Abstract
BACKGROUND: Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma (PMBL) is a rare form of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (Lones/Cairo et al, JCO 2000). We have previously reported a significant decrease in EFS among pediatric and adolescent patients with PMBL compared with other stage III non-PMBL diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients following FAB/LMB 96 therapy, suggesting that new therapeutic targeted agents are needed (Gerrard/Cairo et al, Blood 2013). Activation of the B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway has now emerged as a central oncogenic pathway that promotes growth and survival in both normal and malignant B-cells. The cascade of signaling pathways downstream of the BCR includes BTK, MAPK, NF-κB and AKT. PMBL has a constitutively activated NF-kB pathway (Rosenwald et al, JEM 2003). Ibrutinib is a selective and covalent BTK inhibitor that inhibits chronic active BCR signaling and downstream signaling including the NF-kB pathway (Herman et al, Blood 2014) and is an active agent in ABC-DLBCL, which also has an activated NF-kB pathway (Griner et al, PNAS 2014). Preclinical studies of ibrutinib in CLL and MCL suggested that the inhibitory effects on cell proliferation were seen in the range of 1.0uM to 25.0uM (Herman et al, Blood 2011; Cinar et al, Leuk. Res 2013). Despite these relatively high IC50 values in vitro, ibrutinib has been highly effective in the treatment of patients with refractory CLL and MCL (Byrd et al, NEJM 2013 and Wang et al, NEJM 2013). Ibrutinib was approved by the FDA (IMBRUVICA, USPI) for patients with MCL in November 2013 or CLL in February 2014, who have received at least one prior therapy. However, the antitumor activity against PMBL of ibrutinib alone and in combination with other agents is currently unknown.
OBJECTIVES: We hypothesize that ibrutinib in combination with other agents may be a future targeted agent in the treatment of PMBL. Therefore, we investigated the effect of ibrutinib alone and in combination with dexamethasone, rituximab and carfilzomib on cell proliferation and apoptosis in a PMBL cell line.
METHODS: The Karpas-1106P PMBL cell line (DSMZ, Germany) was treated with ibrutinib alone (0-10uM, generously provided by Janssen R&D LLC) and in combination with dexamethasone (1uM), rituximab (20ug/ml) and carfilzomib (5nM) for 5 days treatment. The MTS cell proliferation assay (Promega) and western blot analysis were performed. Significant differences were determined by Student's t -test.The IC50 values were determined with CompuSyn software (Chou and Martin, ComboSyn, 2005).
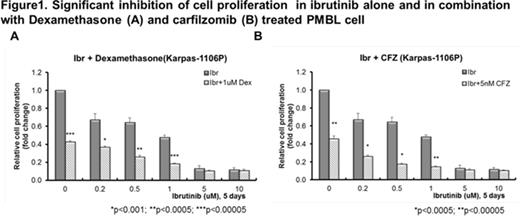
RESULTS: We observed a significant down-regulation of phosphorylated BTK after 5 days with ibrutinib treatment in Karpas-1106P cell line with 1uM ibrutinib (0.178 ± 1.63, p<0.0001) and the expression of total BTK protein was also significantly decreased with 1uM ibrutinib following 5 days of treatment (0.803±0.190, p<0.005) compared to control (1.000±0.00). We also observed a significant dose-dependent decrease in cell proliferation (0-10uM, p<0.0001) in ibrutinib-treated Karpas-1106P PMBL cell line. In combination with dexamethasone, the ibrutinib IC50 values for inhibition of cell proliferation were significantly decreased from 0.71uM ± 0.172 (ibrutinib alone) to 0.04uM ± 0.007 (p<0.005) with 1.0uM dexamethasone combination following 5 days of treatment. Second, in combination with rituximab experiment, the ibrutinib IC50 values was significantly decreased from 0.845uM ± 0.289 (ibrutinib alone) to 0.37uM ± 0.056 (p<0.05) with 20ug/ml rituximab following 5 days of treatment. Lastly, the ibrutinib IC50 values were significantly decreased from 0.72uM ± 0.185 (ibrutinib alone) to 0.002uM ± 0.001 (p<0.005) with 5nM carfilzomib combination following 5 days of treatment.
CONCLUSIONS: Ibrutinib alone and in combination with dexamethasone, rituximab and carfilzomib significantly inhibited cell proliferation in the Karpas-1106P PMBL cell line. Ibrutinib's potential as an adjuvant agent in combination treatment in patients with PMBL is supported by these experiments. Future studies will focus on the in vivo effects of ibrutinib alone and in combination with dexamethasone and carfilzomib in a NOD/SCID PMBL xenograft mouse model.
Galardy:Mission Therapeutics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal