Abstract
Background: Several novel treatments have recently been approved for the treatment of relapsed multiple myeloma (RMM). In the absence of head-to-head comparisons between these novel treatments, clinicians and payers must rely on statistical indirect comparisons. The objective of this analysis is to derive measures of relative effectiveness for carfilzomib + lenalidomide + dexamethasone (KRd) against bortezomib + thalomide + dexamethasone (VTd) in patients with RMM who have been treated with at least one prior therapy and who had an autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
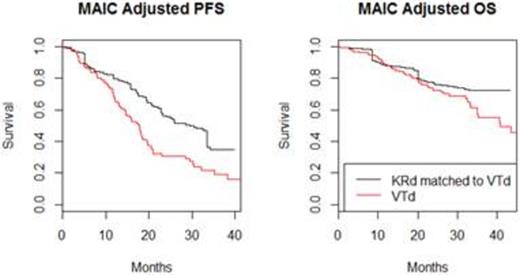
Methods: A matching-adjusted indirect comparison (MAIC) (Signorovitch, 2010) for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was conducted between KRd with results from the Phase III study ASPIRE study (Stewart et al., 2015) and VTd with results from the MMVAR trial (Garderet et al., 2012). The MAIC utilized patient level data from ASPIRE, and adjusted for observed patient population differences. An MAIC uses a propensity score type equation to assign case weights to the KRd patients so that their weighted baseline characteristics match the baseline of the VTd population. This re-weighting process attempts to answer the question: What would the outcomes be if KRd had been administered to the VTd population? Adjustments were made for age, gender, history of ASCT, disease duration, ISS stage, beta-2-microglobulin, and creatinine clearance rate. Cox PH models were fitted to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) for PFS and OS. Weibull survival curves best fit the adjusted survival data and were used to estimate median survival times. A simulated treatment comparison (STC) (Ishak et al., 2015), which adjusts for reported patient population differences using regression equations, was conducted as a cross validation.
Results: The KRd arm in ASPIRE included 396 patients and VTD arm in MMVAR included 135 patients. After successfully matching, the effective sample size (ESS) of the KRd population was 56. See Figure 1 for the MAIC adjusted PFS Kaplan-Meier curves. HRs (95% CIs) from the Cox models for PFS and OS outcome were 0.535 (0.346, 0.828) and 0.694 (0.38, 1.27), respectively. Corresponding HRs from the STC were similar and validate the MAIC results.
Estimates of median PFS and OS in months were 28.6 and 57.9 for KRd compared to 18.0 and 43.2 for VTd, respectively.
Conclusion: This MAIC analysis suggests that KRd provides a consistent benefit relative to VTd in RMM patients who have been treated with at least one prior therapy and an ASCT. Beyond the patient characteristics available from MMVAR, other variables that may potentially influence outcomes were not adjusted for in the analysis. The small ESS is a potential limitation of this analysis.
Rael:Onyx: Consultancy; Evidera: Employment. Benedict:Evidera: Employment; Onyx: Consultancy. Ishak:Evidera: Employment; Onyx: Consultancy. Cadarette:Evidera: Employment; Onyx: Consultancy. Campioni:Amgen: Employment, Equity Ownership. Panjabi:Onyx Pharmaceuticals Inc., An Amgen Subsidiary: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal