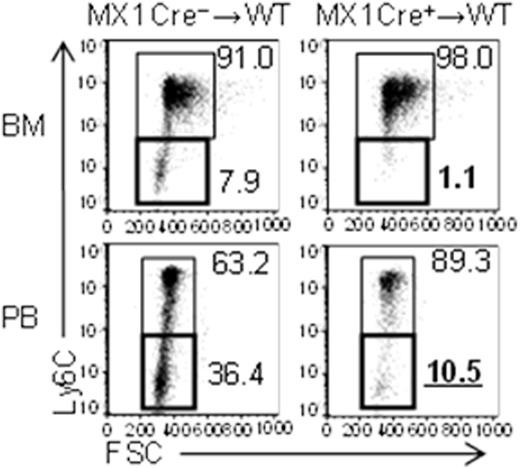
A recent publication demonstrated that Mx1 is preferentially expressed by monocytes and a Mx1 promoter-mediated conditional system targets monocytes without inoculation of polyI:C (Hashimoto et al. Immunity, 2013), suggesting that Mx1-Cre Cebpbf/f mouse is ideal to evaluate the monocyte-specific requirement for C/EBPβ. We confirmed that upregulation of Cebpb mRNA during monopoiesis was significantly impaired after cMoP stage in Mx1-Cre+Cebpbf/f mice. In order to exclude the possible involvement of Cebpβ deficient microenvironment, bone marrow (BM) cells of Mx1-Cre+Cebpβf/f mice (CD45.2+) were transplanted into lethally irradiated CD45.1+ wild type mice. The frequencies of Ly6C− monocytes in the recipients of Mx1-Cre+Cebpbf/f BM cells were significantly reduced when compared to mice that received Mx1-Cre−Cebpbf/f BM cells (Figure). These results strongly suggest that C/EBPβ is specifically required after commitment to monocytes.
In order to investigate the molecular mechanisms involved in the regulation of Csf1r by C/EBPβ, we utilized a combination of a promoter and an enhancer region located in the first intron of Csf1r gene (Fms intronic regulatory element: FIRE) for reporter assay (Pridans et al. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev, 2014). These regulatory elements contain at least 2 consensus binding sites for C/EBPβ (one in the promoter and the other in the enhancer). C/EBPβ significantly enhanced the reporter activity of the regulatory elements in a dose-dependent manner, and introduction of mutations into either of the consensus binding sites abrogated the reporter activity. Next, we engineered EML cells, a mouse HSC line, to express C/EBPβ-estrogen receptor (ER) fusion protein or ER alone. Nuclear translocation of C/EBPβ-ER in the presence of tamoxifen resulted in significant increase of Csf1r mRNA and protein. Using these cells, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation PCR. Upon treatment with tamoxifen, significant enrichment of C/EBPβ at the promoter region and the FIRE region was observed. These data indicated that C/EBPβ regulates Csf1r through direct binding to these regulatory elements.
Collectively, these results demonstrate that C/EBPβ supports survival of Ly6C− monocytes after commitment to monocyte lineage through direct regulation of Csf1r, which is critical for survival and differentiation of monocytes.
Hirai:Kyowa Hakko Kirin: Research Funding; Novartis Pharma: Research Funding. Maekawa:Bristol-Myers K.K.: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal