Abstract
Background: The Philadelphia chromosome negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), including essential thrombocythemia (ET), polycythemia vera (PV) and myelofibrosis (MF) all have a time dependent risk of progression to either an advanced myelofibrotic state (post ET/PV MF) and/or to acute myeloid leukemia. The impact of disease duration upon the MPN symptom burden is not well understood, nor are the precise mechanisms of disease progression. We sought to better understand the impact of disease duration on MPN symptom burden.
Methods:
Symptom burden data was collected utilizing the Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Symptom Assessment Form (MPN-SAF) amongst MPN patients, collected at the time of an office visit in an international cohort of MPN patients as previously described (Scherber et. al.). Symptom burden assessment was a previously validated 27-item symptom burden questionnaire scored on a 0-10 scale (0= as good as it can be, 10 = as bad as it could be). The patient or provider was asked to report the time since MPN diagnosis. MPN duration was determined to be early if the diagnosis was established between 0 to 5 years ago, intermediate if the diagnosis was established between 6 to 10 years ago, and late if the diagnosis was established 11 years ago or more. Anemia was defined as a red blood cell count less than 10 g/dL, leukopenia was defined as a white blood cell count was below 4 x 109, and thrombocytopenia if the platelet count was below 150 x109. Statistical significance was calculated using ANOVA f-test and chi squared.
Results:
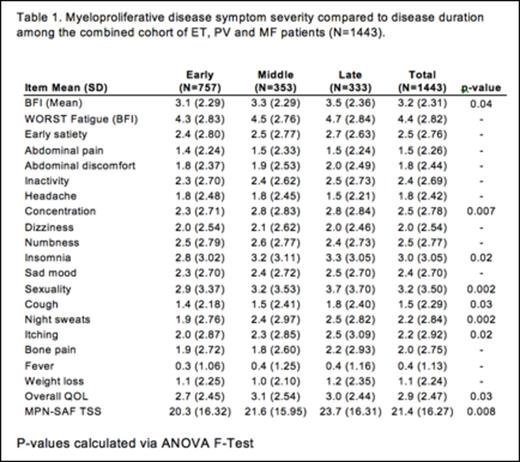
Patient demographics and disease burden: A total of 1443 patients responded to the survey, including 592 (41%) ET, 549 (38%) PV, and 302 (21%) MF patients, including 181 (60%) primary MF, 67 (22%) post-ET MF, and 54 (18%) post-PV MF. Among MF patients, mean duration of MPN diagnosis was 9 years, and mean duration MF diagnosis was 4.7 years. Among respondents, 757 fit criteria for early disease duration, 353 fit criteria for intermediate disease duration, and 333 fit criteria for late disease duration. Respondent mean age was 62 years and approximately half of respondents were female (55%). Patients with longer diagnosis duration tended to be older (p=0.009) and were most likely to have anemia (0.02), leukopenia (p=0.01), or thrombocytopenia (p=0.03). These individuals were also most likely to have a history of hemorrhage (p=0.007) or require red blood cell transfusions (p<0.001).
Combined cohort symptom burden: On average among the combined cohort of ET, PV and MF patients, symptoms tended to worsen with time with this effect being significant for symptom items of fatigue (BFI, p<0.04), concentration (p=0.007), insomnia (p=0.02), sexual difficulties (p=0.002), cough (p=0.03), night sweats (p=0.002), and pruritus (p=0.02). Symptoms of early satiety (p=0.004), concentration difficulties (p=0.01), insomnia (p=0.03), sexual difficulties (p=0.02), cough (p=0.01), and night sweats (p=<0.001) had significantly higher prevalence in those with longer disease duration. Similarly, the total calculated MPN-10 score (p=0.008) and quality of life assessment (0.03) demonstrated worsened outcomes with time (Table 1). No significant differences in symptoms for the combined cohort were observed among individuals diagnosed 0 to 1 years ago compared to those with a diagnosis established between 2 and 5 years ago.
Symptom burden in MPN subtypes. When evaluating specific MPN types, patients with essential thrombocythemia experienced significantly greater sexual difficulties over time (p=0.03). The severity (p=0.01) and incidence (p=0.03) of pruritus and incidence of night sweats (p<0.001) were significantly increased over time for individuals with PV. For those with MF, the severity (p= 0.01) and incidence (p=0.009) of cough also significantly increased with longer diagnosis duration.
Discussion
Overall, significant worsening in symptom burden can be recognized over time for individuals diagnosed with MPNs. Diagnosis may not necessarily correlate with disease duration as the timing of diagnosis may be delayed from onset of disease. Given the intent of this abstract to evaluate changes with disease duration, we did not investigate correlations between symptom burden and cytopenias. We do know that risk factors for survival in the MPNs include older age and thrombosis, however, disease duration should be investigated as an alternative marker of burden in future survival studies.
Harrison:CTI Biopharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Sanofi: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Kiladjian:Incyte Corporation: Consultancy; Novartis: Other: Travel grant; Research Funding paid to institution (Hôpital Saint-Louis et Université Paris Diderot); Novartis: Consultancy. Zweegman:Celgene: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding. Barbui:Novartis: Speakers Bureau. Etienne:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Congress Travel/Accomodations, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; ARIAD: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. te Boekhorst:CTI Biopharma: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy. Vannucchi:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Other: Research Funding paid to institution (University of Florence), Research Funding; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Baxalta: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Mesa:Novartis. Research- incyte, Gilead, cti, Genentech, promedior, NS Pharma: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal