Abstract
Background:
Most patients (pts) diagnosed with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) are older than 60 years. Although intensive induction chemotherapy in medically fit pts is still the standard practice and a prerequisite for long-term survival, elderly pts have a higher risk of treatment related morbidity and lower remission rates than younger AML pts. An optimized induction treatment would combine high complete remission (CR) rates with tolerable toxicity. The combination of intermediate-dose cytarabine plus mitoxantrone (IMA) has been reported to result in high CR rates (73.5%) with acceptable toxicity in 86 elderly AML pts (Niederwieser et al., Blood 2002, abstr. 1337). We present the mature final results of a randomized-controlled trial comparing efficacy and tolerability of IMA with the standard 7+3 induction regimen consisting of daunorubicin plus cytarabine (DA).
Patients and Methods:
In the 60+ trial of the Study Alliance Leukemia (SAL), AML pts >60 years and medically fit for chemotherapy were randomized to receive either intermediate-dose cytarabine (1000 mg/m2 BID days 1,3,5,7) plus mitoxantrone (10 mg/m2 days 1-3) (IMA) or standard induction therapy with cytarabine (100 mg/m2 continuously days 1-7) plus daunorubicin (45 mg/m2 days 3-5) (DA). All pts in CR after DA received intermediate-dose cytarabine plus amsacrine (MAMAC) as consolidation treatment, whereas pts in CR after IMA were consolidated with standard-dose cytarabine plus mitoxantrone (2+5). Primary study endpoint was the CR rate with an expected difference of 15% in favor of IMA. Secondary endpoints were the incidence of serious adverse events (SAEs), time to relapse (TTR), relapse-free survival (RFS), and overall survival (OS).
Results:
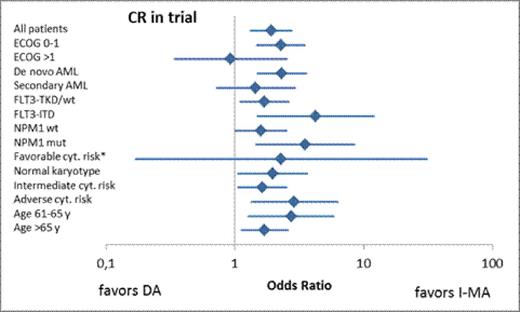
Between February 2005 and October 2009, 852 pts were screened for study inclusion and 485 pts started study treatment, of which 241 pts were randomized for treatment arm A (DA) and 244 for treatment arm B (IMA). The median age was 69 years. Pt characteristics were equally distributed between the two arms. According to a strict definition, all patients with early death, study drop-out, or failed remission assessment were categorized as being not in CR. The CR rate amongst all 485 pts treated in the study was 47%. The CR rate after DA was 39% (95%-CI; 33-45) versus 55% (95%-CI; 49-61) after IMA (OR 1.89, p=0.001). If all first CRs were taken into account including those achieved after trial discontinuation, the CR rates after DA versus IMA induction were 55% versus 64% (p=0.043). Separate analyses addressing age, cytogenetics, de novo AML, NPM1 and FLT3-ITD confirmed higher CR rates after IMA induction throughout these subgroups. Six-week mortality was 14% in both arms. The median duration of ≥ grade 3 neutropenia was 23 days after DA I and 25 days after IMA (p=0.031). The median duration of thrombocytopenia ≥ grade 3 was 16 versus 20 days after DA I and IMA I, respectively (p<0.001). The incidences of non-hematologic toxicities were not significantly different except for a higher incidence of liver toxicity (odds ratio IMA/DA = 0.52; p=0.001) and gastrointestinal symptoms (OR IMA/DA = 0.62; p=0.041) after DA.
In the course of treatment, 11 pts in each arm (5%) received allogeneic stem cell transplantation.
After a median follow-up of 66 months, RFS curves are superimposable in the first year with a similar median RFS of 11 months and 10 months after DA and IMA, respectively. However, a separation of RFS curves developed with longer follow up, resulting in 1-year RFS rates of 45% versus 46%, but 3-year RFS rates of 29% versus 14% in the DA versus IMA arms, respectively (p=0.042). The median OS for all randomized pts was 10 months in both arms; 1-year and 3-year OS rates were 45% and 19% after DA versus 44% and 19% after IMA (p=0.513).
Conclusion:
The results indicate that elderly AML pts benefit from a dose escalation of cytarabine in induction therapy by significantly higher CR rates and similar toxicity compared to a standard 7+3 approach. In our trial, this did not translate into a survival advantage, most likely due to differences in consolidation treatment of the respective treatment arms. In combination with an effective consolidation strategy such as high-dose cytarabine or allogeneic transplantation, our current results favor the use of intermediate dose cytarabine in induction for pts with a curative AML treatment approach.
Einsele:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Amgen/Onyx: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Thiede:Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AgenDix GmBH: Equity Ownership. Platzbecker:Amgen, Inc.: Honoraria; GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Ehninger:Cellex GmbH: Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal