Backround: Most of patients with acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) are elderly and older age is an negative prognostic factor for AML. There is no consensus about treatment of elderly patients with AML. In this study, we evaluated intensive treatment with cytosine arabinoside and idarubicine versus azacitidine treatment. Primary objectives were evaluation of disease free (DFS) and overall survival (OS), the rate of complete remission and the remission duration.
Methods: 45 patients with AML were evaluated retrospectively. We examined peripheral blood smear, bone marrow aspirate and trephine, immunophenotyping and cytogenetic analysis, biochemical evaluation of renal and liver function and coagulation profile in pre-treatment period. Intensive treatment consisted of cytosine arabinoside 200 mg/m2/day for 7 days and idarubicin 12 mg/m2/ for 3 days. Bone marrow examination was done between 14-28 days for intensive treatment and 2-6 cyclus for azacitidine treatment. Consolidation treatment (1-3) was done after intensive treatment if the patients were remission. All patients were ≤ECOG 2. Growth factors were not routinely administered before, during or after chemotherapy. Statistical analyses, differences in baseline characteristics between groups were analyzed using the Student's t-test for continuous variables and differences in OS between groups were then analyzed using the likelihood ratio or log-rank tests.
The main properties of patients with elderly AML
| Treatment arm . | Mean age . | Sex M/F . | Leucocyte mean . | Hb gr/dl . | FAB (n) . | MDS history(n) . | LDH . | Complete remission . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 73±9 | 26/19 | 34.029±6870 | 8.53±1,2 | M0:15, M1:6, M2:15,M4:4,M5:2 | Yes:21 No:24 | 276±151 | 15 |
| Intensive | 72±7 | 18/10 | 44.176±12390 | 6.91±2 | M0:6, M1:4, M2:12, M4:3, M5:1 | yes: 14 | 299±101 | 13 |
| Azacitidine | 74±8 | 8/9 | 31.289±4013 | 8,95±1.6 | M0:9, M1:2, M2:3, M4:1, M5:1 | yes:7 | 256±72 | 2 |
| Treatment arm . | Mean age . | Sex M/F . | Leucocyte mean . | Hb gr/dl . | FAB (n) . | MDS history(n) . | LDH . | Complete remission . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 73±9 | 26/19 | 34.029±6870 | 8.53±1,2 | M0:15, M1:6, M2:15,M4:4,M5:2 | Yes:21 No:24 | 276±151 | 15 |
| Intensive | 72±7 | 18/10 | 44.176±12390 | 6.91±2 | M0:6, M1:4, M2:12, M4:3, M5:1 | yes: 14 | 299±101 | 13 |
| Azacitidine | 74±8 | 8/9 | 31.289±4013 | 8,95±1.6 | M0:9, M1:2, M2:3, M4:1, M5:1 | yes:7 | 256±72 | 2 |
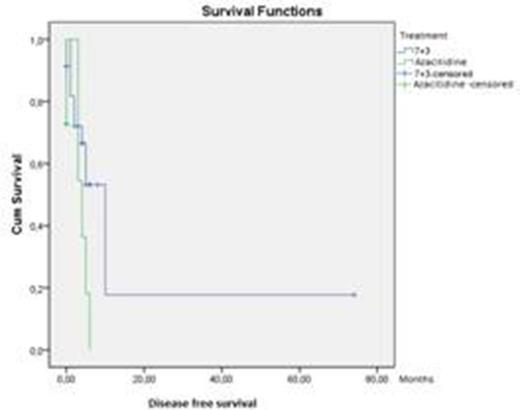
Results: Total patient number were 45 and they were ≥ 65 years (yrs). Male/female ratio was 29/16. Two patients rejected leukemia treatment. One patient were not evaluated for treatment response. Intensive arm consisted of 26 patients and azacitidine arm 16 patients. Disease free survival and overall survival for intensive arm and azacitidine arm were 12,1±9,4, 16,7±22,4, respectively. The most importance factors were leucocyte counts, hb level.
Picture 1-2: Disease free survival and overall survival for intensive arm and azacitidine arm
Conclusions: These results showed that intensive treatment is more effective than azacitidine in elderly AML patients with ECOC≤2. There is need for large studies which include higher number of patients with AML in order to evaluate efficiency of intensive treatment.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal