Abstract
Introduction: Transformed B-cell lymphomas (t-BCL) harbor features of indolent and aggressive disease and it is assumed that transformation conveys an unfavorable prognosis. Because of the ambiguous pathological findings these lymphomas are rarely included into clinical trials. As a result, there is a lack of information about t-BCL patients' short-term and long-term outcomes although very recently a large retrospective analysis detailed the outcomes of transformed follicular lymphoma (t-FL) (Blood June 23, 2015; DOI 10.1182/blood-2015-01-621375). t-BCLs can be separated into a primary type, i.e. transformation at the time of diagnosis, and a secondary type, i.e. transformation after a previous diagnosis of indolent BCL. The present study reports the outcome of patients with t-BCL and also includes indolent lymphomas other than FL.
Methods: This is a retrospective, single center analysis of patients with t-BCL seen at the Dept. of Hematology and the Dept. of Medical Oncology at the University Hospital Essen between 1999 and 2015. The departments' archives were screened for patients with primary or secondary t-BCL. A lymphoma was considered transformed when the diagnosis of indolent lymphoma (FL grade 1, 2, 3A; extranodal marginal zone lymphoma (EMZL), nodal marginal zone lymphoma (NMZL), splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL)) preceded a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or other aggressive lymphoma or was simultaneously present. Lymphomas were classified according to WHO 2008 terminology whenever possible. FL with simultaneous grade 3A and grade 3B portions were classified as primary t-BCL. Central pathology review was not performed. Demographic parameters, treatment history, response and outcome data were collected. Survival analyses were performed using the Kaplan-Meier method. The log rank test was used to calculate survival differences, p values > 0,05 were considered statistically significant. Multivariable Cox regression analysis was used where appropriate. The ethics committee of the faculty of medicine, University of Duisburg-Essen, approved this study (14-5497-BO).
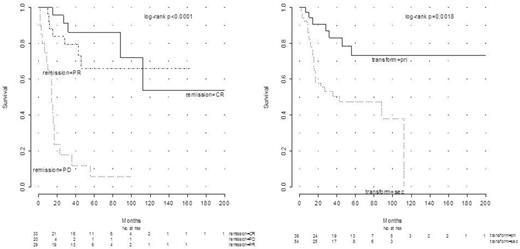
Results: 92 patients treated between 1999 and 2015 were identified. 47 (51 %) were female. 38 (41%) suffered from primary and 54 (59%) from secondary t-BCL. Median age at transformation was 60 years (30-87). For secondary t-BCL, time to transformation spanned 2-275 months with a median of 40.5. The treatment approach influenced time to transformation: 33.3 (median) months for observation only (n=20) and 66 months (median) for chemotherapy or rituximab-chemotherapy (n=20; p=0.02). After radiation therapy (n=10) median time to transformation was 32 months. 4 patients received chemotherapy and radiation therapy. FL grade1-3 was diagnosed in 67 patients (73%). Other diagnoses included EMZL (n=9), LPL (n=5), NMZL (n=3) SLL (n=3), SMZL (n=2) and other low-grade lymphomas (n=3). Histology at transformation was DLBCL in 86 patients. FL grade 3B, Burkitt-like lymphoma and aggressive lymphoma, unclassified, were diagnosed in 2 patients each. In primary t-BCL Ann Arbor stages III or IV were found in 25 patients (63 %), extranodal disease was present in 13 (34%), and 7 (18%) suffered from B symptoms. In secondary t-BCL Ann Arbor stages III or IV were found in 41 patients (66 %), extranodal disease was present in 12 (22%), and 11 (20%) suffered from B symptoms. Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index high risk categories at time of transformation were evaluable for 42/67 FL patients and more frequent in secondary t-FL (n=33 (79%)) than in primary t-BCL (n=9 (21%)). Treatment of primary vs secondary t-BCL included CHOP (5/5), R-CHOP (29/23), R-ASHAP (0/10), Burkitt-type protocol (1/2), R-GemOx (0/2), R-ICE (0/2), radiation only (6/0), BEAM + ASCT (0/8), and other regimens. Overall survival (OS) at 5 years was dependent on remission status after first treatment of transformation with 86% for patients in CR, 66% for PR (CR vs PR p=n.s.) and 6% [CI=4.6-38.3] for PD (CR vs PD: p<0.0001) (Figure; 82 evaluable patients). 5-year OS for primary t-BCL was 73.3% and 47.6% for secondary t-BCL, respectively (p=0.0018) (Figure; 92 evaluable patients).
Conclusion:
In this study primary t-BCL had a favorable outcome when compared with secondary t-BCL. The assumed adverse prognostic impact of transformation may not hold true for primary t-BCL.
Dührsen:Alexion Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding. Hüttmann:Roche: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy, Other: Travel support; Celgene: Other: Travel support, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal