Abstract
Introduction:
Patients with chronic kidney disease who progress to end stage renal disease (ESRD) require renal replacement therapy to assume some functions of the diseased kidney and sustain life. Hemodialysis (HD) is the most common option for renal replacement therapy in ESRD patients and includes routine treatments 3 times per week to filter uremic toxins and remove excess fluid from the blood. The prevalence of anemia is high in the ESRD population with about 80% of HD patients being treated with an erythropoietin stimulating agent (ESA) for management of anemia (United States Renal Data System. 2015 USRDS annual data report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, MD, 2015). Until recently, there had only been a few of choices for ESA therapies in the United States, epoetin alfa, which is considered short-lasting (dosing generally greater than once per week), and darbepoetin alfa, which is middle-lasting (dosing generally once per week). Methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta is a long lasting ESA (dosing once per 2-4 weeks) that has been recently approved and permitted to be used for treatment of patients with anemia in the United States. At Fresenius Medical Care North America (FMCNA), we began the conversion from use of short- or middle-lasting ESAs to Methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta in our HD facilities in December of 2014. In this analysis, we aimed to determine the profiles of hemoglobin (Hgb) levels in this large national population of anemic HD patients treated with methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta.
Methods:
We retrospectively studied data on HD patients treated at FMCNA facilities that converted from epoetin alfa or darbepoetin alfa to using methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta for the standard of care treatment of anemia. Data for the weekly Hgb levels that were used to conduct anemia management using the ESAs was analyzed for comparisons. The target goal for ESA treatment at FMCNA is to maintain patient Hgb levels between 10 to 11 g/dL. We computed the 3 months profiles of mean Hgb levels associated with the routine clinical use of methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta in all (n=118,681) HD patients receiving the long-lasting ESA therapy at FMCNA during May to July of 2016. Additionally, evaluations of mean Hgb levels before and after the conversion to the long-lasting ESA was performed using patient data from September 2014 to July of 2015; this analysis included 24,223, 7,494, and 1,345 anemic HD patients who received methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta for maintenance of anemia for at least 2, 4 and 6 months, respectively.
Results:
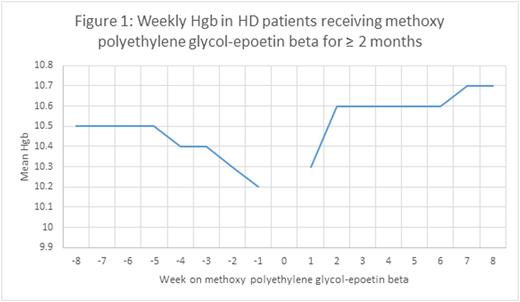
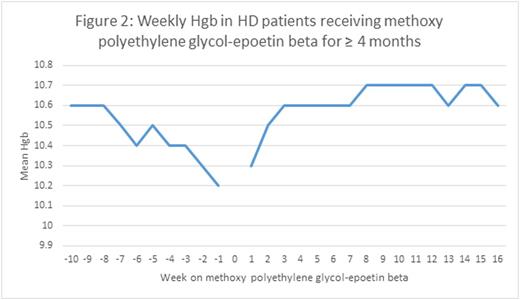
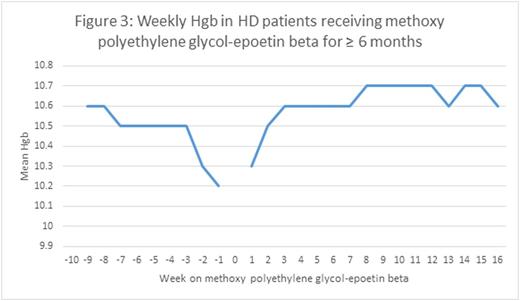
We found that treatment of anemia in HD patients with methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta maintained Hgb levels steady at a mean value of 10.7g/dL for the population from May to July of 2016. In an evaluation of Hgb levels before and after the conversion from epoetin alfa or darbepoetin alfa to methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta, we observed a slight increase of 0.18, 0.17, and 0.15 g/dL in mean Hgb levels after 2, 4, and 6 months of patients receiving the long-lasting ESA for maintenance of anemia (Figures 1-3). There was a slight nadir mean Hgb level of 10.2 g/dL that occurred 1 week prior to conversion to the long-lasting ESA. This was a result of anemia protocols that had patients with higher Hgb values wait until the level had decreased before converting to the long-lasting ESA.
Conclusions:
The findings of this retrospective investigation indicate that the long-lasting ESA methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta maintains Hgb levels in target range for HD patients. The conversion from a short- or middle-lasting ESA to the long-lasting ESA methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta may be associated with overall a minor increase in mean Hgb levels that are on average within normal limits.
Stennett:Fresenius Medical Care North America: Employment. Ofsthun:Fresenius Medical Care North America: Employment, Equity Ownership. Larkin:Fresenius Medical Care North America: Employment. Reviriego-Mendoza:Fresenius Medical Care North America: Employment. Usvyat:Fresenius Medical Care North America: Employment, Equity Ownership. Maddux:American National Bank & Trust (NASDAQ: AMNB): Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Fresenius Medical Care North America: Employment, Equity Ownership, Other: Founder: Scholarships Expanding Education 501c3 non profit, Research Funding; Kidney Care Partners: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pacific Renal Care Foundation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Specialty Care: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sound Physicians: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Mid Atlantic Renal Coalition: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Hymes:Nephroceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Fresenius Medical Care North America: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal