Abstract
Introduction: Anemia is one of the commonest presenting features of MDS and approximately 30-40% of patients require regular RBC-transfusion. RBC-transfusion dependency (RBC-TD) is a poor-prognostic factor independent of revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R) (Hiwase et al ASH 2014). Although RBC transfusion increases the risk of alloimmunization, there is limited literature characterizing this risk in MDS patients as compared to other hematological disorders (such as thalassemia).
Methods: This retrospective study assessed the alloimmunization rate in 784 MDS and AML (20-30% blasts) patients registered in the South Australian-MDS registry (SA-MDS registry) between 1991 and 2015. RBC-TD was defined as ≥1 unit of RBC transfused every eight weeks for four months according to WHO based Prognostic Scoring System. The cumulative incidence of RBC-alloimmunization was calculated using competing risk analysis (death being the competing risk). Factors associated with increased rate of RBC antibody formation were investigated by Cox regression analysis.
Results: The median age of the 784 patients at diagnosis was 75 years with 66% males. The estimated median follow up time was 7.3 years. 70% of patients (549/784) were diagnosed with primary MDS, while the remaining patients were diagnosed with AML (20-30% blasts; n=57), CMML (n=91) or therapy-related myeloid neoplasm (T-MN; n=87). At last follow-up 30% patients were alive, 67% were deceased and 3% were lost to follow-up.
During the study period, 658 (84%) patients required ≥1 unit of RBC transfusion and median RBC units transfused were 29 (range 0-708). The WPSS definition of RBC-TD was met in 47% (366/784 patients), while 36% (282/784) patients required intermittent RBC-transfusions (RBC-TI).
During follow up, 83 (13%) patients formed 155 RBC-alloantibodies and 50% of these cases (42/83) developed >1 RBC-alloantibody. Autoantibodies were also detected in 31 cases, mainly in association with RBC-alloantibodies (n=27; complex alloimmunization) while 4 cases had only autoantibodies. Interestingly, in 19/27 of cases autoantibodies were detected only after alloimmunization. The pathophysiologic mechanism of this remains unclear.
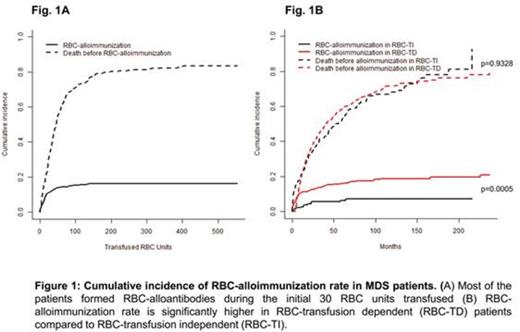
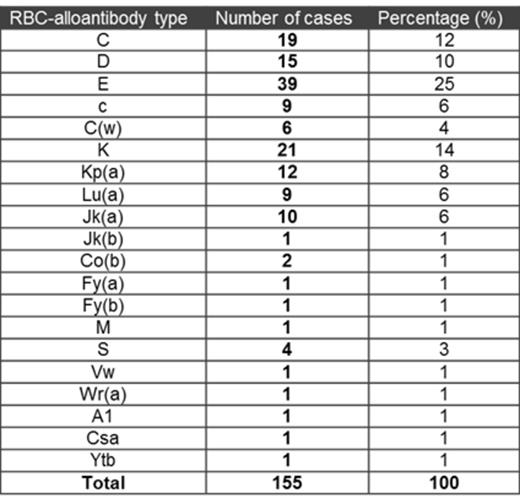
The most common alloantibody specificities were Rh (57%) and Kell (21%) (Table 1). The median interval between 1st RBC transfusion and antibody detection was 10 (0.2-225) months. In 9 cases (6 females) alloantibodies were detected prior to the 1st unit of RBC-transfused. The incidence of RBC alloimmunization reached a plateau at 16% by 100 units of RBC (Fig. 1A), however 80% of antibodies were detectable by 30-40 RBC units transfused. It indicates that most "responders" will form antibodies during the first 30-40 units of RBC transfused.
Since most chronically transfused MDS patients do not form RBC alloantibodies it is important from a clinical and resource-utilization standpoint to identify who is at greatest risk of RBC alloimmunization. Multivariate analysis using Cox-regression model was performed. The only factor which was associated with significantly higher risk of RBC alloimmunization was RBC-TD (HR 2.52; p=0.0005). Age, sex, IPSS-R category and number of RBC units transfused did not independently predict alloimmunization rate. Using competing risk analysis, the cumulative incidence of RBC-alloimmunization was significantly higher in RBC-TD group compared to RBC-TI group (p=0.0004; Fig. 1B).
Conclusion: RBC-alloimmunization is a substantial risk in MDS patients, especially in RBC-transfusion dependent cases. Extended phenotype matching (D,C,c,E,e and Kell) could have prevented alloantibody formation in 79% of alloimmunized MDS patients.
Yeung:Ariad: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal