Abstract
Patients with a variety of blood cancers and metabolic diseases may require a stem cell transplant as part of their treatment. However, 70% of patients do not have a suitable genetic match in their family. Stem cell donor-databases are used to match potential unrelated donors to patients worldwide. In Canada, individuals aged 17-35 years can register as donors online or at a stem cell drive where they provide consent and a tissue sample (buccal-swab) for Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) allele typing. To date, no guidelines have been published to recommend a process for stem cell donor recruitment at drives. Here, I outline a Canadian approach to stem cell drive design, which features evidence-based strategies to identify and recruit the most-needed stem cell donors and to minimize donor ambivalence and withdrawal from the registry. This model of stem cell drive design includes five stations: pre-screening, informed consent, registration, swabbing, and reconciliation. Registrant confidentiality and privacy is maintained at each station, and quality control is emphasized throughout.
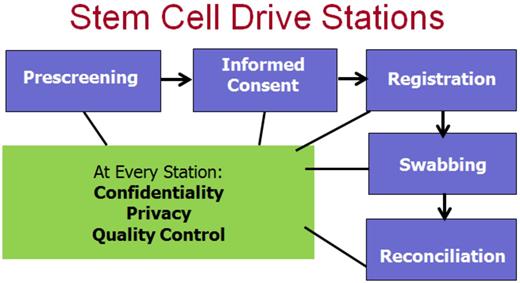
Registrants are first pre-screened to ensure donor eligibility. Recruiters at the prescreening station target the most-needed stem cell donors according to the literature: young, healthy, and ethnically-diverse males. Non-optimal and ineligible registrants are redirected to help out in other ways. Recruiters then explain the principles of stem cell donation and educate registrants about the stem cell donation process. Next, registrants proceed to the informed consent station, which is designed to meet the requirements of the World Marrow Donor Association's suggested procedures for procurement of informed consent at time of recruitment (2003). Here, recruiters hand registrants an information pamphlet, and explain blood and marrow stem cell collection procedure diagrams. The risks of donation are outlined, and registrants are informed of their right to withdraw at any time and about donor and patient anonymity. Registrants are subsequently guided through registration, where they provide their contact/demographic information, complete a health questionnaire, and sign a consent form to join the registry. Recruiters at this station error check registrants' forms to ensure correct completion, and educate registrants about the data collection, storage, usage, and confidentiality. Following registration, registrants proceed to swabbing, where they swab their cheeks to provide a tissue/DNA sample. Recruiters at this station affix barcode stickers to each swab kit component. While registrants swab their cheeks, volunteers perform an informed consent checkpoint by asking registrants if they understand the donation process, the risks involved, and the right to withdraw at any time. Finally, registrants visit reconciliation, where their paperwork is error checked again, their understanding of the donation process is assessed a final time to verify informed consent, and their kit processed for shipping. In summary, the five-station approach to stem cell drive design outlined in this presentation represents a new model for effective stem cell donor recruitment.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal